Dagger 2: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
fun car(): Car | fun car(): Car | ||
... | ... | ||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Using the component we just to the following | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="kotlin"> | |||
class SomeActivity: AppCompatActivity() { | |||
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { | |||
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) | |||
var component = DaggerAppComponent | |||
.builder() | |||
.build() | |||
var car = component.car() | |||
var client = component.OkHttpClient() | |||
} | |||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 23:30, 19 December 2020
Introduction
Dagger is made by Google. Dagger allows you to
- Scope dependencies
- Bind single instance to life cycles
- Only need to build them once
- Generates the code at compile time
Example Without Dagger
fun buildCar: Car =
Car(SturdyFrame(),
Wheels(),
RocketEngine())
With Dagger
fun buildCar: Car =
DaggerAppComponent
.builder()
.build()
.buildCar()
Modules
Modules in Dagger are responsible for providing object we want to inject. They contain the methods which return the objects.
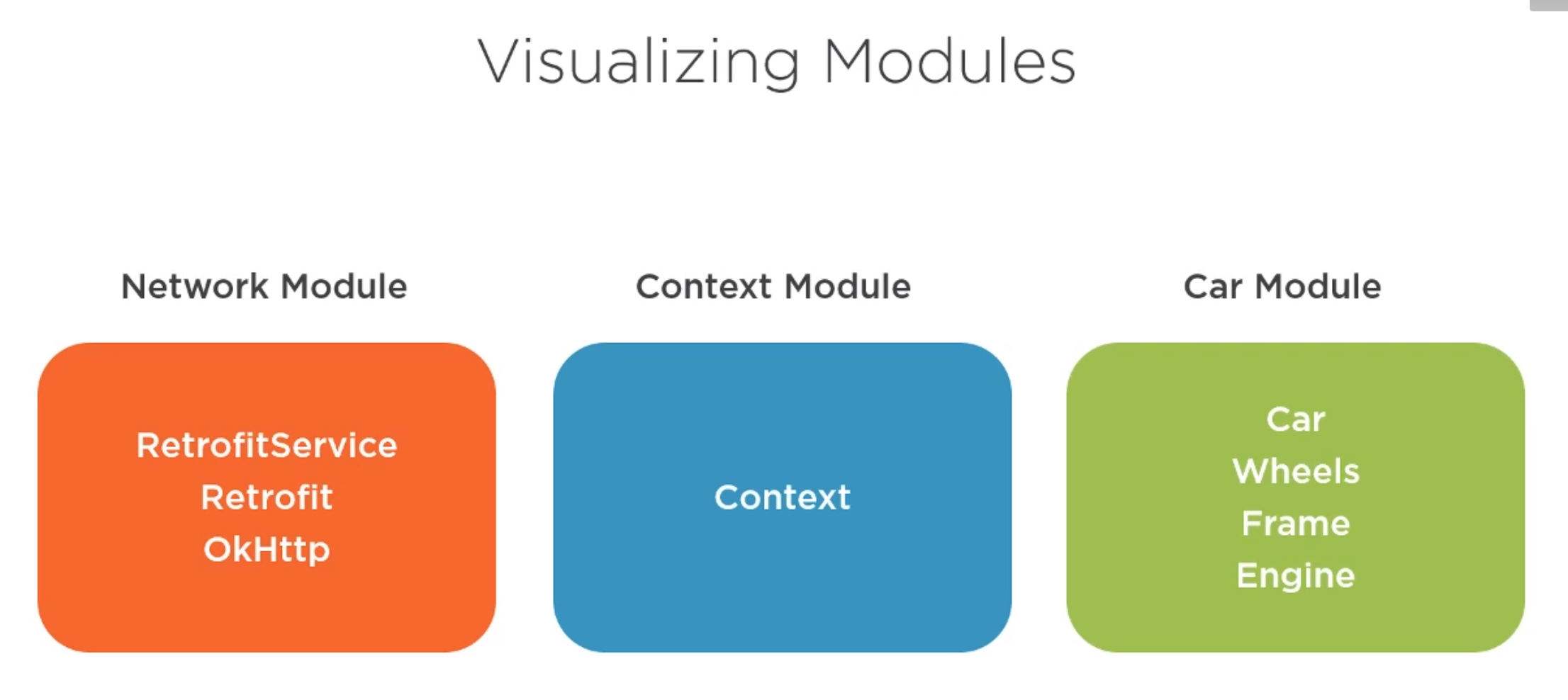 Modules are decorated with @module and the objects are decorated with @provides
Modules are decorated with @module and the objects are decorated with @provides
@Module
fun CarModule {
@Provides
fun provideEngine() : Engine = Engine()
@Provides
fun provideFrame() : Frame = Frame()
@Provides
fun provideWheels() : Wheels = Wheels()
@Provides
fun provideCar(engine: Engine, wheels: Wheels, frame: Frame) : Car {
return Car(frame, wheels, engine)
}
}
To share a module across modules add the include to the modules decorator
@Module(includes = [EngineModule::class])
fun CarModule {
@Provides
fun provideFrame() : Frame = Frame()
...
@Provides
fun provideCar(engine: Engine, wheels: Wheels, frame: Frame) : Car {
return Car(frame, wheels, engine)
}
}
Components
A Dagger Component is something which contains a set of modules.
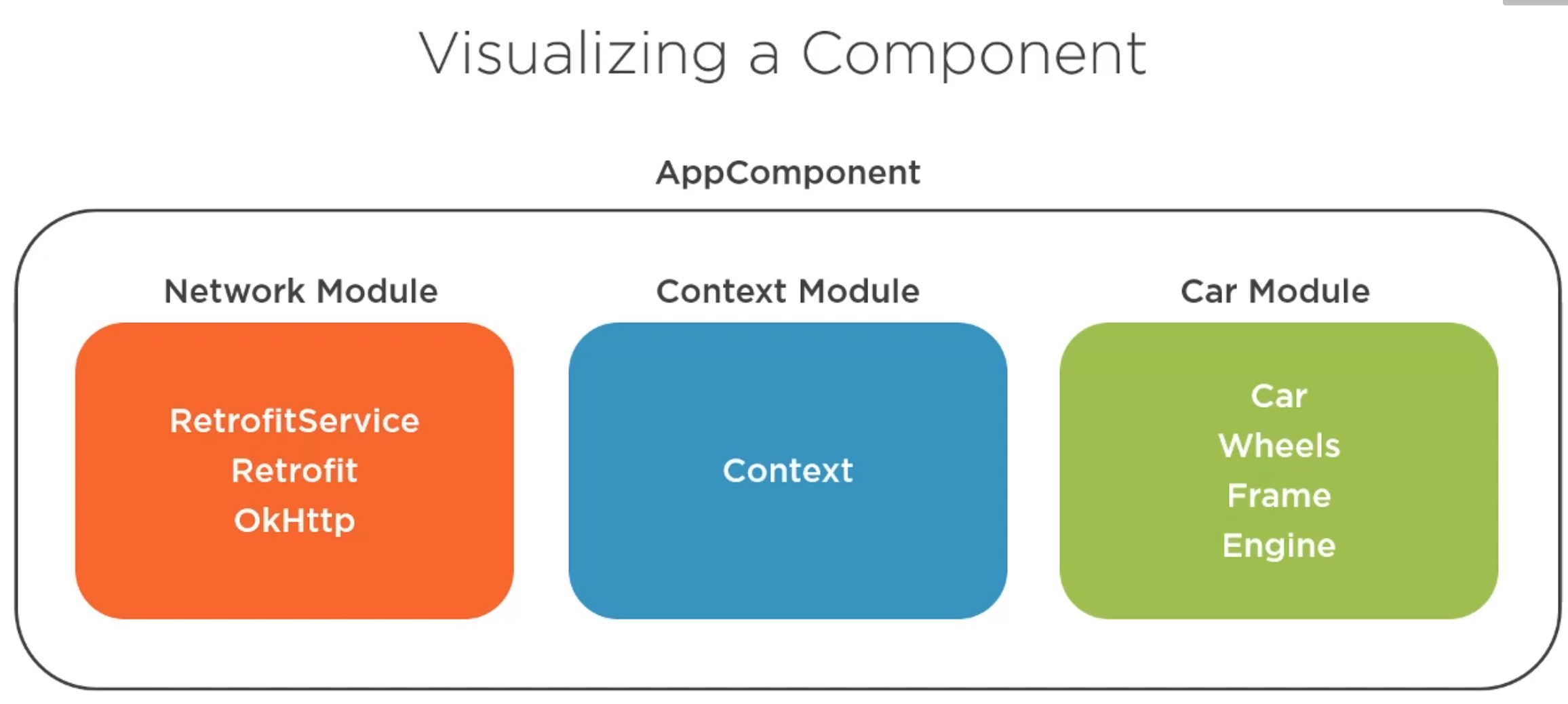 The component is an interface which allows access to our module instances. The underlying code is generated at build time so the interface is simple to write. We just need the @Component keyword and the modules required
The component is an interface which allows access to our module instances. The underlying code is generated at build time so the interface is simple to write. We just need the @Component keyword and the modules required
@Component(modules = [NetworkModule::class, ContextModule::class, CarModule::class])
interface AppCommponent {
fun okHttpClient(): okHttpClient
fun car(): Car
...
}
Using the component we just to the following
class SomeActivity: AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
var component = DaggerAppComponent
.builder()
.build()
var car = component.car()
var client = component.OkHttpClient()
}
}