Android Picasso: Difference between revisions
Created page with "=Introduction= Picasso is a library for managing images on Android <syntaxhighlight lang="kotlin"> Picasso.with(getContext()).load(sampleURI).into(imageView) </syntaxhighlight>" |
|||
| (47 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
Picasso is a library for managing images on Android | Picasso is a library for managing images on Android and is very simple to use | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="kotlin"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="kotlin"> | ||
Picasso.with(getContext()).load(sampleURI).into(imageView) | Picasso.with(getContext()).load(sampleURI).into(imageView) | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
[[File:Picasso rendering.png|800px]] | |||
Picasso Provides | |||
*Flexible Source Locations | |||
*Caching | |||
*Image Trnasformations | |||
*Error Handling | |||
*Logging | |||
*Request Management | |||
To add it to our projects we simply add it to the gradle. At the time this was | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="groovy"> | |||
implementation 'com.squareup.picasso:picasso:2.71828' | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
<br> | |||
Resources for this can be found at<br> | |||
https://github.com/alex-wolf-ps/android-picasso | |||
=Comparison= | |||
Here are some comparisons on the competition at the time, Glide and Fresco. I guess I am more interested in the items to compare as this points to the problem people are trying to solve. | |||
<table> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Criterion</th> | |||
<th>[[File:Picasso.jpeg|165px]]</th> | |||
<th>[[File:Glide2.png|165px]]</th> | |||
<th>[[File:Fresco.png|165px]]</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td class="weight">Size</td> | |||
<td>121 Kb/td><p></p> | |||
</td><td>440 Kb</td> | |||
<td>500 kb</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td class="weight">Convenience of use</td> | |||
<td>high</td> | |||
<td>high</td> | |||
<td>middle</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td class="weight">Web Download Speed</td> | |||
<td>high</td> | |||
<td>slightly lower due to lengthy caching processing</td> | |||
<td>high</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td class="weight">Cache Download Speed</td> | |||
<td>average</td> | |||
<td>high</td> | |||
<td>high</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td class="weight">Built-in Transformation Features</td> | |||
<td>basic set of operations</td> | |||
<td>basic set plus rounding</td> | |||
<td>wide range of transformation capabilities, but with limitations</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td class="weight">Additional tools</td> | |||
<td>Absent.</td> | |||
<td>Loading a frame from video as a picture and GIF, using any type of model, a flexible API with the ability to connect any network stack.</td> | |||
<td>Saving images not in Java Heap, but in ashmem heap, the ability to crop images around any point, resize JPEG using native resources, support for Progressive JPEG images.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
=Loading Images= | |||
==Sources== | |||
Picasso supports loading images from either | |||
*String, "https:://www.bibble.co.nz/myimage.png | |||
*Resource ID, images stored in the app drawable e.g. R.drawable.myimage | |||
*URI, Maybe an image from the phone using an intent | |||
*File, a Android File Object | |||
==File Types== | |||
Picasso supports many file types include JPEG, PNG and SVG. JPEG and PNG are '''raster images''' and SVGs are '''vector Images'''. Vector images are stored as a series of paths curves and points. Where as raster images of pixels which makes them less unable to scale | |||
<br> | |||
[[File:Raster vs vector.png|center|400px]] | |||
<br> | |||
==Error Handling== | |||
We just create a handler for Picasso and then we can add a breakpoint on the listener. All of the problems I have had have been I forget they do not process svgs. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="kotlin"> | |||
val picasso = Picasso.Builder(context) | |||
.listener { picasso, uri, exception -> | |||
Log.e("Picasso Error", "Errored out, hiding view"); | |||
} | |||
.build() | |||
viewHolder.viewBinding.imgViewState.setImageBitmap(R.drawable.ic_green_arrow_up) | |||
picasso.load(R.drawable.ic_green_arrow_up) | |||
.into(viewHolder.viewBinding.imgViewState) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Example 1 Drawable PNG== | |||
Create drawables in your res/drawable folder. | |||
We can create an appropriate folder for different resolutions e.g. | |||
*/drawable-ldpi For low density screens. | |||
*/drawable-mdpi For medium density screens. | |||
*/drawable-hdpi For high resolution screens. | |||
*/drawable-xhdpi For extra high resolution screens. | |||
Note that the these folders are at the same level as drawable and not inside. From there it is a simple case of getting the Resource ID and loading it into the control. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
ImageView banner = view.findViewById(R.id.banner); | |||
Picasso.with(getContext()).load(R.drawable.beans).into(banner); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Example 2 Drawable Icon== | |||
Using the code | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
ImageView imgAboutOne = view.findViewById(R.id.icon_wait); | |||
Picasso.with(getContext()).load(R.drawable.ic_done).into(imgAboutOne); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
I struggled to get this to work as Android Studio now supports vectors. When you create an icon the result includes a vector. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | |||
Failed to create image decoder with message 'unimplemented' | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
To resolve this updated the version of picasso and achieved nothing except understanding the new syntax which does not require the context. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
ImageView imgAboutOne = view.findViewById(R.id.icon_wait); | |||
Picasso.get().load(R.drawable.ic_done).into(imgAboutOne); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Then found that icons are stored under mipmap so this all worked on the old picasso with | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
ImageView imageView1 = view.findViewById(R.id.icon_drivethru); | |||
Picasso.with(getContext()).load(R.mipmap.ic_done).into(imageView1); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Using with a GridView== | |||
This is of course trivial and a big repetitive but here goes for reference. It just loads the images as above | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@Override | |||
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) { | |||
if (convertView == null) { | |||
LayoutInflater inflater = ((Activity) context).getLayoutInflater(); | |||
convertView = inflater.inflate(layoutResourceId, parent, false); | |||
} | |||
Picasso.with(context). | |||
load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + this.data.get(position)). | |||
into((ImageView) convertView); | |||
return convertView; | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Using with a RecyclerView== | |||
Much the same story. For this I needed to pass the context and then amend the view holder. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@Override | |||
public void onBindViewHolder(ItemViewHolder holder, int position) { | |||
holder.mItemDesc.setText(mItems.get(position).getDescription()); | |||
holder.mItemName.setText(mItems.get(position).getName()); | |||
Picasso.with(mContext). | |||
load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + mItems.get(position).getImageUrl()) | |||
.into(holder.mImageView); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Using an Intent (Downloads, Gallery)== | |||
The picasso code is exactly the same but this is a great example | |||
===Create Button and ImageView=== | |||
Let's create a button and image view | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="xml"> | |||
<LinearLayout | |||
android:layout_width="match_parent" | |||
android:layout_margin="6dp" | |||
android:weightSum="2" | |||
android:layout_height="wrap_content"> | |||
<TextView | |||
android:layout_width="wrap_content" | |||
android:layout_height="wrap_content" | |||
android:textAlignment="center" | |||
android:layout_weight="1" | |||
android:text="Share Your Experience!" /> | |||
<Button | |||
android:id="@+id/btn_submit" | |||
android:layout_width="wrap_content" | |||
android:layout_height="wrap_content" | |||
android:layout_gravity="center" | |||
android:layout_weight="1" | |||
android:text="Upload Image" /> | |||
</LinearLayout> | |||
<ImageView | |||
android:id="@+id/image_submission" | |||
android:layout_width="wrap_content" | |||
android:layout_height="wrap_content" | |||
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" /> | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Create Click Event=== | |||
Create a click event implementation | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
Button btnSubmit = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.btn_submit); | |||
btnSubmit.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { | |||
@Override | |||
public void onClick(View v) { | |||
Intent intent = new Intent().setType("image/*").setAction(Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT); | |||
startActivityForResult(intent, 1); | |||
} | |||
}); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Populate ImageView=== | |||
After the intent ends lets populate the image view | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@Override | |||
public void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) { | |||
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); | |||
Uri imgUri = data.getData(); | |||
ImageView imgPreview = (ImageView) getActivity().findViewById(R.id.image_submission); | |||
Picasso.with(getContext()).load(imgUri).into(imgPreview); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=Transformations= | |||
==Scaling== | |||
Picasso provides 3 types of scaling. Probably does not need more information | |||
[[File:Picasso scaling.png|700px]] | |||
==Resizing== | |||
Some function are available for resizing. | |||
==Rotation== | |||
We can rotate images with a number of degrees and a pivot point. An a example of random is | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
int twiceMax = 20; | |||
int actualMax = 10; | |||
int degrees = new Random().nextInt(twiceMax) - actualMax; | |||
Picasso.with(context). | |||
load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + this.data.get(position)) | |||
.rotate(degrees) | |||
.fit() | |||
.centerCrop() | |||
.into((ImageView) convertView); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
<br> | |||
[[File:Picasso Coffee.png|300px]] | |||
==Custom Transformations== | |||
===Recommend Classes for Image=== | |||
*Canvas | |||
*Paint | |||
*ColorMatrix | |||
*Bitmap | |||
===Example=== | |||
A bit disappointing but this allows you to run some code prior to the image being rendered. You do all of the work. Just create and instance to a transform | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
public class BannerTransformation implements Transformation { | |||
@Override | |||
public Bitmap transform(Bitmap source) { | |||
int originalHeight = source.getHeight(); | |||
int totalMargin = originalHeight / 2; | |||
int croppedImageHeight = originalHeight / 2; | |||
Bitmap croppedImage = | |||
Bitmap.createBitmap(source, 0, totalMargin / 2, source.getWidth(), croppedImageHeight); | |||
if (croppedImage != source) { | |||
source.recycle(); | |||
} | |||
return croppedImage; | |||
} | |||
@Override | |||
public String key() { | |||
return "BannerTransformation"; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
And use it | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
Picasso.with(getContext()) | |||
.load(R.drawable.beans) | |||
.transform(new BannerTransformation()) | |||
.into(imageBanner); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=Caching= | |||
==Introduction== | |||
Picasso default loading process is as follows | |||
[[File:Picasso Caching.png|800px]] | |||
==Policies== | |||
There are two policies you can implement | |||
*disk policy | |||
*memory policy | |||
These are independent, i.e. if you turn one off the other is checked. | |||
<br> | |||
We can also | |||
*log the activity for debugging purposes. | |||
*add indicator to image to show where the image was from e.g memory, disk, network | |||
===Example Indicators=== | |||
This is a global setting | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
Picasso.with(getContext()).setIndicatorsEnabled(true); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Example Turning off Cache=== | |||
We can do this on a per usage basis | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
Picasso.with(mContext) | |||
.load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + mItems.get(position).getImageUrl()) | |||
.memoryPolicy(MemoryPolicy.NO_CACHE) | |||
.networkPolicy(NetworkPolicy.NO_CACHE) | |||
.into(holder.mImageView); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Example Logging=== | |||
This is set simple by | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
Picasso.with(mContext).setLoggingEnabled(true); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
[[File:Picasso logs.png|800px]] | |||
=Managing Requests= | |||
==Prefetch== | |||
Because Picasso uses caching we can prefetch images but call fetch earlier. So calling fetch on the front screen will mean that the second screen loads faster. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
String[] array = new String[] { | |||
"ground.jpg", | |||
"table.jpg", | |||
"beans.jpg", | |||
"granola.jpg", | |||
"bag.jpg", | |||
}; | |||
for(String url : array) { | |||
Picasso.with(this).load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + url).fetch(); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Placeholder and Errors== | |||
We can have a default image if all does not go well on loading and use the '''error''' function. We can also specify a pre-image placeholder with the '''placeholder''' function | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
Picasso.with(context). | |||
load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + this.data.get(position)) | |||
.error(R.drawable.default) | |||
.placeholder(R.drawable.initial) | |||
.rotate(degrees) | |||
.fit() | |||
.centerCrop() | |||
.into((ImageView) convertView); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Tagging== | |||
===Introduction=== | |||
We can group images by name (Tag). We can Cancel, Pause and Resume groups of images using tags. | |||
[[File:Picasso tags.png|800px]] | |||
The use case was a gallery. To implement this we implement the onScrollListener and tag the images in the adapter (not shown) with the function Picasso function tag("gallery"). | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@Override | |||
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState) { | |||
if (scrollState == SCROLL_STATE_IDLE || scrollState == SCROLL_STATE_TOUCH_SCROLL) { | |||
Picasso.with(mContext).resumeTag("gallery"); | |||
} else { | |||
Picasso.with(mContext).pauseTag("gallery"); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
@Override | |||
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount, int totalItemCount) | |||
{ | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Targets== | |||
This allow custom logic to run much like the transformation. We | |||
*Create a class | |||
*Implement the methods | |||
*Attach it to the load | |||
===Create a class=== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
Target mTarget; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Implement the methods=== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
mTarget = new Target() { | |||
@Override | |||
public void onBitmapLoaded(Bitmap bitmap, Picasso.LoadedFrom from) { | |||
imageView1.setImageBitmap(bitmap); | |||
} | |||
@Override | |||
public void onBitmapFailed(Drawable errorDrawable) { | |||
Toast.makeText(context, "Your connection needs espresso", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); | |||
} | |||
@Override | |||
public void onPrepareLoad(Drawable placeHolderDrawable) { | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Attach it to the load=== | |||
And finally instead of the image view we specify the target. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
Picasso.with(this) | |||
.load("http://www.alexwolfps.com/images/logo.png") | |||
.into(mTarget); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 02:10, 5 February 2021
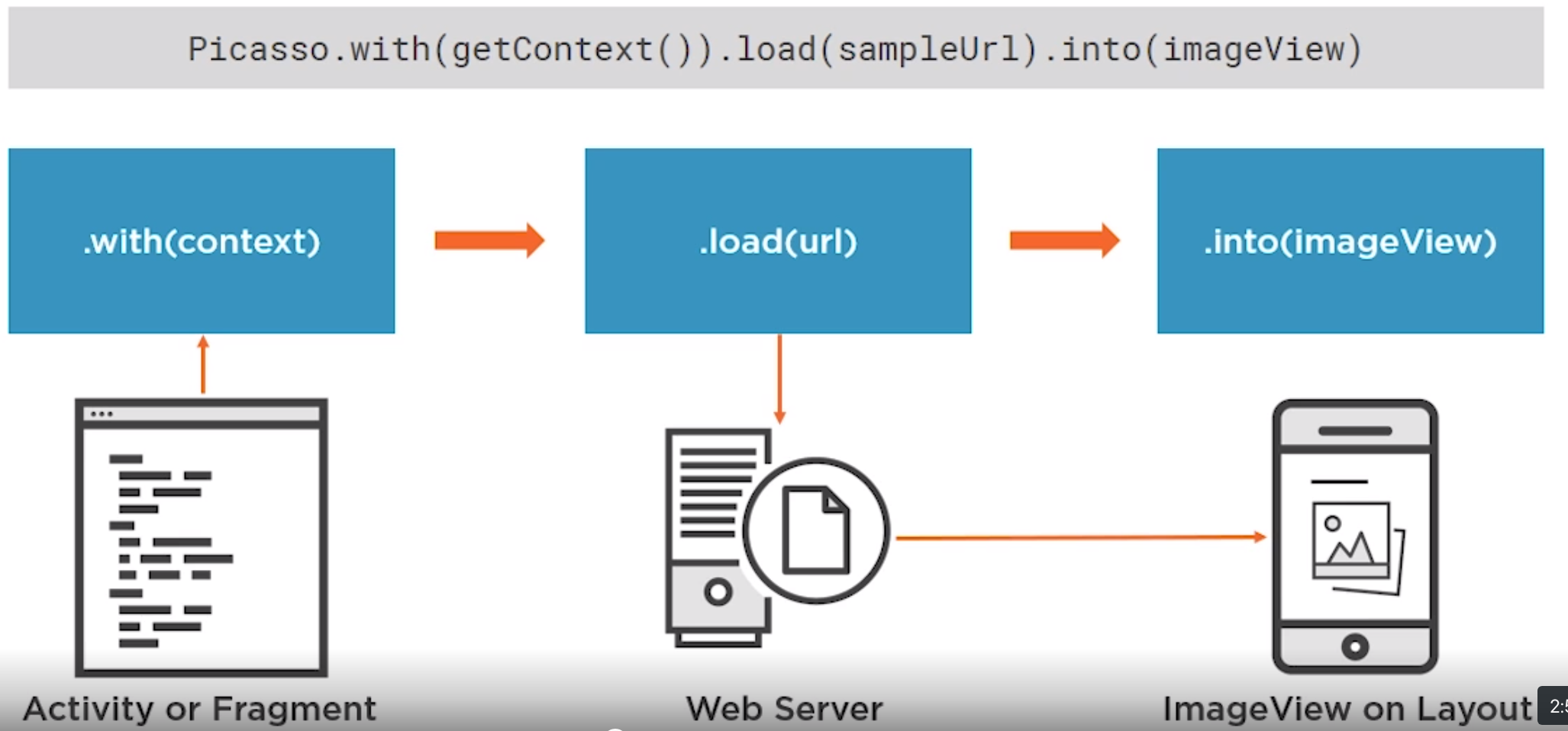
Introduction
Picasso is a library for managing images on Android and is very simple to use
Picasso.with(getContext()).load(sampleURI).into(imageView)
- Flexible Source Locations
- Caching
- Image Trnasformations
- Error Handling
- Logging
- Request Management
To add it to our projects we simply add it to the gradle. At the time this was
implementation 'com.squareup.picasso:picasso:2.71828'
Resources for this can be found at
https://github.com/alex-wolf-ps/android-picasso
Comparison
Here are some comparisons on the competition at the time, Glide and Fresco. I guess I am more interested in the items to compare as this points to the problem people are trying to solve.
Loading Images
Sources
Picasso supports loading images from either
- String, "https:://www.bibble.co.nz/myimage.png
- Resource ID, images stored in the app drawable e.g. R.drawable.myimage
- URI, Maybe an image from the phone using an intent
- File, a Android File Object
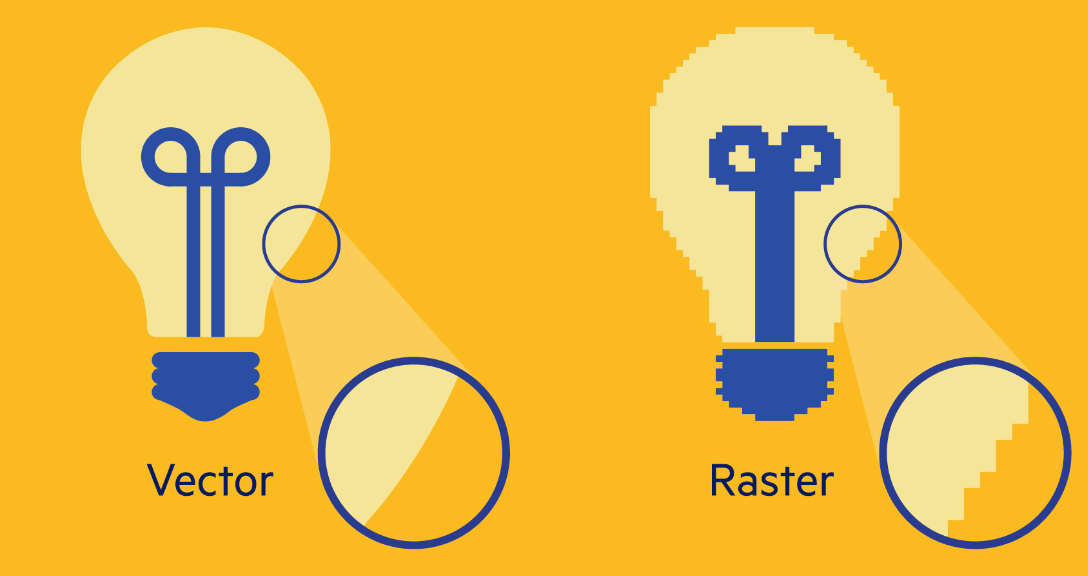
File Types
Picasso supports many file types include JPEG, PNG and SVG. JPEG and PNG are raster images and SVGs are vector Images. Vector images are stored as a series of paths curves and points. Where as raster images of pixels which makes them less unable to scale
Error Handling
We just create a handler for Picasso and then we can add a breakpoint on the listener. All of the problems I have had have been I forget they do not process svgs.
val picasso = Picasso.Builder(context)
.listener { picasso, uri, exception ->
Log.e("Picasso Error", "Errored out, hiding view");
}
.build()
viewHolder.viewBinding.imgViewState.setImageBitmap(R.drawable.ic_green_arrow_up)
picasso.load(R.drawable.ic_green_arrow_up)
.into(viewHolder.viewBinding.imgViewState)
Example 1 Drawable PNG
Create drawables in your res/drawable folder. We can create an appropriate folder for different resolutions e.g.
- /drawable-ldpi For low density screens.
- /drawable-mdpi For medium density screens.
- /drawable-hdpi For high resolution screens.
- /drawable-xhdpi For extra high resolution screens.
Note that the these folders are at the same level as drawable and not inside. From there it is a simple case of getting the Resource ID and loading it into the control.
ImageView banner = view.findViewById(R.id.banner);
Picasso.with(getContext()).load(R.drawable.beans).into(banner);
Example 2 Drawable Icon
Using the code
ImageView imgAboutOne = view.findViewById(R.id.icon_wait);
Picasso.with(getContext()).load(R.drawable.ic_done).into(imgAboutOne);
I struggled to get this to work as Android Studio now supports vectors. When you create an icon the result includes a vector.
Failed to create image decoder with message 'unimplemented'
To resolve this updated the version of picasso and achieved nothing except understanding the new syntax which does not require the context.
ImageView imgAboutOne = view.findViewById(R.id.icon_wait);
Picasso.get().load(R.drawable.ic_done).into(imgAboutOne);
Then found that icons are stored under mipmap so this all worked on the old picasso with
ImageView imageView1 = view.findViewById(R.id.icon_drivethru);
Picasso.with(getContext()).load(R.mipmap.ic_done).into(imageView1);
Using with a GridView
This is of course trivial and a big repetitive but here goes for reference. It just loads the images as above
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
if (convertView == null) {
LayoutInflater inflater = ((Activity) context).getLayoutInflater();
convertView = inflater.inflate(layoutResourceId, parent, false);
}
Picasso.with(context).
load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + this.data.get(position)).
into((ImageView) convertView);
return convertView;
}
Using with a RecyclerView
Much the same story. For this I needed to pass the context and then amend the view holder.
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(ItemViewHolder holder, int position) {
holder.mItemDesc.setText(mItems.get(position).getDescription());
holder.mItemName.setText(mItems.get(position).getName());
Picasso.with(mContext).
load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + mItems.get(position).getImageUrl())
.into(holder.mImageView);
}
Using an Intent (Downloads, Gallery)
The picasso code is exactly the same but this is a great example
Create Button and ImageView
Let's create a button and image view
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="6dp"
android:weightSum="2"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="Share Your Experience!" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_submit"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="Upload Image" />
</LinearLayout>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/image_submission"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" />
Create Click Event
Create a click event implementation
Button btnSubmit = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.btn_submit);
btnSubmit.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent().setType("image/*").setAction(Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT);
startActivityForResult(intent, 1);
}
});
Populate ImageView
After the intent ends lets populate the image view
@Override
public void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
Uri imgUri = data.getData();
ImageView imgPreview = (ImageView) getActivity().findViewById(R.id.image_submission);
Picasso.with(getContext()).load(imgUri).into(imgPreview);
}
Transformations
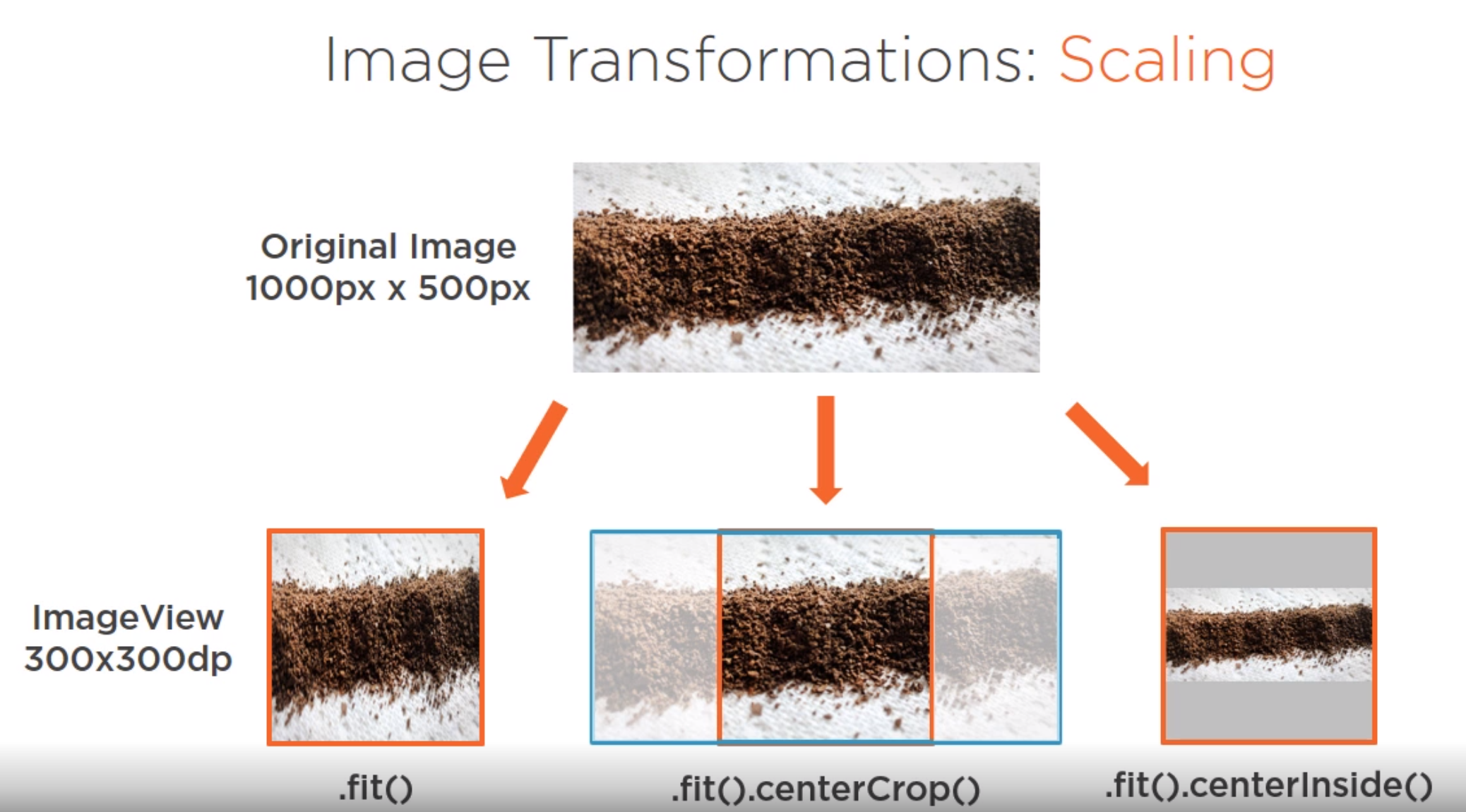
Scaling
Picasso provides 3 types of scaling. Probably does not need more information
Resizing
Some function are available for resizing.
Rotation
We can rotate images with a number of degrees and a pivot point. An a example of random is
int twiceMax = 20;
int actualMax = 10;
int degrees = new Random().nextInt(twiceMax) - actualMax;
Picasso.with(context).
load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + this.data.get(position))
.rotate(degrees)
.fit()
.centerCrop()
.into((ImageView) convertView);
Custom Transformations
Recommend Classes for Image
- Canvas
- Paint
- ColorMatrix
- Bitmap
Example
A bit disappointing but this allows you to run some code prior to the image being rendered. You do all of the work. Just create and instance to a transform
public class BannerTransformation implements Transformation {
@Override
public Bitmap transform(Bitmap source) {
int originalHeight = source.getHeight();
int totalMargin = originalHeight / 2;
int croppedImageHeight = originalHeight / 2;
Bitmap croppedImage =
Bitmap.createBitmap(source, 0, totalMargin / 2, source.getWidth(), croppedImageHeight);
if (croppedImage != source) {
source.recycle();
}
return croppedImage;
}
@Override
public String key() {
return "BannerTransformation";
}
}
And use it
Picasso.with(getContext())
.load(R.drawable.beans)
.transform(new BannerTransformation())
.into(imageBanner);
Caching
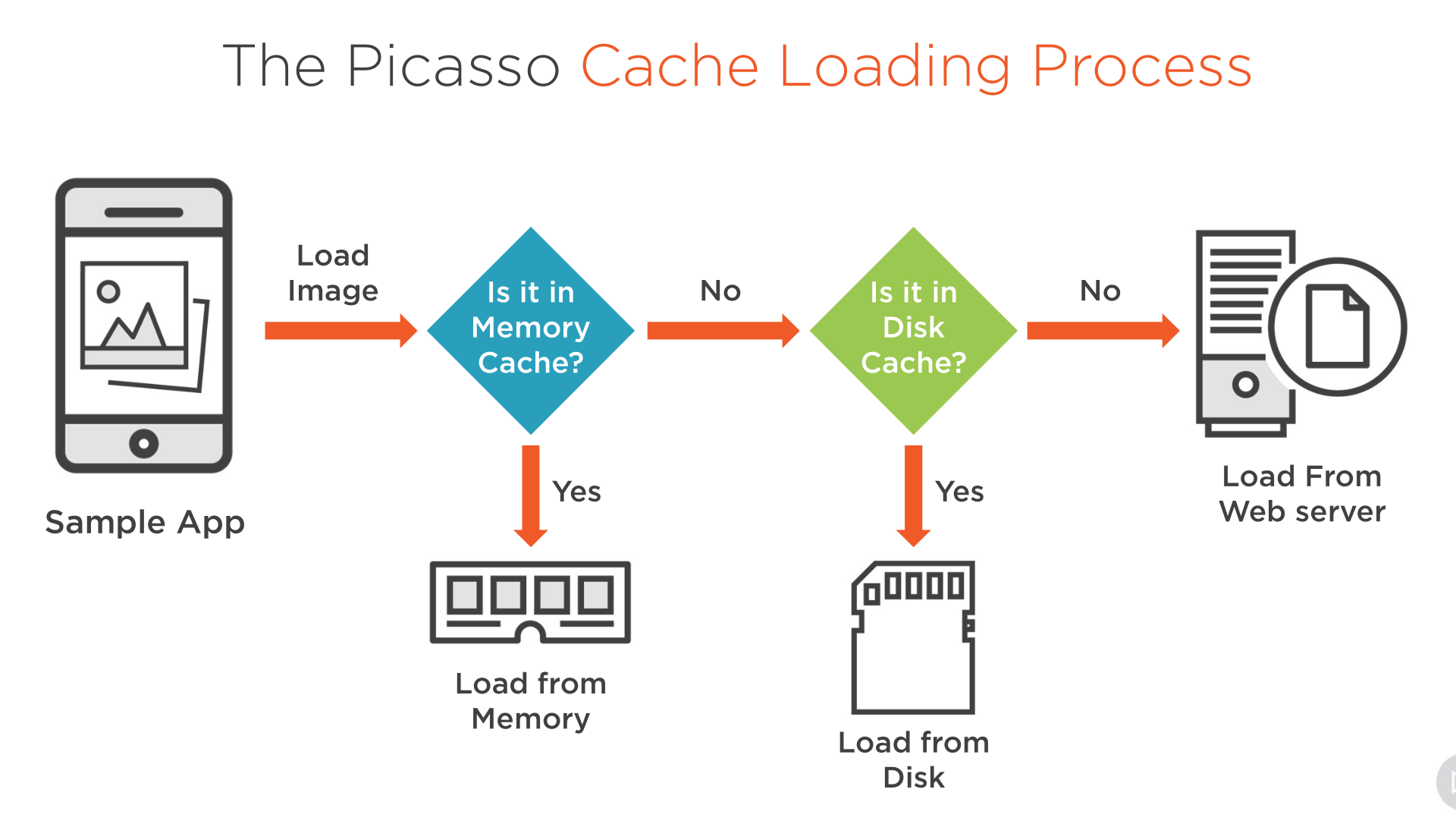
Introduction
Picasso default loading process is as follows
Policies
There are two policies you can implement
- disk policy
- memory policy
These are independent, i.e. if you turn one off the other is checked.
We can also
- log the activity for debugging purposes.
- add indicator to image to show where the image was from e.g memory, disk, network
Example Indicators
This is a global setting
Picasso.with(getContext()).setIndicatorsEnabled(true);
Example Turning off Cache
We can do this on a per usage basis
Picasso.with(mContext)
.load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + mItems.get(position).getImageUrl())
.memoryPolicy(MemoryPolicy.NO_CACHE)
.networkPolicy(NetworkPolicy.NO_CACHE)
.into(holder.mImageView);
Example Logging
This is set simple by
Picasso.with(mContext).setLoggingEnabled(true);
Managing Requests
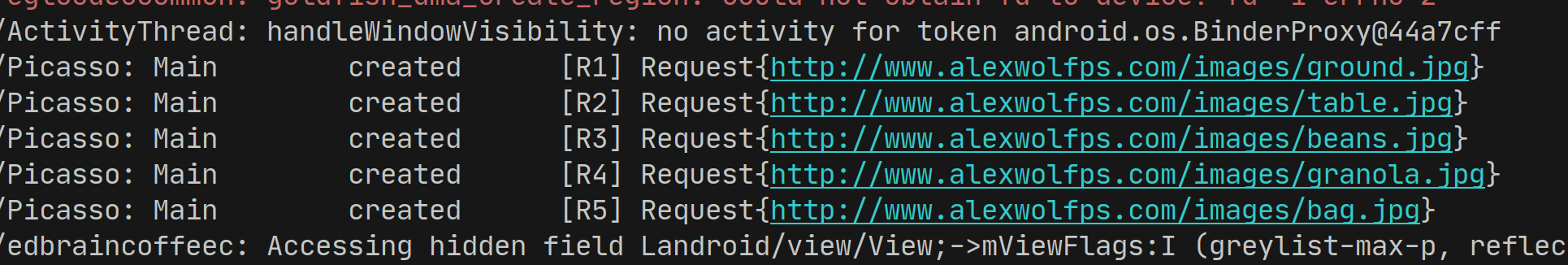
Prefetch
Because Picasso uses caching we can prefetch images but call fetch earlier. So calling fetch on the front screen will mean that the second screen loads faster.
String[] array = new String[] {
"ground.jpg",
"table.jpg",
"beans.jpg",
"granola.jpg",
"bag.jpg",
};
for(String url : array) {
Picasso.with(this).load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + url).fetch();
}
Placeholder and Errors
We can have a default image if all does not go well on loading and use the error function. We can also specify a pre-image placeholder with the placeholder function
Picasso.with(context).
load(UrlHelper.BaseUrl + this.data.get(position))
.error(R.drawable.default)
.placeholder(R.drawable.initial)
.rotate(degrees)
.fit()
.centerCrop()
.into((ImageView) convertView);
Tagging
Introduction
We can group images by name (Tag). We can Cancel, Pause and Resume groups of images using tags.
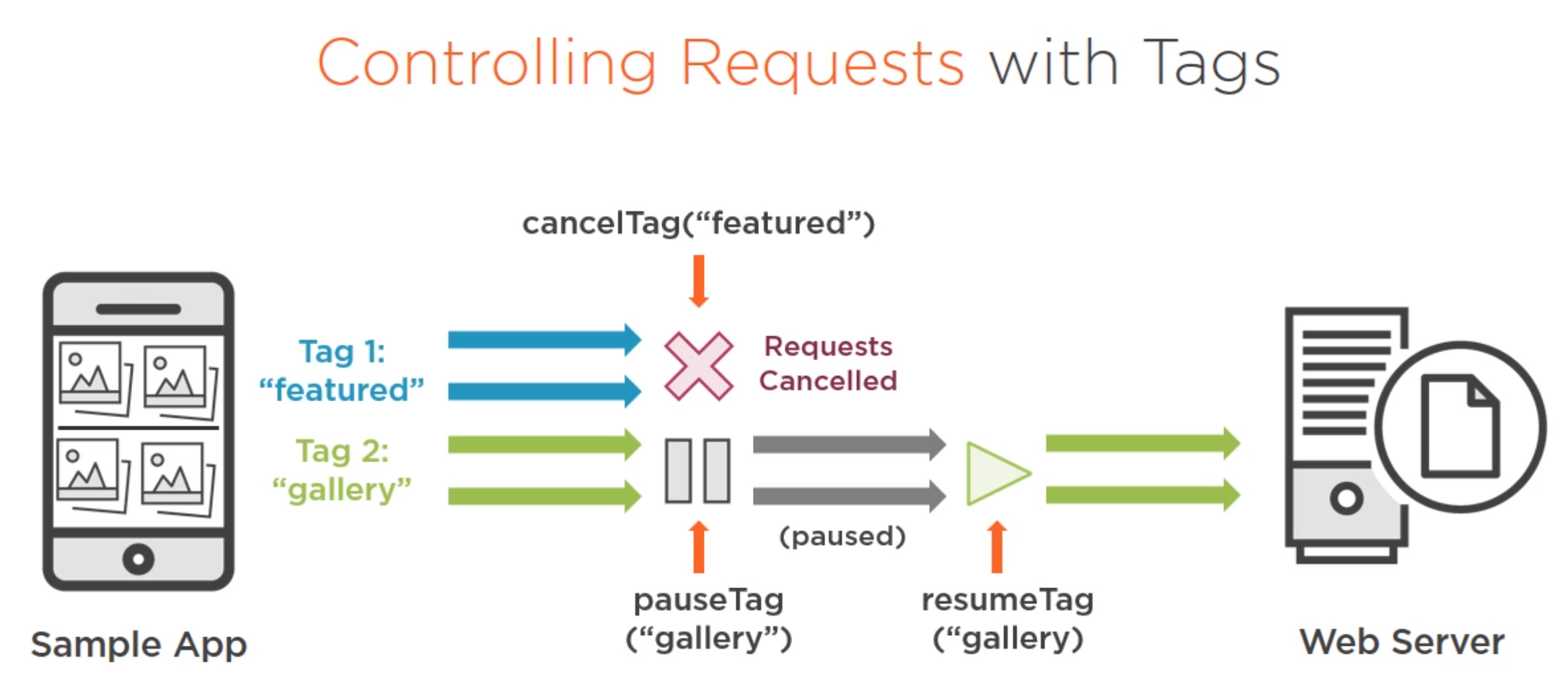 The use case was a gallery. To implement this we implement the onScrollListener and tag the images in the adapter (not shown) with the function Picasso function tag("gallery").
The use case was a gallery. To implement this we implement the onScrollListener and tag the images in the adapter (not shown) with the function Picasso function tag("gallery").
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState) {
if (scrollState == SCROLL_STATE_IDLE || scrollState == SCROLL_STATE_TOUCH_SCROLL) {
Picasso.with(mContext).resumeTag("gallery");
} else {
Picasso.with(mContext).pauseTag("gallery");
}
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount, int totalItemCount)
{
}
Targets
This allow custom logic to run much like the transformation. We
- Create a class
- Implement the methods
- Attach it to the load
Create a class
Target mTarget;
Implement the methods
mTarget = new Target() {
@Override
public void onBitmapLoaded(Bitmap bitmap, Picasso.LoadedFrom from) {
imageView1.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
}
@Override
public void onBitmapFailed(Drawable errorDrawable) {
Toast.makeText(context, "Your connection needs espresso", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
@Override
public void onPrepareLoad(Drawable placeHolderDrawable) {
}
};
Attach it to the load
And finally instead of the image view we specify the target.
Picasso.with(this)
.load("http://www.alexwolfps.com/images/logo.png")
.into(mTarget);