React Forms: Difference between revisions
Created page with "=Introduction= *Controlled Forms *using Formik *Validation *Creating reusable custom form elements *Uncontrolled forms using React *React Hook Form to create uncontrolled for..." |
|||
| (34 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
*Controlled Forms | *Controlled Forms | ||
* | *Uncontrolled Forms | ||
*Using Formik Library | |||
*Validation | *Validation | ||
*Creating reusable custom form elements | *Creating reusable custom form elements | ||
*Uncontrolled forms using React | *Uncontrolled forms using React | ||
*React Hook Form to create uncontrolled forms | *React Hook Form to create uncontrolled forms | ||
=Controlled forms= | =Controlled forms= | ||
In react we can pass state management to the react component. This is what a controlled form is. It's advantages are | In react we can pass state management to the react component. This is what a controlled form is. It's advantages are | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
*Formats the input data e.g. dates 25-03-2001 | *Formats the input data e.g. dates 25-03-2001 | ||
==Example using UseState== | ==Example using UseState== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=" | <syntaxhighlight lang="jsx"> | ||
const [password, setPassword] = useState(""); | const [password, setPassword] = useState(""); | ||
... | ... | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
... | ... | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Uncontrolled forms are when the DOM maintains the states and a reference is stored to it in react. | |||
==Using React Components== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="jsx"> | |||
import React from "react"; | |||
class EmailForm extends React.Component { | |||
constructor(props) { | |||
super(props); | |||
} | |||
this.state = {value: ''}; | |||
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this); | |||
handleChange(event) { | |||
this.setState({value: event.target.value}); | |||
} | |||
render() { | |||
return ( | |||
<form> | |||
<input type="email" value={this.state.value} onChange={this.handleChange} /> | |||
</form> | |||
); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=Uncontrolled Forms= | |||
==Introduction== | |||
Uncontrolled forms are when the DOM maintains the states and a reference is stored to it in react. To use an uncontrolled Form you need to | |||
*Create a reference using React.createRef() | |||
*Assign reference using ref prop on form element | |||
*Extract value using the reference created in the constructor | |||
==Example== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="jsx"> | |||
import React from "react"; | |||
class TestForm extends React.Component { | |||
constructor(props) { | |||
super(props); | |||
this.submit = this.submit.bind(this); | |||
this.input = React.createRef(); | |||
} | |||
submit(event) { | |||
// eslint-disable-next-line no-alert | |||
alert(`Value${this.input.current.value}`); | |||
event.preventDefault(); | |||
} | |||
render() { | |||
return ( | |||
<form onSubmit={this.submit}> | |||
<input type="text" ref={this.input} /> | |||
<input type="submit" value="Submit" /> | |||
</form> | |||
); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
export default TestForm; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==When to Use== | |||
*For read-only elements like file input | |||
*When using a non-react library | |||
*To reduce re-rending form in a complex DOM | |||
==Using useForm Hook== | |||
*Uses uncontrolled elements | |||
*Therefore minimizes re-rendering | |||
*Works with Controlled components & UI libraries | |||
*Provides Validation helpers and support for schema validators | |||
==Example useForm Hook== | |||
*Import the hook | |||
*Get props from hook | |||
*Set the callback to envoke if validation does fail on submit | |||
*Set the forms handleSubmit function | |||
*Register the input tag with a name | |||
*If errors render them | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
import {useForm} from "react-hook-form"; | |||
export default App() { | |||
const {register, handleSubmit, errors} = useForm() | |||
const mySubmit = data => console.log(`Add validation on submit here ${data}`) | |||
return ( | |||
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(mySubmit)}> | |||
<input {...register("email")} /> | |||
{errors.email && <span>this field is required</span>} | |||
<input type="submit" /> | |||
</form> | |||
) | |||
} | |||
export default TestReactHookForm; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Validation with useForm== | |||
We can pass the standard HTML validation when we register the field. Any HTML validation can be used. e.g. min or max | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
<input {...register("email", {required: "error messsage"})} /> | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
We can also use a schema by installing the appropriate resolver e.g. yup resolver and setting the schema to use when we define the useForm hook | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
const {register, handleSubmit, errors} = useForm({ | |||
{ resolver: yupResolver(schema)}) | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Watch with useFrom== | |||
This will watch specified inputs and return their values. It is useful for determining what to render. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="jsx"> | |||
import React from "react"; | |||
import { useForm } from "react-hook-form"; | |||
function App() { | |||
const { register, watch, formState: { errors }, handleSubmit } = useForm(); | |||
const watchShowAge = watch("showAge", false); // you can supply default value as second argument | |||
const watchAllFields = watch(); // when pass nothing as argument, you are watching everything | |||
const watchFields = watch(["showAge", "number"]); // you can also target specific fields by their names | |||
const onSubmit = data => console.log(data); | |||
return ( | |||
<> | |||
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(onSubmit)}> | |||
<input type="checkbox" {...register("showAge")} /> | |||
{/* based on yes selection to display Age Input*/} | |||
{watchShowAge && <input type="number" {...register("age", { min: 50 })} />} | |||
<input type="submit" /> | |||
</form> | |||
</> | |||
); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=Using Formik Library= | |||
==Advantages== | |||
This is what is suggests. | |||
*Reduces Verbosity | |||
*Reduces code for state and callbacks | |||
*Reduces errors | |||
*Tracks values, errors and visited fields | |||
*Hooks up appropriate callback functions | |||
*Helpers for sync and async validation and showing errors | |||
*Sensible defaults | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Components of Formik== | |||
Here are the components which make up a Formik form. The first being the component responsible for controlling the form | |||
*Formik | |||
*Form | |||
*Field | |||
*ErrorMessage | |||
Internally Formik maintains three maps. | |||
[[File:Formik State.png|400px]] | |||
==Formik Using Components== | |||
This is the example with components. This now been re-implemented using hooks. It does use styled components around the controls which I personally found to be a bit hard to debug. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="jsx"> | |||
import React from "react"; | |||
import styled from "styled-components"; | |||
import { Formik, Field, Form, ErrorMessage } from "formik"; | |||
const SigninForm = styled(Form)` | |||
display: flex; | |||
flex-direction: column; | |||
padding: 30px; | |||
border: 1px solid black; | |||
`; | |||
const Container = styled.div` | |||
display: flex; | |||
flex-direction: column; | |||
flex: 1; | |||
height: 100%; | |||
align-items: center; | |||
`; | |||
const ContentContainer = styled.div` | |||
display: flex; | |||
flex-direction: column; | |||
width: 600px; | |||
margin-top: 50px; | |||
`; | |||
const Title = styled.h1` | |||
white-space: pre-line; | |||
`; | |||
const Label = styled.label` | |||
margin-top: 20px; | |||
font-size: 24px; | |||
`; | |||
const EmailField = styled(Field)` | |||
height: 40px; | |||
font-size: 24px; | |||
`; | |||
const ErrorLabel = styled.div` | |||
color: red; | |||
font-size: 26px; | |||
`; | |||
const PasswordField = styled(Field)` | |||
height: 40px; | |||
font-size: 24px; | |||
`; | |||
const CheckboxContainer = styled.div` | |||
display: flex; | |||
height: 50px; | |||
align-items: center; | |||
`; | |||
const RememberMeCheckboxField = styled(Field)` | |||
margin-top: 10px; | |||
`; | |||
const CheckboxLabel = styled(Label)` | |||
margin-top: 7px; | |||
margin-left: 10px; | |||
`; | |||
class LoginFormik extends React.Component { | |||
constructor(props) { | |||
super(props); | |||
this.handleSubmit = LoginFormik.handleSubmit.bind(this); | |||
this.handleValidation = LoginFormik.handleValidation.bind(this); | |||
} | |||
static handleSubmit(values) { | |||
return new Promise((resolve) => { | |||
setTimeout(() => { | |||
resolve(); | |||
// eslint-disable-next-line no-alert | |||
alert(JSON.stringify(values)); | |||
}, 5000); | |||
}); | |||
} | |||
static handleValidation(values) { | |||
const errors = {}; | |||
if (!values.email) { | |||
errors.email = "Email cannot be empty"; | |||
} | |||
if (!values.password) { | |||
errors.password = "Password cannot be empty"; | |||
} else if (values.password.length < 8) { | |||
errors.password = "Password must be at least 8 characters"; | |||
} | |||
return errors; | |||
} | |||
render() { | |||
return ( | |||
<Container> | |||
<ContentContainer> | |||
<Title>Signin Form</Title> | |||
<Formik | |||
initialValues={{ email: "", password: "", rememberMe: false }} | |||
onSumbit={this.handleSumbit} | |||
validate={this.handleValidation} | |||
> | |||
{() => ( | |||
<SigninForm> | |||
<Label>Email</Label> | |||
<EmailField name="email" type="email" /> | |||
<ErrorMessage name="email"> | |||
{(error) => <ErrorLabel>{error}</ErrorLabel>} | |||
</ErrorMessage> | |||
<Label>Password</Label> | |||
<PasswordField name="password" type="password" /> | |||
<ErrorMessage name="password"> | |||
{(error) => <ErrorLabel>{error}</ErrorLabel>} | |||
</ErrorMessage> | |||
<CheckboxContainer> | |||
<RememberMeCheckboxField type="checkbox" name="rememberMe" /> | |||
<CheckboxLabel>Remember Me</CheckboxLabel> | |||
</CheckboxContainer> | |||
</SigninForm> | |||
)} | |||
</Formik> | |||
</ContentContainer> | |||
</Container> | |||
); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
export default LoginFormik; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=Formik Validation= | |||
Formik provides two types of validation and they are not a surprise | |||
*Field level | |||
*Form level | |||
==Field Level== | |||
Note the returning of undefined '''not''' null | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="jsx"> | |||
... | |||
class LoginFormik extends React.Component { | |||
static validatePassword(value) { | |||
if (!value) { | |||
return "Password cannot be empty"; | |||
} | |||
if (value.length < 5) { | |||
return "Very Weak"; | |||
} | |||
if (value.length < 8) { | |||
return "Weak"; | |||
} | |||
return undefined; | |||
} | |||
... | |||
<Label>Password</Label> | |||
<PasswordField | |||
name="password" | |||
type="password" | |||
validate={LoginFormik.validatePassword} | |||
/> | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Form Level== | |||
This is done by defining a function on the Formik validate property. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
<Formik | |||
initialValues={{ email: "", password: "", rememberMe: false }} | |||
onSumbit={this.handleSumbit} | |||
validate={this.handleValidation} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=Formik Schema Validation (e.g. yup)= | |||
==Introduction== | |||
Define the field, the error conditions and the error. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
const schema = Yup.object().shape({ | |||
name: Yup.string() | |||
.min(2, 'Too Short!') | |||
.max(50, 'Too Long!') | |||
.required('Required'), | |||
email: Yup.string() | |||
.email('Invalid email') | |||
.required('Required'), | |||
}) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Implementation in code== | |||
The password validation can be done with | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
import * as Yup from "yup"; | |||
... | |||
const passwordSchema = Yup.object().shape({ | |||
password: Yup.string() | |||
.required("Password cannot be empty") | |||
.test("len", "Very Weak", (val) => val.length > 5) | |||
.test("len", "Weak", (val) => val.length > 8), | |||
}); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Implementation in JSX=== | |||
We can use the schema either directly from the Formik | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
<Formik | |||
initialValues={{ email: "", password: "", rememberMe: false }} | |||
onSumbit={this.handleSumbit} | |||
validationSchema={PasswordSchema} | |||
> | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
For on a field level | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="jsx"> | |||
static validatePassword(value) { | |||
let error; | |||
try { | |||
passwordSchema.validateSync({ password: value }); | |||
} catch (validationError) { | |||
[error] = validationError.errors; | |||
} | |||
return error; | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=useField Hook= | |||
==Input== | |||
useField hook accepts as input | |||
*a field name string | |||
*a props object A list of props you want to be able to set on the field. E.g. label. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
// passing a name like email | |||
const [field, meta, helpers] = useField('email'); | |||
// passing a props object | |||
const MyTextField = ({ label, ...props }) => { | |||
const [field, meta, helpers] = useField(props); | |||
return ( | |||
<> | |||
<label> | |||
{label} | |||
<input {...field} {...props} /> | |||
</label> | |||
{meta.touched && meta.error ? ( | |||
<div className="error">{meta.error}</div> | |||
) : null} | |||
</> | |||
); | |||
}; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Output== | |||
It returns an array of | |||
*FieldInputProps | |||
*FieldMetaProps | |||
*FieldHelperProps | |||
===FieldInputProps=== | |||
Key values are | |||
*name | |||
*value | |||
*checked, multiple | |||
*onBlur, onChange | |||
===FieldMetaProps=== | |||
Contains computed meta data. | |||
*error | |||
*touched | |||
*value | |||
initialValue | |||
===FieldHelperProps=== | |||
Contains methods for updating the value, touched or error status for the field. This can be done but using the | |||
*setValue | |||
*setTouched | |||
*setError | |||
These | |||
==Example 1== | |||
In this example we pass label as a prop to the useField. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="js"> | |||
/* eslint-disable react/jsx-props-no-spreading */ | |||
import React from "react"; | |||
import PropTypes from "prop-types"; | |||
import { useField } from "formik"; | |||
// Note passing the non-standard prop label separately. | |||
const TestTextInput = ({ label, ...props }) => { | |||
// Get the default field and meta props | |||
const [field, meta] = useField(props); | |||
// Add our label to the JSX | |||
// Pass the field and props to the input | |||
// Manage the display of the error | |||
return ( | |||
<> | |||
<label htmlFor={props.name}>{label}</label> | |||
<input {...field} {...props} /> | |||
{meta.touched && meta.error ? <div>{meta.error}</div> : null} | |||
</> | |||
); | |||
}; | |||
TestTextInput.propTypes = { | |||
label: PropTypes.string, | |||
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired, | |||
}; | |||
TestTextInput.defaultProps = { | |||
label: null, | |||
}; | |||
export default TestTextInput; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==Example 2== | |||
Here is a rating button example. | |||
[[File:UseFieldRatingComponent.png|500px]] | |||
<br> | |||
An below is the usage of this field. | |||
[[File:UseFieldRatingUsage.png|500px]] | |||
=Formik with Functional Components= | |||
Here is the sample from the Formik help showing how to make a similar form with the Formik hooks. The documentation is pretty good. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="jsx"> | |||
import React from 'react'; | |||
import { Formik } from 'formik'; | |||
import * as Yup from 'yup'; | |||
const SignupForm = () => { | |||
return ( | |||
<Formik | |||
initialValues={{ firstName: '', lastName: '', email: '' }} | |||
validationSchema={Yup.object({ | |||
firstName: Yup.string() | |||
.max(15, 'Must be 15 characters or less') | |||
.required('Required'), | |||
lastName: Yup.string() | |||
.max(20, 'Must be 20 characters or less') | |||
.required('Required'), | |||
email: Yup.string().email('Invalid email address').required('Required'), | |||
})} | |||
onSubmit={(values, { setSubmitting }) => { | |||
setTimeout(() => { | |||
alert(JSON.stringify(values, null, 2)); | |||
setSubmitting(false); | |||
}, 400); | |||
}} | |||
> | |||
{formik => ( | |||
<form onSubmit={formik.handleSubmit}> | |||
<label htmlFor="firstName">First Name</label> | |||
<input | |||
id="firstName" | |||
type="text" | |||
{...formik.getFieldProps('firstName')} | |||
/> | |||
{formik.touched.firstName && formik.errors.firstName ? ( | |||
<div>{formik.errors.firstName}</div> | |||
) : null} | |||
<label htmlFor="lastName">Last Name</label> | |||
<input | |||
id="lastName" | |||
type="text" | |||
{...formik.getFieldProps('lastName')} | |||
/> | |||
{formik.touched.lastName && formik.errors.lastName ? ( | |||
<div>{formik.errors.lastName}</div> | |||
) : null} | |||
<label htmlFor="email">Email Address</label> | |||
<input id="email" type="email" {...formik.getFieldProps('email')} /> | |||
{formik.touched.email && formik.errors.email ? ( | |||
<div>{formik.errors.email}</div> | |||
) : null} | |||
<button type="submit">Submit</button> | |||
</form> | |||
)} | |||
</Formik> | |||
); | |||
}; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Usage of this would look like this where we are passing a label to always be associated with the field. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="jsx"> | |||
<TestTextInput | |||
label="First Name" | |||
name="firstname" | |||
type="text" | |||
placeholder="jane" | |||
/> | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:30, 12 July 2021
Introduction
- Controlled Forms
- Uncontrolled Forms
- Using Formik Library
- Validation
- Creating reusable custom form elements
- Uncontrolled forms using React
- React Hook Form to create uncontrolled forms
Controlled forms
In react we can pass state management to the react component. This is what a controlled form is. It's advantages are
- Instant Feedback
- Disable controls dynamically
- Formats the input data e.g. dates 25-03-2001
Example using UseState
const [password, setPassword] = useState("");
...
<Form onSubmit={handleSubmit} className="row g-3 needs-validation">
<div>
<div className="col-md-4">
<Form.Group size="lg" controlId="password">
<Form.Label>Password</Form.Label>
<Form.Control
type="password"
value={password}
onChange={(e) => onPasswordChange(e)}
/>
<div className="invalid-feedback">{passwordError}</div>
<div className="valid-feedback">Password looks good!</div>
</Form.Group>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<div className="col-12">
<Button
type="submit"
className="btn btn-primary"
disabled={isSubmitting || !formValid}
>{`${isSubmitting ? "Logging In" : "Login"}`}</Button>
</div>
</div>
</Form>
...
Using React Components
import React from "react";
class EmailForm extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
this.state = {value: ''};
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
handleChange(event) {
this.setState({value: event.target.value});
}
render() {
return (
<form>
<input type="email" value={this.state.value} onChange={this.handleChange} />
</form>
);
}
}
Uncontrolled Forms
Introduction
Uncontrolled forms are when the DOM maintains the states and a reference is stored to it in react. To use an uncontrolled Form you need to
- Create a reference using React.createRef()
- Assign reference using ref prop on form element
- Extract value using the reference created in the constructor
Example
import React from "react";
class TestForm extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.submit = this.submit.bind(this);
this.input = React.createRef();
}
submit(event) {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-alert
alert(`Value${this.input.current.value}`);
event.preventDefault();
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.submit}>
<input type="text" ref={this.input} />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
);
}
}
export default TestForm;
When to Use
- For read-only elements like file input
- When using a non-react library
- To reduce re-rending form in a complex DOM
Using useForm Hook
- Uses uncontrolled elements
- Therefore minimizes re-rendering
- Works with Controlled components & UI libraries
- Provides Validation helpers and support for schema validators
Example useForm Hook
- Import the hook
- Get props from hook
- Set the callback to envoke if validation does fail on submit
- Set the forms handleSubmit function
- Register the input tag with a name
- If errors render them
import {useForm} from "react-hook-form";
export default App() {
const {register, handleSubmit, errors} = useForm()
const mySubmit = data => console.log(`Add validation on submit here ${data}`)
return (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(mySubmit)}>
<input {...register("email")} />
{errors.email && <span>this field is required</span>}
<input type="submit" />
</form>
)
}
export default TestReactHookForm;
Validation with useForm
We can pass the standard HTML validation when we register the field. Any HTML validation can be used. e.g. min or max
<input {...register("email", {required: "error messsage"})} />
We can also use a schema by installing the appropriate resolver e.g. yup resolver and setting the schema to use when we define the useForm hook
const {register, handleSubmit, errors} = useForm({
{ resolver: yupResolver(schema)})
}
Watch with useFrom
This will watch specified inputs and return their values. It is useful for determining what to render.
import React from "react";
import { useForm } from "react-hook-form";
function App() {
const { register, watch, formState: { errors }, handleSubmit } = useForm();
const watchShowAge = watch("showAge", false); // you can supply default value as second argument
const watchAllFields = watch(); // when pass nothing as argument, you are watching everything
const watchFields = watch(["showAge", "number"]); // you can also target specific fields by their names
const onSubmit = data => console.log(data);
return (
<>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(onSubmit)}>
<input type="checkbox" {...register("showAge")} />
{/* based on yes selection to display Age Input*/}
{watchShowAge && <input type="number" {...register("age", { min: 50 })} />}
<input type="submit" />
</form>
</>
);
}
Using Formik Library
Advantages
This is what is suggests.
- Reduces Verbosity
- Reduces code for state and callbacks
- Reduces errors
- Tracks values, errors and visited fields
- Hooks up appropriate callback functions
- Helpers for sync and async validation and showing errors
- Sensible defaults
Components of Formik
Here are the components which make up a Formik form. The first being the component responsible for controlling the form
- Formik
- Form
- Field
- ErrorMessage
Internally Formik maintains three maps.
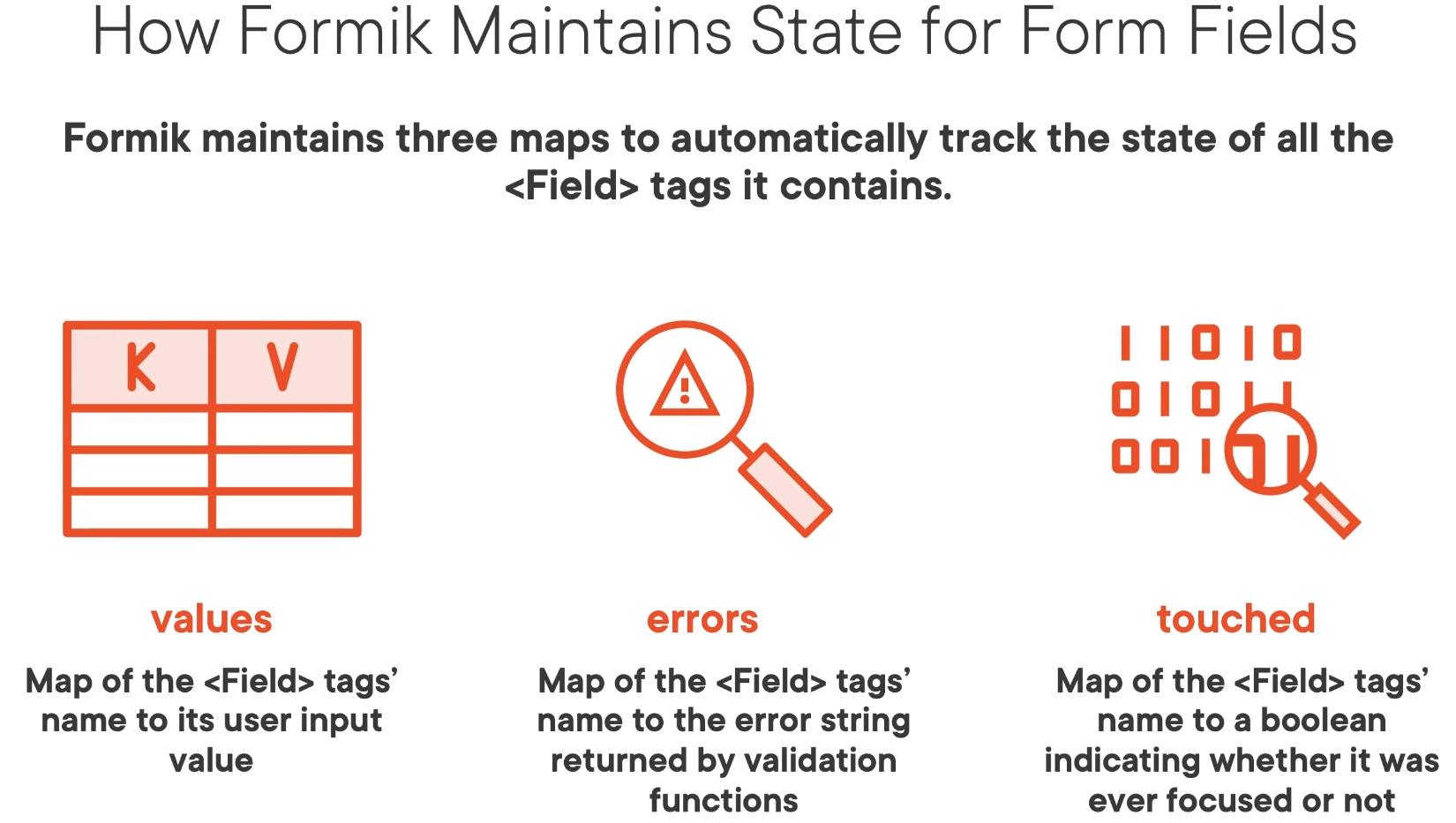
Formik Using Components
This is the example with components. This now been re-implemented using hooks. It does use styled components around the controls which I personally found to be a bit hard to debug.
import React from "react";
import styled from "styled-components";
import { Formik, Field, Form, ErrorMessage } from "formik";
const SigninForm = styled(Form)`
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
padding: 30px;
border: 1px solid black;
`;
const Container = styled.div`
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
flex: 1;
height: 100%;
align-items: center;
`;
const ContentContainer = styled.div`
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
width: 600px;
margin-top: 50px;
`;
const Title = styled.h1`
white-space: pre-line;
`;
const Label = styled.label`
margin-top: 20px;
font-size: 24px;
`;
const EmailField = styled(Field)`
height: 40px;
font-size: 24px;
`;
const ErrorLabel = styled.div`
color: red;
font-size: 26px;
`;
const PasswordField = styled(Field)`
height: 40px;
font-size: 24px;
`;
const CheckboxContainer = styled.div`
display: flex;
height: 50px;
align-items: center;
`;
const RememberMeCheckboxField = styled(Field)`
margin-top: 10px;
`;
const CheckboxLabel = styled(Label)`
margin-top: 7px;
margin-left: 10px;
`;
class LoginFormik extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleSubmit = LoginFormik.handleSubmit.bind(this);
this.handleValidation = LoginFormik.handleValidation.bind(this);
}
static handleSubmit(values) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
// eslint-disable-next-line no-alert
alert(JSON.stringify(values));
}, 5000);
});
}
static handleValidation(values) {
const errors = {};
if (!values.email) {
errors.email = "Email cannot be empty";
}
if (!values.password) {
errors.password = "Password cannot be empty";
} else if (values.password.length < 8) {
errors.password = "Password must be at least 8 characters";
}
return errors;
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<ContentContainer>
<Title>Signin Form</Title>
<Formik
initialValues={{ email: "", password: "", rememberMe: false }}
onSumbit={this.handleSumbit}
validate={this.handleValidation}
>
{() => (
<SigninForm>
<Label>Email</Label>
<EmailField name="email" type="email" />
<ErrorMessage name="email">
{(error) => <ErrorLabel>{error}</ErrorLabel>}
</ErrorMessage>
<Label>Password</Label>
<PasswordField name="password" type="password" />
<ErrorMessage name="password">
{(error) => <ErrorLabel>{error}</ErrorLabel>}
</ErrorMessage>
<CheckboxContainer>
<RememberMeCheckboxField type="checkbox" name="rememberMe" />
<CheckboxLabel>Remember Me</CheckboxLabel>
</CheckboxContainer>
</SigninForm>
)}
</Formik>
</ContentContainer>
</Container>
);
}
}
export default LoginFormik;
Formik Validation
Formik provides two types of validation and they are not a surprise
- Field level
- Form level
Field Level
Note the returning of undefined not null
...
class LoginFormik extends React.Component {
static validatePassword(value) {
if (!value) {
return "Password cannot be empty";
}
if (value.length < 5) {
return "Very Weak";
}
if (value.length < 8) {
return "Weak";
}
return undefined;
}
...
<Label>Password</Label>
<PasswordField
name="password"
type="password"
validate={LoginFormik.validatePassword}
/>
Form Level
This is done by defining a function on the Formik validate property.
<Formik
initialValues={{ email: "", password: "", rememberMe: false }}
onSumbit={this.handleSumbit}
validate={this.handleValidation}
Formik Schema Validation (e.g. yup)
Introduction
Define the field, the error conditions and the error.
const schema = Yup.object().shape({
name: Yup.string()
.min(2, 'Too Short!')
.max(50, 'Too Long!')
.required('Required'),
email: Yup.string()
.email('Invalid email')
.required('Required'),
})
Implementation in code
The password validation can be done with
import * as Yup from "yup";
...
const passwordSchema = Yup.object().shape({
password: Yup.string()
.required("Password cannot be empty")
.test("len", "Very Weak", (val) => val.length > 5)
.test("len", "Weak", (val) => val.length > 8),
});
Implementation in JSX
We can use the schema either directly from the Formik
<Formik
initialValues={{ email: "", password: "", rememberMe: false }}
onSumbit={this.handleSumbit}
validationSchema={PasswordSchema}
>
For on a field level
static validatePassword(value) {
let error;
try {
passwordSchema.validateSync({ password: value });
} catch (validationError) {
[error] = validationError.errors;
}
return error;
}
useField Hook
Input
useField hook accepts as input
- a field name string
- a props object A list of props you want to be able to set on the field. E.g. label.
// passing a name like email
const [field, meta, helpers] = useField('email');
// passing a props object
const MyTextField = ({ label, ...props }) => {
const [field, meta, helpers] = useField(props);
return (
<>
<label>
{label}
<input {...field} {...props} />
</label>
{meta.touched && meta.error ? (
<div className="error">{meta.error}</div>
) : null}
</>
);
};
Output
It returns an array of
- FieldInputProps
- FieldMetaProps
- FieldHelperProps
FieldInputProps
Key values are
- name
- value
- checked, multiple
- onBlur, onChange
FieldMetaProps
Contains computed meta data.
- error
- touched
- value
initialValue
FieldHelperProps
Contains methods for updating the value, touched or error status for the field. This can be done but using the
- setValue
- setTouched
- setError
These
Example 1
In this example we pass label as a prop to the useField.
/* eslint-disable react/jsx-props-no-spreading */
import React from "react";
import PropTypes from "prop-types";
import { useField } from "formik";
// Note passing the non-standard prop label separately.
const TestTextInput = ({ label, ...props }) => {
// Get the default field and meta props
const [field, meta] = useField(props);
// Add our label to the JSX
// Pass the field and props to the input
// Manage the display of the error
return (
<>
<label htmlFor={props.name}>{label}</label>
<input {...field} {...props} />
{meta.touched && meta.error ? <div>{meta.error}</div> : null}
</>
);
};
TestTextInput.propTypes = {
label: PropTypes.string,
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
};
TestTextInput.defaultProps = {
label: null,
};
export default TestTextInput;
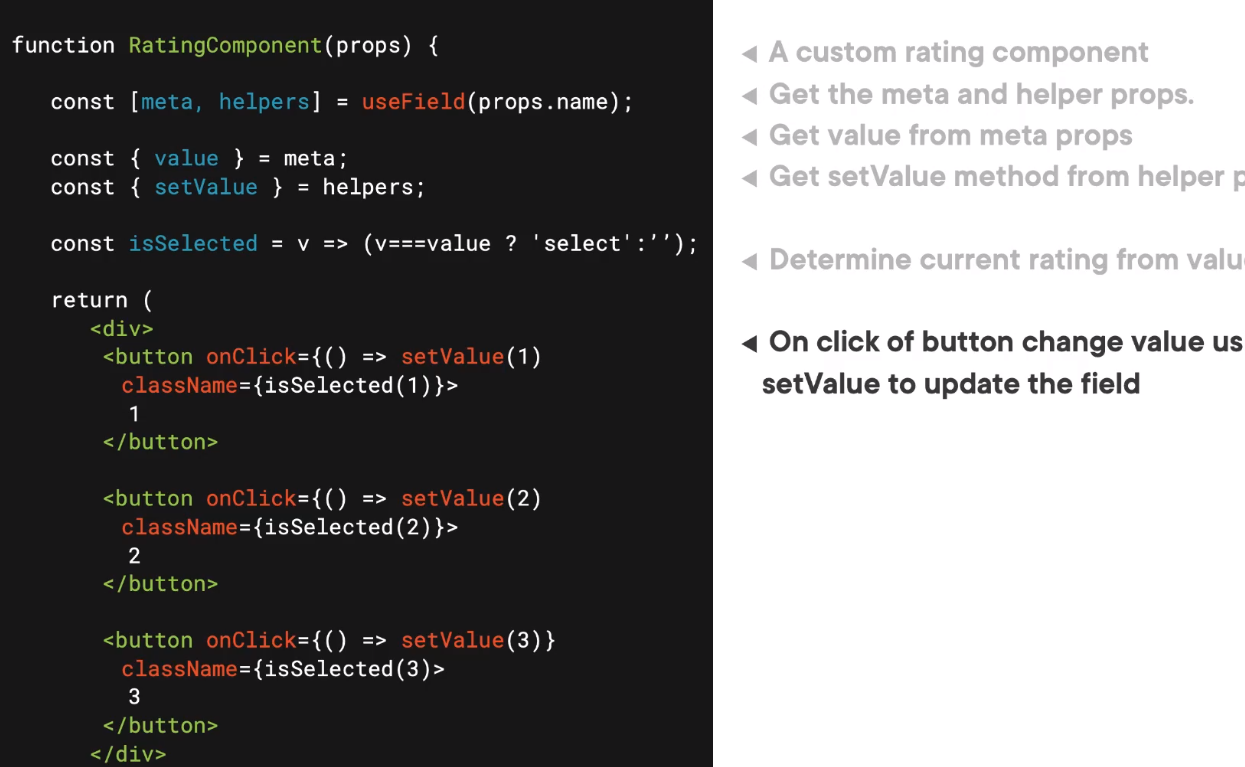
Example 2
Here is a rating button example.
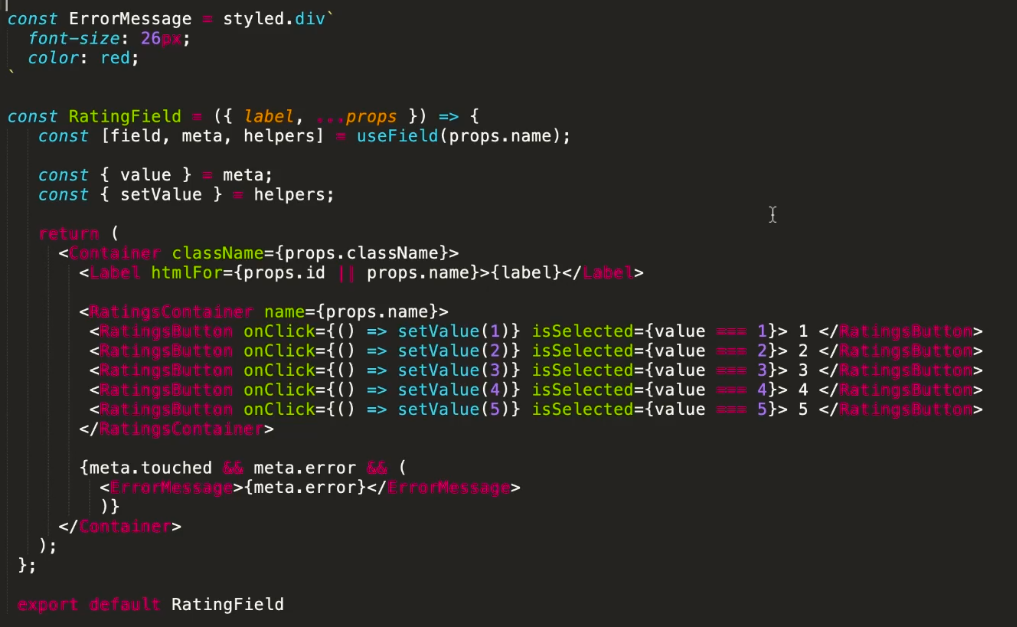
An below is the usage of this field.
Formik with Functional Components
Here is the sample from the Formik help showing how to make a similar form with the Formik hooks. The documentation is pretty good.
import React from 'react';
import { Formik } from 'formik';
import * as Yup from 'yup';
const SignupForm = () => {
return (
<Formik
initialValues={{ firstName: '', lastName: '', email: '' }}
validationSchema={Yup.object({
firstName: Yup.string()
.max(15, 'Must be 15 characters or less')
.required('Required'),
lastName: Yup.string()
.max(20, 'Must be 20 characters or less')
.required('Required'),
email: Yup.string().email('Invalid email address').required('Required'),
})}
onSubmit={(values, { setSubmitting }) => {
setTimeout(() => {
alert(JSON.stringify(values, null, 2));
setSubmitting(false);
}, 400);
}}
>
{formik => (
<form onSubmit={formik.handleSubmit}>
<label htmlFor="firstName">First Name</label>
<input
id="firstName"
type="text"
{...formik.getFieldProps('firstName')}
/>
{formik.touched.firstName && formik.errors.firstName ? (
<div>{formik.errors.firstName}</div>
) : null}
<label htmlFor="lastName">Last Name</label>
<input
id="lastName"
type="text"
{...formik.getFieldProps('lastName')}
/>
{formik.touched.lastName && formik.errors.lastName ? (
<div>{formik.errors.lastName}</div>
) : null}
<label htmlFor="email">Email Address</label>
<input id="email" type="email" {...formik.getFieldProps('email')} />
{formik.touched.email && formik.errors.email ? (
<div>{formik.errors.email}</div>
) : null}
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
)}
</Formik>
);
};
Usage of this would look like this where we are passing a label to always be associated with the field.
<TestTextInput
label="First Name"
name="firstname"
type="text"
placeholder="jane"
/>