SAML 2.0: Difference between revisions
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
**Implementation is largely in the Identify Provider | **Implementation is largely in the Identify Provider | ||
=SAML Detail= | =SAML Detail= | ||
==Introduction== | |||
More terminalogy. Auth requests are sent to the IdP SSO endpoint and responses are returned to the Service Providers ACS Endpoint | More terminalogy. Auth requests are sent to the IdP SSO endpoint and responses are returned to the Service Providers ACS Endpoint | ||
*SSO Endpoint Single Sign on Endpoint | *SSO Endpoint Single Sign on Endpoint | ||
*ACS Endpoint Assertion Consumer Service Endpoint | *ACS Endpoint Assertion Consumer Service Endpoint | ||
==Relay State== | |||
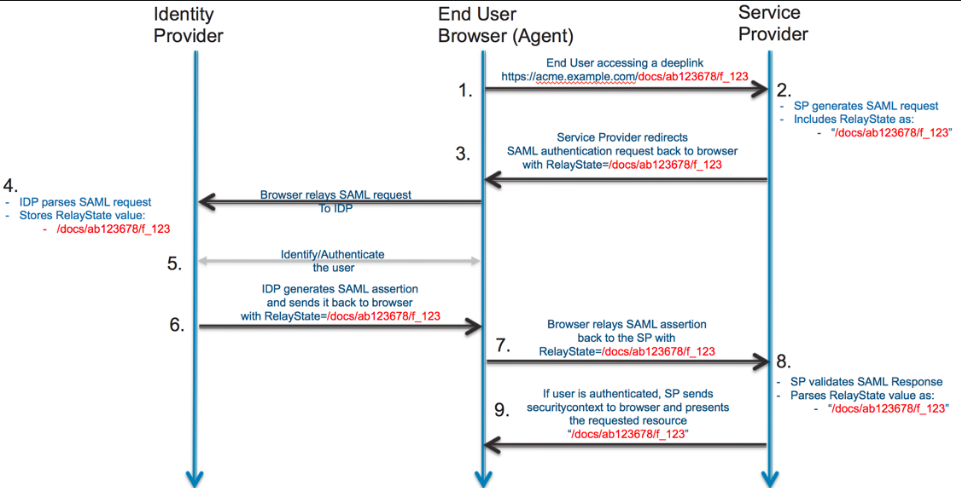
In the case of a deep link, the SP sets the RelayState of the SAML request with the deep-link value. When the SAML response comes back, the SP can use the RelayState value and take the authenticated user to the right resource.<br> | |||
[[File:SAML RelayState.png|500px]] | |||
Revision as of 01:27, 17 July 2021
Introduction
What is SSO (Single Sign On)
Some definitions
- Authentication Verifying an identify
- Authorization Verifying user has permission and access
- Federation is when authentication is happen across multi vendor apps
SSO is the ability to authenticate via one authority.
Benefits are
- Authentication under your control (Audit, turn off/on etc)
- One set of credentials
- Login once per session
SAML
SAML stands for Security Assertion Markup Language and defines the syntax and processing semantics of assertions made about a subject by a system entity.
In SAML the thing providing the service is the Service Provider (SP) e.g. HR System and the thing providing the Authentication is the Identity Provider (IdP)
Here is an example for a typical workflow where Citrix is the service provider.
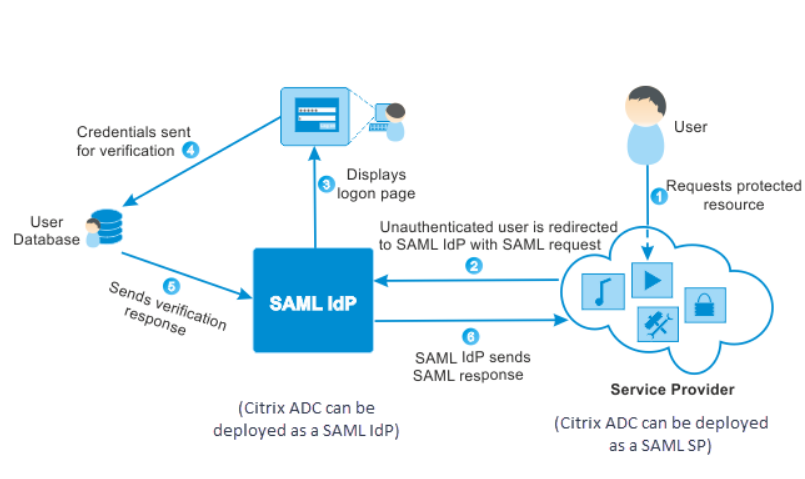
If you already have a session and want to access a second service provider no credentials are prompted for and you are logged in automatically.
History
Here is a timeline for some of the protocols in use today in this space.
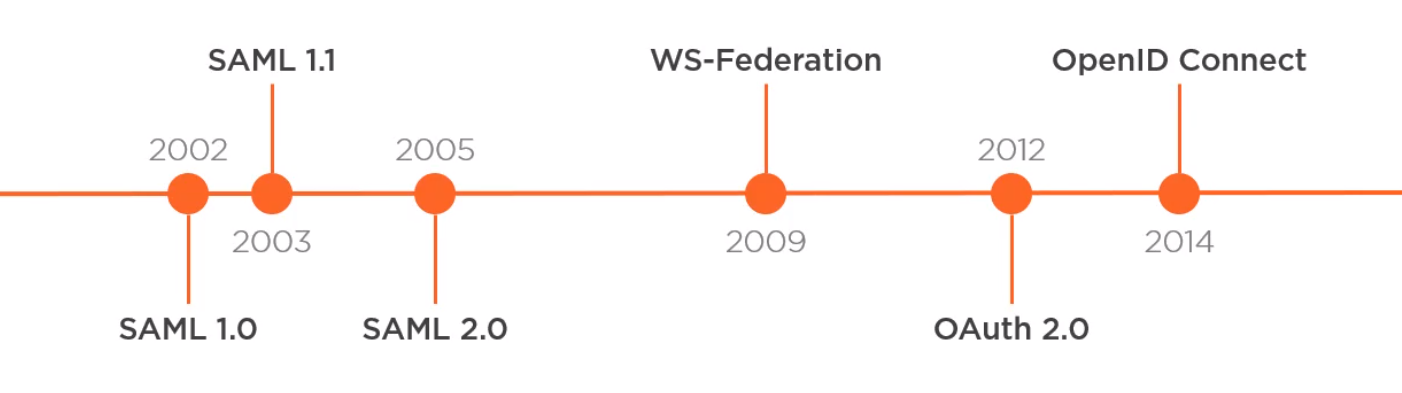
SAML 1.0 and 1.1 are dead as they relied on SOAP.
For SAML 2.0 parts of the specification are :
Not really used now
- Authorization functionality
- Name ID Management & mapping profiles
Are used
- Web SSO (Single Sign on)
- SLO (Single Logout)
- Artifact Binding
SAML vs OpenID
- SAML
- Created before OpenID Connect 2005
- Uses XML and XMLSig which has created security issues
- Designed for Server-side Web Apps
- Poor support for JavaScript SPA or Native App like mobile App with Url length limits
- Implementation is split between service and the Identify Provider
- OpenID Connect
- Newer than SAML Created in 2014
- Uses JSON and JWTs
- Built on OAuth and supports API access and delegation
- Designed for all modern authentication types including browserless e.g. TV
- Implementation is largely in the Identify Provider
SAML Detail
Introduction
More terminalogy. Auth requests are sent to the IdP SSO endpoint and responses are returned to the Service Providers ACS Endpoint
- SSO Endpoint Single Sign on Endpoint
- ACS Endpoint Assertion Consumer Service Endpoint
Relay State
In the case of a deep link, the SP sets the RelayState of the SAML request with the deep-link value. When the SAML response comes back, the SP can use the RelayState value and take the authenticated user to the right resource.