Angular Reactive forms: Difference between revisions
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==Template Creation== | ==Template Creation== | ||
We specify the form using the formGroup | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="html"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="html"> | ||
<div class="card-body"> | <div class="card-body"> | ||
| Line 90: | Line 91: | ||
[formGroup]="customerForm"> | [formGroup]="customerForm"> | ||
... | ... | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
We add fields with '''formControlName''' tag. Note getting this wrong, e.g. the name or the tag will result in the form not being rendered correctly. You can test this by adding a <div>MEEEEE{{formName.dirty}} to find out where the error is. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="html"> | |||
<input class="form-control" | |||
id="emailId" | |||
type="email" | |||
placeholder="Email (required)" | |||
required | |||
email | |||
formControlName='email' | |||
[ngClass]="{'is-invalid': (customerForm.get('email').touched || customerForm.get('email').dirty) && !customerForm.get('email').valid }" /> | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 04:44, 7 September 2020
Angular Forms
Introduction
Angular provides two types of forms
- Template Driven
- Easy to use
- Familar to Angular JS
- Two-way data binding-> minimal component code
- Automatically tracks from and input element state
- Reactive (model driven
- More flexible
- Immutable data model
- Easier to perform an action on value change
- Access Reactive transformations such as DebounceTime or DistinctUntilChanged
- Easily add input elements dynamically
- Easier unit testing
Template driven forms put the responsibility in the template using basic HTML and data binding, Reactive forms move most of the responsibility to the component class
Template-Driven-Forms
In the Template we have
- Form elements
- Input elements
- Data binding to the component
- Validation rules (attributes)
- Validation error messages
- Form model (automatically generated)
In the Component Class we have
- Properties for data binding
- Method for form Operations such as submit
Directives used are
- ngForm
- ngModel
- ngModelGroup
Example form
<form (ngSubmit)="save()">
<input id="firstNameId" type="text"
[(ngMode)]="customer.firstname"
name="firstname"
#firstNameVar="ngModel" />
</form>
Reactive Forms
In the template we have
- Form elements
- Input elements
- Binding to form model
In the class we have
- Form model which we create
- Validation rules
- Validation error messages
- Properties for managing data (data model)
- Methods for form Operations such as submit
Directives used (ReactiveFormsModule)
- formGroup
- formControl
- formControlName
- formGroupName
- formArrayName
Template vs Reactive Example
Template form example
Reactive form example
Create Reactive Form
Preparation
Make sure we import the ReactiveFormsModule in app.module.ts
Component Creation
Create a FormGroup in ngInit. Note we can initialize the controls at creation
export class CustomerComponent implements OnInit {
...
customerForm :FormGroup
ngOnInit(): void {
this.customerForm = new FormGroup({
firstName: new FormControl(),
lastName: new FormControl(),
emailName: new FormControl(),
sendCatog: new FormControl(true)
})
}
...
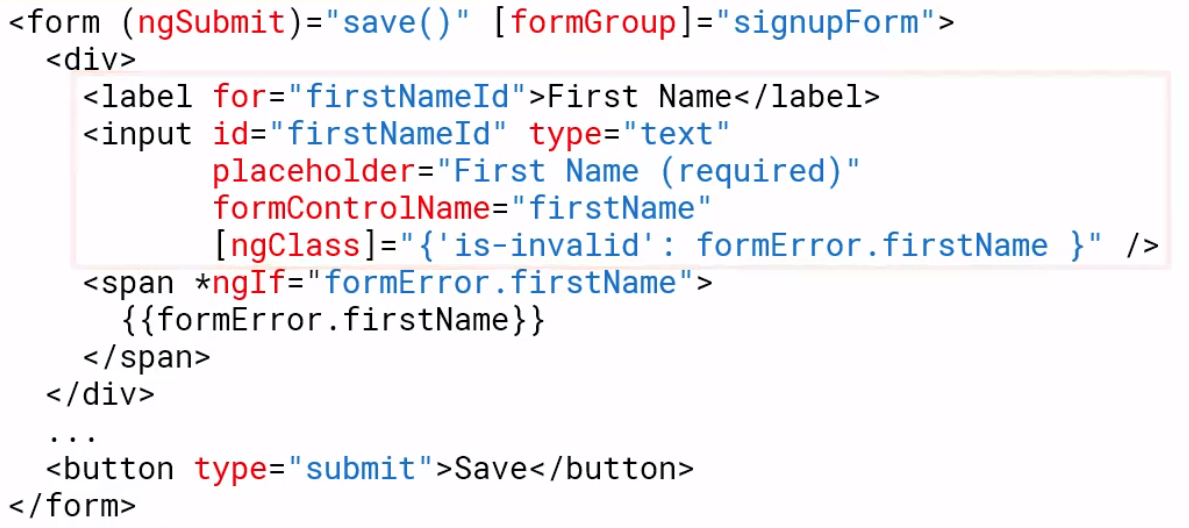
Template Creation
We specify the form using the formGroup
<div class="card-body">
<form novalidate
(ngSubmit)="save()"
[formGroup]="customerForm">
...
We add fields with formControlName tag. Note getting this wrong, e.g. the name or the tag will result in the form not being rendered correctly. You can test this by adding a
<input class="form-control"
id="emailId"
type="email"
placeholder="Email (required)"
required
email
formControlName='email'
[ngClass]="{'is-invalid': (customerForm.get('email').touched || customerForm.get('email').dirty) && !customerForm.get('email').valid }" />
Accessing Form Model Properties
In the template we can use
customerForm.controls.firstName.valid
customerForm.get('firstName').valid
Or create a reference in the component to be used, in this case firstName
this.customerFrom = new FormGroup({
firstName: this.firstName
})