Python Bytes Reading Example: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
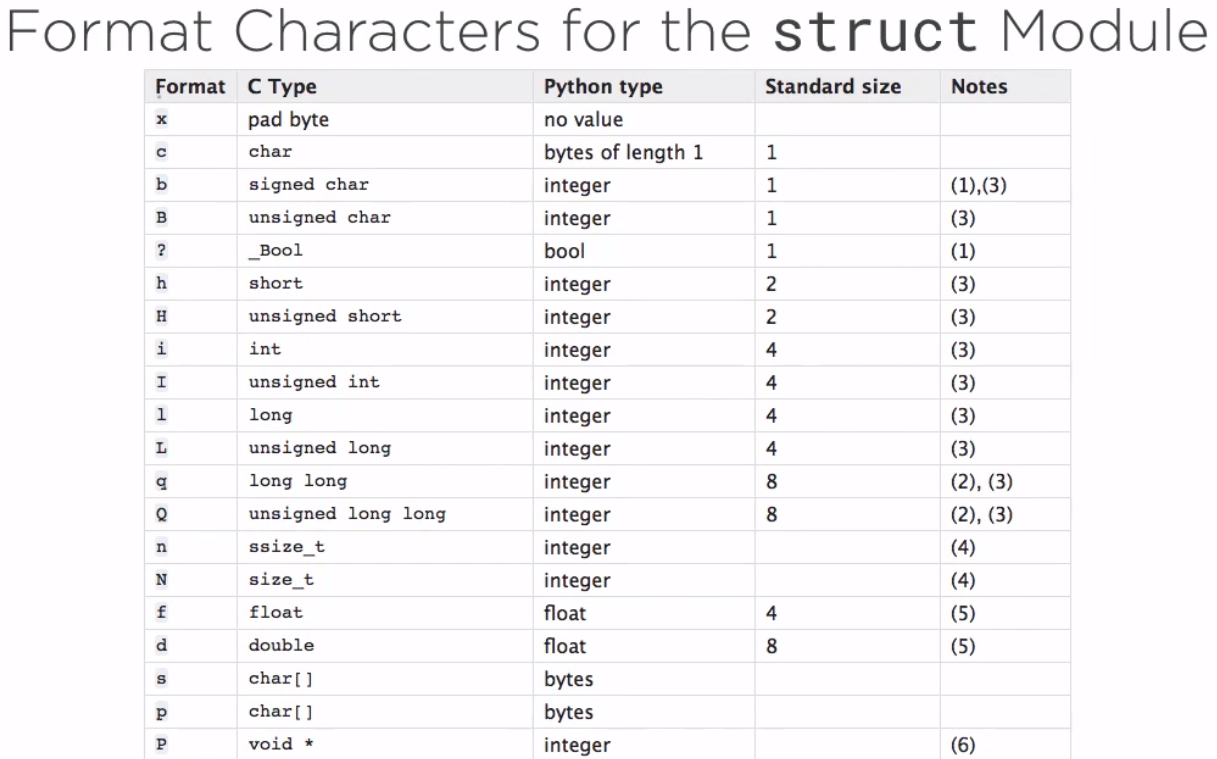
Which allows the program to read types, in this case fffhhh into a buffer. The xx represents the packing which is required due to the use of the compiler at the time. This may vary. | Which allows the program to read types, in this case fffhhh into a buffer. The xx represents the packing which is required due to the use of the compiler at the time. This may vary. | ||
[[File:Format_chars_struct.png|upright=0. | [[File:Format_chars_struct.png|upright=0.25]] | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | ||
Revision as of 07:38, 22 July 2020
C Program
This generates a binary file for reading via Python
/**
* colorpoints.c
*
* A C99 program to write a colored vertex
* structures to a binary file.
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
struct Vector {
float x;
float y;
float z;
};
struct Color {
unsigned short int red;
unsigned short int green;
unsigned short int blue;
};
struct Vertex {
struct Vector position;
struct Color color;
};
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
struct Vertex vertices[] = {
{ .position = { 3323.176, 6562.231, 9351.231 },
.color = { 3040, 34423, 54321 } },
{ .position = { 7623.982, 2542.231, 9823.121 },
.color = { 32736, 5342, 2321 } },
{ .position = { 6729.862, 2347.212, 3421.322 },
.color = { 45263, 36291, 36701 } },
{ .position = { 6352.121, 3432.111, 9763.232 },
.color = { 56222, 36612, 11214 } } };
FILE* file = fopen("colors.bin", "wb");
if (file == NULL) {
return -1;
}
fwrite(vertices, sizeof(struct Vertex), 4, file);
fclose(file);
return 0;
}
Python Program
This demonstrates the use of
struct.iter_unpack('@3f3Hxx', buffer)
Which allows the program to read types, in this case fffhhh into a buffer. The xx represents the packing which is required due to the use of the compiler at the time. This may vary.
import struct
from pprint import pprint as pp
from binascii import hexlify
class Vector:
def __init__(self, x, y, z):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.z = z
def __repr__(self):
return 'Vector({}, {}, {})'.format(self.x, self.y, self.z)
class Color:
def __init__(self, red, green, blue):
self.red = red
self.green = green
self.blue = blue
def __repr__(self):
return 'Color({}, {}, {})'.format(self.red, self.green, self.blue)
class Vertex:
def __init__(self, vector, color):
self.vector = vector
self.color = color
def __repr__(self):
return 'Vertex({!r}, {!r})'.format(self.vector, self.color)
def make_colored_vertex(x, y, z, red, green, blue):
return Vertex(Vector(x, y, z),
Color(red, green, blue))
def main():
with open('colors.bin', 'rb') as f:
buffer = f.read()
print("buffer: {} bytes".format(len(buffer)))
indexes = ' '.join(str(n).zfill(2) for n in range(len(buffer)))
print(indexes)
hex_buffer = hexlify(buffer).decode('ascii')
hex_pairs = ' '.join(hex_buffer[i:i+2] for i in range(0, len(hex_buffer), 2))
print(hex_pairs)
vertices = []
for fields in struct.iter_unpack('@3f3Hxx', buffer):
vertex = make_colored_vertex(*fields)
vertices.append(vertex)
pp(vertices)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()