React Forms
Introduction
- Controlled Forms
- Uncontrolled Forms
- Using Formik Library
- Validation
- Creating reusable custom form elements
- Uncontrolled forms using React
- React Hook Form to create uncontrolled forms
Controlled forms
In react we can pass state management to the react component. This is what a controlled form is. It's advantages are
- Instant Feedback
- Disable controls dynamically
- Formats the input data e.g. dates 25-03-2001
Example using UseState
const [password, setPassword] = useState("");
...
<Form onSubmit={handleSubmit} className="row g-3 needs-validation">
<div>
<div className="col-md-4">
<Form.Group size="lg" controlId="password">
<Form.Label>Password</Form.Label>
<Form.Control
type="password"
value={password}
onChange={(e) => onPasswordChange(e)}
/>
<div className="invalid-feedback">{passwordError}</div>
<div className="valid-feedback">Password looks good!</div>
</Form.Group>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<div className="col-12">
<Button
type="submit"
className="btn btn-primary"
disabled={isSubmitting || !formValid}
>{`${isSubmitting ? "Logging In" : "Login"}`}</Button>
</div>
</div>
</Form>
...
Using React Components
import React from "react";
class EmailForm extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
this.state = {value: ''};
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
handleChange(event) {
this.setState({value: event.target.value});
}
render() {
return (
<form>
<input type="email" value={this.state.value} onChange={this.handleChange} />
</form>
);
}
}
Uncontrolled Forms
Uncontrolled forms are when the DOM maintains the states and a reference is stored to it in react.
Using Formik Library
Advantages
This is what is suggests.
- Reduces Verbosity
- Reduces code for state and callbacks
- Reduces errors
- Tracks values, errors and visited fields
- Hooks up appropriate callback functions
- Helpers for sync and async validation and showing errors
- Sensible defaults
Components of Formik
Here are the components which make up a Formik form. The first being the component responsible for controlling the form
- Formik
- Form
- Field
- ErrorMessage
Internally Formik maintains three maps.
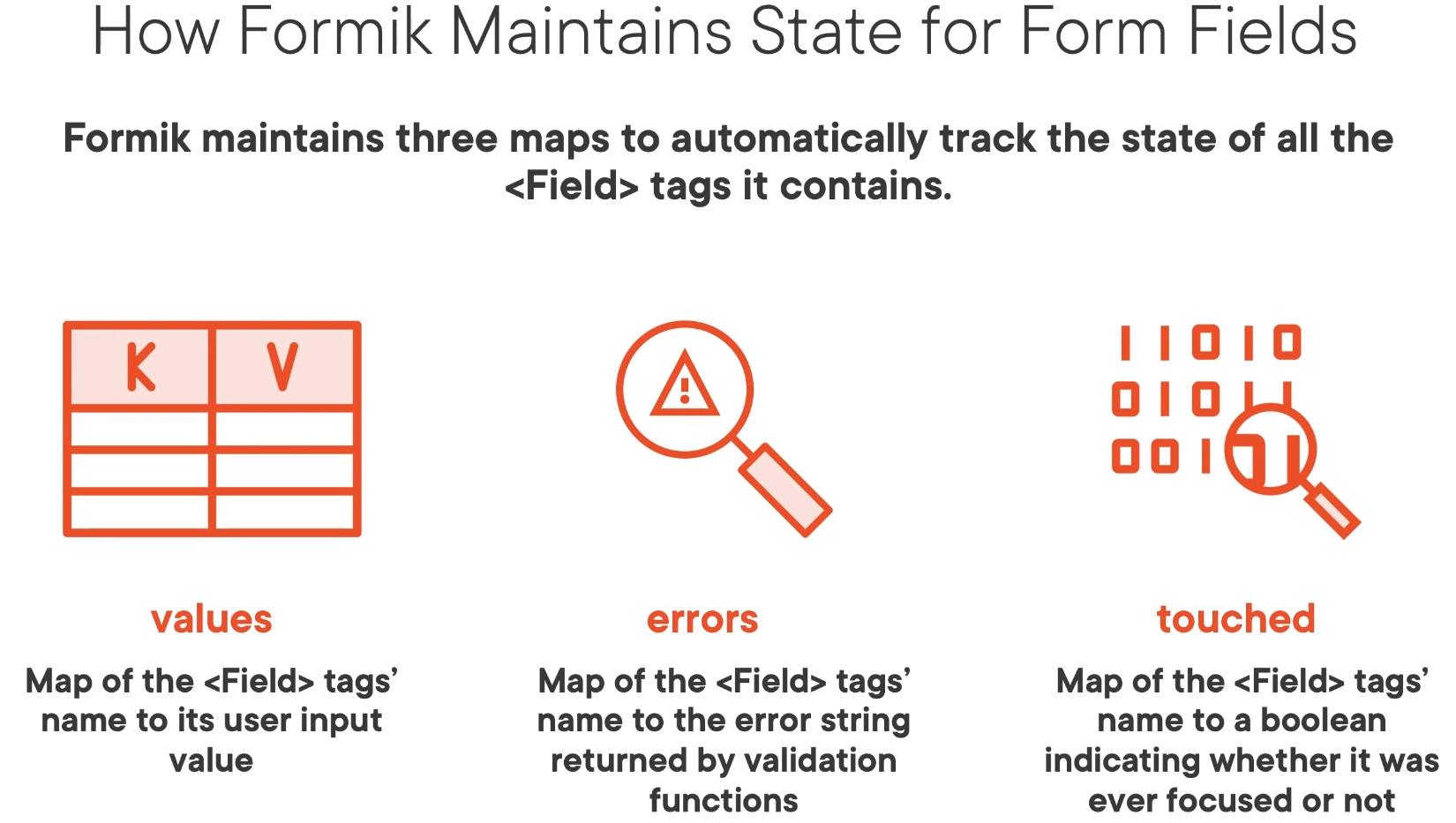
Formik Using Components
This is the example with components. This now been re-implemented using hooks. It does use styled components around the controls which I personally found to be a bit hard to debug. <syntaxhighlighting lang="js"> import React from "react"; import styled from "styled-components"; import { Formik, Field, Form, ErrorMessage } from "formik";
const SigninForm = styled(Form)`
display: flex; flex-direction: column; padding: 30px; border: 1px solid black;
`;
const Container = styled.div`
display: flex; flex-direction: column; flex: 1; height: 100%; align-items: center;
`;
const ContentContainer = styled.div`
display: flex; flex-direction: column; width: 600px; margin-top: 50px;
`;
const Title = styled.h1`
white-space: pre-line;
`;
const Label = styled.label`
margin-top: 20px; font-size: 24px;
`;
const EmailField = styled(Field)`
height: 40px; font-size: 24px;
`;
const ErrorLabel = styled.div`
color: red; font-size: 26px;
`;
const PasswordField = styled(Field)`
height: 40px; font-size: 24px;
`;
const CheckboxContainer = styled.div`
display: flex; height: 50px; align-items: center;
`;
const RememberMeCheckboxField = styled(Field)`
margin-top: 10px;
`;
const CheckboxLabel = styled(Label)`
margin-top: 7px; margin-left: 10px;
`;
class LoginFormik extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleSubmit = LoginFormik.handleSubmit.bind(this); this.handleValidation = LoginFormik.handleValidation.bind(this); }
static handleSubmit(values) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
// eslint-disable-next-line no-alert
alert(JSON.stringify(values));
}, 5000);
});
}
static handleValidation(values) {
const errors = {};
if (!values.email) {
errors.email = "Email cannot be empty";
}
if (!values.password) {
errors.password = "Password cannot be empty";
} else if (values.password.length < 8) {
errors.password = "Password must be at least 8 characters";
}
return errors;
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<ContentContainer>
<Title>Signin Form</Title>
<Formik
initialValues=Template:Email: "", password: "", rememberMe: false
onSumbit={this.handleSumbit}
validate={this.handleValidation}
>
{() => (
<SigninForm>
<Label>Email</Label>
<EmailField name="email" type="email" />
<ErrorMessage name="email">
{(error) => <ErrorLabel>{error}</ErrorLabel>}
</ErrorMessage>
<Label>Password</Label>
<PasswordField name="password" type="password" />
<ErrorMessage name="password">
{(error) => <ErrorLabel>{error}</ErrorLabel>}
</ErrorMessage>
<CheckboxContainer>
<RememberMeCheckboxField type="checkbox" name="rememberMe" />
<CheckboxLabel>Remember Me</CheckboxLabel>
</CheckboxContainer>
</SigninForm>
)}
</Formik>
</ContentContainer>
</Container>
);
}
} export default LoginFormik; </syntaxhighlighting>