React Using APIs: Difference between revisions
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 178: | Line 178: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==Refactoring Thunk== | ==Refactoring Thunk== | ||
We need to | |||
*Create the GET function | |||
*Create and Wrap the CRUD Functions | |||
*Change Reducer Accept Generic CRUD Functions | |||
*Implement new calls to helper functions | |||
*Change UI from Promises Object | |||
*Add Thunk Middleware | |||
*Create and Pass Wrapped Store | |||
This is quite a bit of work to get right. | |||
===Create the GET function=== | |||
Let make the GET a function. | Let make the GET a function. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | ||
| Line 193: | Line 203: | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Now we create function for each CRUD operation and we wrap it in a function that | ===Create and Wrap the CRUD Functions=== | ||
Now we create function for each CRUD operation and we wrap it in a function that returns the cart and accepts dispatch and getState as the arguments. Here is ADD. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | ||
export function addCart(id) { | export function addCart(id) { | ||
| Line 213: | Line 224: | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
===Change Reducer Accept Generic CRUD Functions=== | |||
Within the original reducer we now have this becase the "refresh" functions passes the action to the refresh function which we will see in a moment. | Within the original reducer we now have this becase the "refresh" functions passes the action to the refresh function which we will see in a moment. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | ||
| Line 232: | Line 244: | ||
}; | }; | ||
export default CartReducer; | export default CartReducer; | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Implement new calls to helper functions=== | |||
Using the this we can create an instance of dispatch and pass the addCart function. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
... | |||
const dispatch = useDispatch(); | |||
<button> type="button" ... onClick={() => dispatch(addCart()event.id)}...</button> | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Change UI from Promises Object=== | |||
We now return an object and now a promise so. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
const state = CartStore.getState(); | |||
if (state) { | |||
state.then((state) = { | |||
const cart = state.cart; | |||
const totalAmount = state.cart.reduce((p, n) => p + n.quantity * n.price, 0); | |||
setCart(cart); | |||
setTotalAmount(totalAmount); | |||
}) | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Becomes | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
const state = CartStore.getState(); | |||
if (state) { | |||
const cart = state.cart; | |||
const totalAmount = state.cart.reduce((p, n) => p + n.quantity * n.price, 0); | |||
setCart(cart); | |||
setTotalAmount(totalAmount); | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Add Thunk Middleware=== | |||
We now need to add our redux-thunk middleware to the user. Similar to express we create an instance and add it to the arguments of the store. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js" highlight="3,6,8"> | |||
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux"; | |||
import thunkMiddleware from "redux-thunk"; | |||
import CartReducer from "./CartReducer"; | |||
const thunkMiddle = applyMiddleware(thunkMiddleware); | |||
const CartStore = createStore(CartReducer, thunkMiddle); | |||
export default CartStore; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Create and Pass Wrapped Store=== | |||
Similar to NodeJS which we create instances in React we use mark up to create the instances and pass them though the app. So before we had | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
import React from "react"; | |||
import ReactDOM from "react-dom"; | |||
import { Provider } from "react-redux"; | |||
import "./index.css"; | |||
import App from "./App"; | |||
import CartStore from "./CartStore"; | |||
ReactDOM.render( | |||
<React.StrictMode> | |||
<App /> | |||
</React.StrictMode>, | |||
document.getElementById('root') | |||
); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Becomes | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
import React from "react"; | |||
import ReactDOM from "react-dom"; | |||
import { Provider } from "react-redux"; | |||
import "./index.css"; | |||
import App from "./App"; | |||
import CartStore from "./CartStore"; | |||
ReactDOM.render( | |||
<React.StrictMode> | |||
<Provider store={CartStore}> | |||
<App /> | |||
</Provider> | |||
</React.StrictMode>, | |||
document.getElementById('root') | |||
); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Example using Axios== | |||
Here is the update request using Axios. Note the body is called data and the method is in the call. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
export function updateCart(id, quantity) { | |||
return async function updateCartThunk(dispatch, getState) { | |||
if (quantity === 0) { | |||
await axios.delete( | |||
"http://localhost:3333/cart", { | |||
headers: { | |||
"Content-Type": "application/json", | |||
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value | |||
}, | |||
data: { | |||
id: id | |||
} | |||
}); | |||
} else { | |||
await axios.patch( | |||
"http://localhost:3333/cart", | |||
{ | |||
id: id, | |||
quantity: quantity | |||
}, | |||
{ | |||
headers: { | |||
"Content-Type": "application/json", | |||
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value | |||
} | |||
}); | |||
} | |||
let cart = await _getCart(); | |||
dispatch({ type: "refresh", payload: cart }); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=Advanced Data Retrieval= | |||
Some things we might like to do are | |||
*caching/Pagination | |||
*Clumsy state management | |||
*Ceremony (lot of code for wiring up app - captures irrelevant detail) | |||
==React Query== | |||
This allows you to define a query with a name. Naming means that the results can be cached automatically. We need to create a QueryClient and QueryClientProvider in the App() but wrapping it as you would for the Store above. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
const query = useQuery( | |||
"events", | |||
() => axios.get(url) | |||
}; | |||
// query == { status, data, error, isloading} | |||
if (isLoading) { | |||
return (<div>Loading.... </div>); | |||
} | |||
return ( | |||
query.data.map(...) | |||
}; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
As a tip and often needed here is a delay for the loading. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
app.use((req, res, next) => setTimeout(next, 2000)); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Mutations== | |||
Part of React Query. This allows the application to get notification when a dispatch has been successful. You need to | |||
*Create an instance | |||
*Replace the dispatch with a wrapped Mutation | |||
*Add a reset to the instance | |||
Taking the add as an example we create the instance and add a reset after to 2s. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
const mutation = useMutation( | |||
id => dispatch(addCart(id)), | |||
{ | |||
onSuccess: () => { | |||
setTimeout(() => { mutation.reset(); }, 2000); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
We replace the dispatch with the wrapped mutation. We add some mark up for success (and some to reserve space when not success) | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
<button type="button" className="btn btn-primary btn-primary-themed btn-md font-upper" | |||
onClick={() => mutation.mutate(event.id)}>Add to | |||
Cart</button> | |||
{ mutation.isSuccess ? | |||
<span className="bi bi-bag-check-fill font-xxl ms-2 fadeout"></span> : | |||
<span className="bi bi-bag-check-fill text-white font-xxl ms-2 fadeout"></span>} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Finally we add CSS to perform a fade. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="css"> | |||
.fadeout { | |||
animation: fadeOut 2s; | |||
} | |||
@keyframes fadeOut { | |||
0% { opacity: 1; } | |||
100% { opacity: 0; } | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=Testing= | |||
==json-server== | |||
To create a simple CRUD API with json-server we just need to create a json file with our data. This will no only provide a server for get requests but will allow post and delete as well. | |||
==Error Handling Using Redux== | |||
This is more about the management of the error data than the error its self. Really liked the simplicity of it with redux. | |||
===Create a Reducer=== | |||
This allow you to set an error or close an error. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
const ErrorReducer = (state = { error: null }, action) => { | |||
const { error, type } = action; | |||
if (type === "ERROR_CLOSE") { | |||
return { | |||
error: null | |||
} | |||
} else if (type === "ERROR_SET") { | |||
return { | |||
error: error | |||
} | |||
} else { | |||
return state; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
export default ErrorReducer; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Create a Store=== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
import { createStore } from "redux"; | |||
import ErrorReducer from "./ErrorReducer"; | |||
const ErrorStore = createStore(ErrorReducer); | |||
export default ErrorStore; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Create a Banner Component=== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
import React from "react"; | |||
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from "react-redux"; | |||
export default function ErrorBanner() { | |||
const dispatch = useDispatch(); | |||
const error = useSelector(state => state.error); | |||
const isClosed = useSelector(state => state.isClosed); | |||
let handleCloseClick = () => { | |||
dispatch({ type: "ERROR_CLOSE" }); | |||
}; | |||
return ( | |||
error && !isClosed && | |||
<div className="alert alert-warning p-5"> | |||
<p className="lead">{ error.message }</p> | |||
<button type="button" id="btnClose" | |||
onClick={handleCloseClick} | |||
className="btn btn-primary btn-primary-themed btn-md font-upper">Close</button> | |||
</div> | |||
); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Error Boundaries== | |||
React Introduced the concept of ErrorBoundaries. This is a component that can wrap the app and catch the errors. Use static getDerivedStateFromError() to render a fallback UI after an error has been thrown. Use componentDidCatch() to log error information. We return this.props.fallback in the case of error. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
import React from "react"; | |||
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component { | |||
constructor(props) { | |||
super(props); | |||
this.state = { | |||
hasError: false, | |||
error: null | |||
}; | |||
} | |||
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) { | |||
// Update state so the next render will show the fallback UI. | |||
return { | |||
hasError: true, | |||
error | |||
}; | |||
} | |||
render() { | |||
if (this.state.hasError) { | |||
return this.props.fallback; | |||
} else { | |||
return this.props.children; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
export default ErrorBoundary; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
We can then wrap the desired component and render the fallback property. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
function App() { | |||
return ( | |||
<Router> | |||
<Header /> | |||
<ErrorBoundary fallback={<div className="mt-5 ms-5">Error!</div>}> | |||
<Route exact path="/" component={Eventlist} /> | |||
</ErrorBoundary> | |||
... | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:19, 24 June 2021
Introduction
This page is for how to use APIs with React.
When to call APIs
When using API here is where you should call the APIs
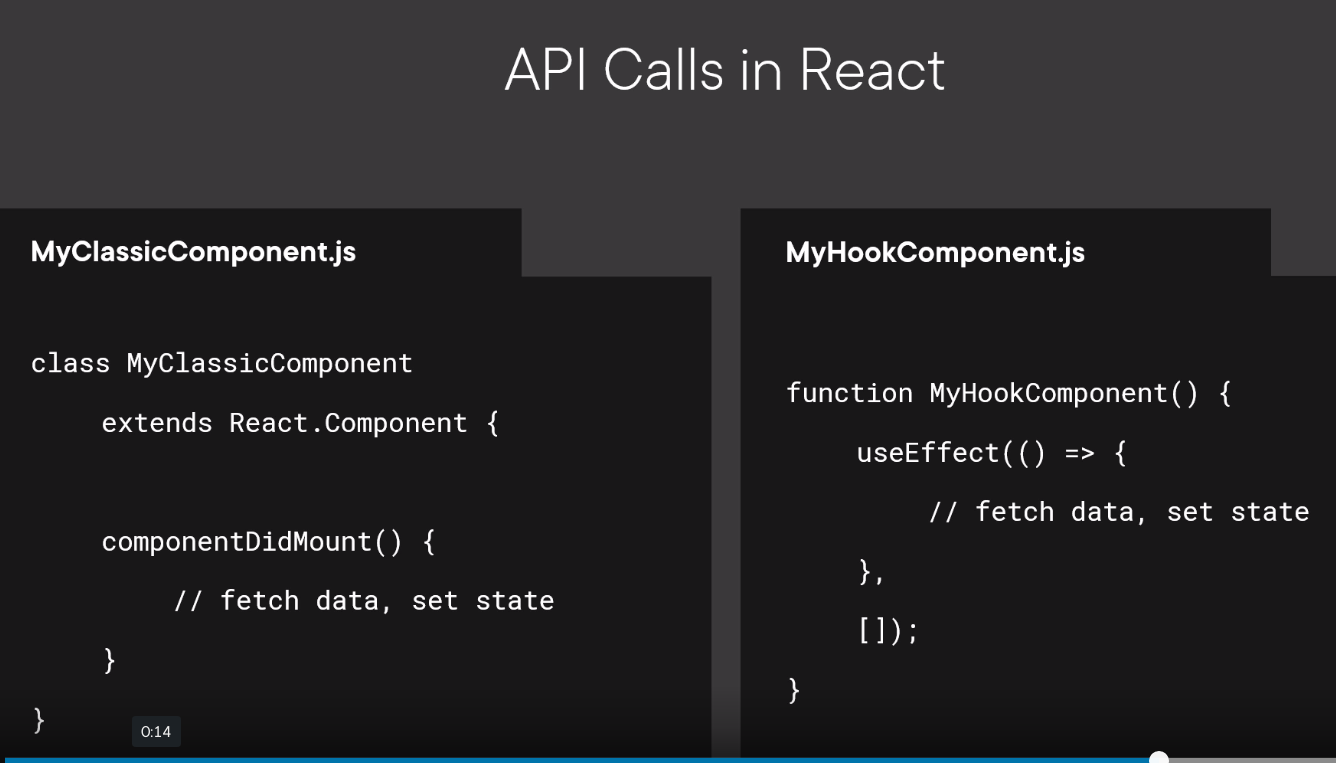
API for calling APIs
Options
There were 4 options offered.
- Fetch API (Newish but OK)
- Axios (Believe it is popular and have used)
- JQuery (Never used)
- XMLHttpRequest (old and liked - no surprise there)
Using Fetch
Here are the to ways to use fetch.
fetch("/path/to/API")
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {/* */})
const response = await fetch("/path/to/API");
const data = await response.json();
fetch("/path/to/API", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(data),
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
})
So within React this would look like this
const [events, setEvents] = useState([])
useEffect(() => {
fetch("/path/to/API")
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
setEvents(data)
})
}, [])
Example Reducer
Here is an example of using a reducer with an API
import UuidStore from "./UuidStore";
const CartReducer = async (state = { cart: [] }, action) => {
let cart = state.cart;
let response;
switch (action.type) {
case "add":
await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart",
{
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
},
body: JSON.stringify({
id: action.payload.id
})
}
);
response = await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart",
{
method: "GET",
headers: {
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
}
}
);
cart = await response.json();
return {
...state,
cart: cart
};
case "update":
if (action.payload.quantity === 0) {
await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart", {
method: "DELETE",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
},
body: JSON.stringify({
id: action.payload.event_id
})
});
} else {
await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart", {
method: "PATCH",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
},
body: JSON.stringify({
id: action.payload.event_id,
quantity: action.payload.quantity
})
});
}
response = await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
}
});
cart = await response.json();
return {
...state,
cart: cart
};
case "delete":
await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart", {
method: "DELETE",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
},
body: JSON.stringify({
id: action.payload.event_id
})
});
response = await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
}
});
cart = await response.json();
return {
...state,
cart: cart
};
case "clear":
await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart", {
method: "DELETE",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
}
});
response = await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
}
});
cart = await response.json();
return {
...state,
cart: cart
};
default:
return {
...state,
cart: cart
};
}
};
export default CartReducer;
Refactoring Thunk
We need to
- Create the GET function
- Create and Wrap the CRUD Functions
- Change Reducer Accept Generic CRUD Functions
- Implement new calls to helper functions
- Change UI from Promises Object
- Add Thunk Middleware
- Create and Pass Wrapped Store
This is quite a bit of work to get right.
Create the GET function
Let make the GET a function.
async function _getCart() {
response = await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
}
});
cart = await response.json();
return cart;
}
Create and Wrap the CRUD Functions
Now we create function for each CRUD operation and we wrap it in a function that returns the cart and accepts dispatch and getState as the arguments. Here is ADD.
export function addCart(id) {
return async function addCartThunk(dispatch, getState) {
await fetch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
},
body: JSON.stringify({
id: id
})
});
let cart = await _getCart();
dispatch({type: "refresh". payload: cart });
}
}
Change Reducer Accept Generic CRUD Functions
Within the original reducer we now have this becase the "refresh" functions passes the action to the refresh function which we will see in a moment.
const CartReducer = (state = { cart: [] }, action) => {
let cart = state.cart;
switch (action.type) {
case "refresh":
return {
...state,
cart: action.payload
};
default:
return {
...state,
cart: cart
};
}
};
export default CartReducer;
Implement new calls to helper functions
Using the this we can create an instance of dispatch and pass the addCart function.
...
const dispatch = useDispatch();
<button> type="button" ... onClick={() => dispatch(addCart()event.id)}...</button>
Change UI from Promises Object
We now return an object and now a promise so.
const state = CartStore.getState();
if (state) {
state.then((state) = {
const cart = state.cart;
const totalAmount = state.cart.reduce((p, n) => p + n.quantity * n.price, 0);
setCart(cart);
setTotalAmount(totalAmount);
})
}
};
Becomes
const state = CartStore.getState();
if (state) {
const cart = state.cart;
const totalAmount = state.cart.reduce((p, n) => p + n.quantity * n.price, 0);
setCart(cart);
setTotalAmount(totalAmount);
}
};
Add Thunk Middleware
We now need to add our redux-thunk middleware to the user. Similar to express we create an instance and add it to the arguments of the store.
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux";
import thunkMiddleware from "redux-thunk";
import CartReducer from "./CartReducer";
const thunkMiddle = applyMiddleware(thunkMiddleware);
const CartStore = createStore(CartReducer, thunkMiddle);
export default CartStore;
Create and Pass Wrapped Store
Similar to NodeJS which we create instances in React we use mark up to create the instances and pass them though the app. So before we had
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
import "./index.css";
import App from "./App";
import CartStore from "./CartStore";
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
Becomes
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
import "./index.css";
import App from "./App";
import CartStore from "./CartStore";
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<Provider store={CartStore}>
<App />
</Provider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
Example using Axios
Here is the update request using Axios. Note the body is called data and the method is in the call.
export function updateCart(id, quantity) {
return async function updateCartThunk(dispatch, getState) {
if (quantity === 0) {
await axios.delete(
"http://localhost:3333/cart", {
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
},
data: {
id: id
}
});
} else {
await axios.patch(
"http://localhost:3333/cart",
{
id: id,
quantity: quantity
},
{
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-SESSION-TOKEN": UuidStore.value
}
});
}
let cart = await _getCart();
dispatch({ type: "refresh", payload: cart });
}
}
Advanced Data Retrieval
Some things we might like to do are
- caching/Pagination
- Clumsy state management
- Ceremony (lot of code for wiring up app - captures irrelevant detail)
React Query
This allows you to define a query with a name. Naming means that the results can be cached automatically. We need to create a QueryClient and QueryClientProvider in the App() but wrapping it as you would for the Store above.
const query = useQuery(
"events",
() => axios.get(url)
};
// query == { status, data, error, isloading}
if (isLoading) {
return (<div>Loading.... </div>);
}
return (
query.data.map(...)
};
As a tip and often needed here is a delay for the loading.
app.use((req, res, next) => setTimeout(next, 2000));
Mutations
Part of React Query. This allows the application to get notification when a dispatch has been successful. You need to
- Create an instance
- Replace the dispatch with a wrapped Mutation
- Add a reset to the instance
Taking the add as an example we create the instance and add a reset after to 2s.
const mutation = useMutation(
id => dispatch(addCart(id)),
{
onSuccess: () => {
setTimeout(() => { mutation.reset(); }, 2000);
}
}
)
We replace the dispatch with the wrapped mutation. We add some mark up for success (and some to reserve space when not success)
<button type="button" className="btn btn-primary btn-primary-themed btn-md font-upper"
onClick={() => mutation.mutate(event.id)}>Add to
Cart</button>
{ mutation.isSuccess ?
<span className="bi bi-bag-check-fill font-xxl ms-2 fadeout"></span> :
<span className="bi bi-bag-check-fill text-white font-xxl ms-2 fadeout"></span>}
Finally we add CSS to perform a fade.
.fadeout {
animation: fadeOut 2s;
}
@keyframes fadeOut {
0% { opacity: 1; }
100% { opacity: 0; }
}
Testing
json-server
To create a simple CRUD API with json-server we just need to create a json file with our data. This will no only provide a server for get requests but will allow post and delete as well.
Error Handling Using Redux
This is more about the management of the error data than the error its self. Really liked the simplicity of it with redux.
Create a Reducer
This allow you to set an error or close an error.
const ErrorReducer = (state = { error: null }, action) => {
const { error, type } = action;
if (type === "ERROR_CLOSE") {
return {
error: null
}
} else if (type === "ERROR_SET") {
return {
error: error
}
} else {
return state;
}
}
export default ErrorReducer;
Create a Store
import { createStore } from "redux";
import ErrorReducer from "./ErrorReducer";
const ErrorStore = createStore(ErrorReducer);
export default ErrorStore;
Create a Banner Component
import React from "react";
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from "react-redux";
export default function ErrorBanner() {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const error = useSelector(state => state.error);
const isClosed = useSelector(state => state.isClosed);
let handleCloseClick = () => {
dispatch({ type: "ERROR_CLOSE" });
};
return (
error && !isClosed &&
<div className="alert alert-warning p-5">
<p className="lead">{ error.message }</p>
<button type="button" id="btnClose"
onClick={handleCloseClick}
className="btn btn-primary btn-primary-themed btn-md font-upper">Close</button>
</div>
);
}
Error Boundaries
React Introduced the concept of ErrorBoundaries. This is a component that can wrap the app and catch the errors. Use static getDerivedStateFromError() to render a fallback UI after an error has been thrown. Use componentDidCatch() to log error information. We return this.props.fallback in the case of error.
import React from "react";
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
hasError: false,
error: null
};
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// Update state so the next render will show the fallback UI.
return {
hasError: true,
error
};
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return this.props.fallback;
} else {
return this.props.children;
}
}
}
export default ErrorBoundary;
We can then wrap the desired component and render the fallback property.
function App() {
return (
<Router>
<Header />
<ErrorBoundary fallback={<div className="mt-5 ms-5">Error!</div>}>
<Route exact path="/" component={Eventlist} />
</ErrorBoundary>
...