Docker and Kubernetes
Introduction
Containers
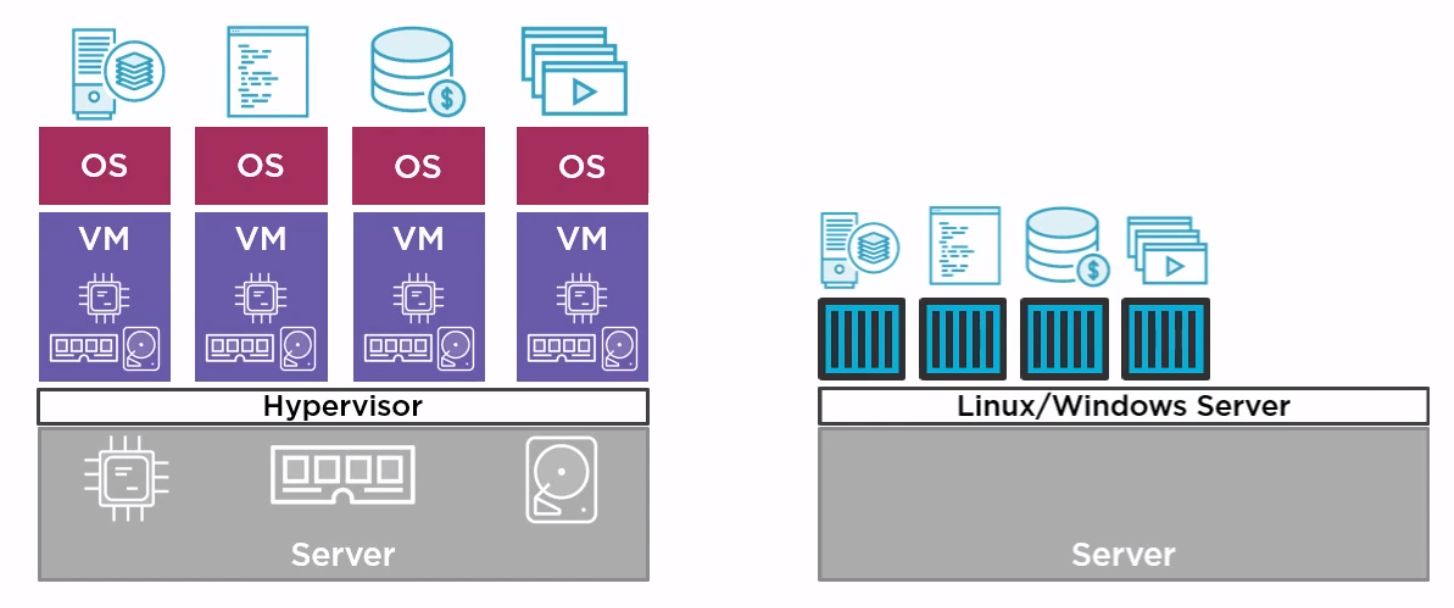
This all started with VMWare where the total resource could be divided up to run more than one application on difference virtual machines. But VMWare required an OS on every machine and licenses in the case of Windows. They also needed managing, e.g. patching, Anti-virus and patching. Along came containers which shared the OS.
Docker
Introduction
Docker Inc. Docker is a company which gave the word technology for containers. They are now a company which provides services around the company.
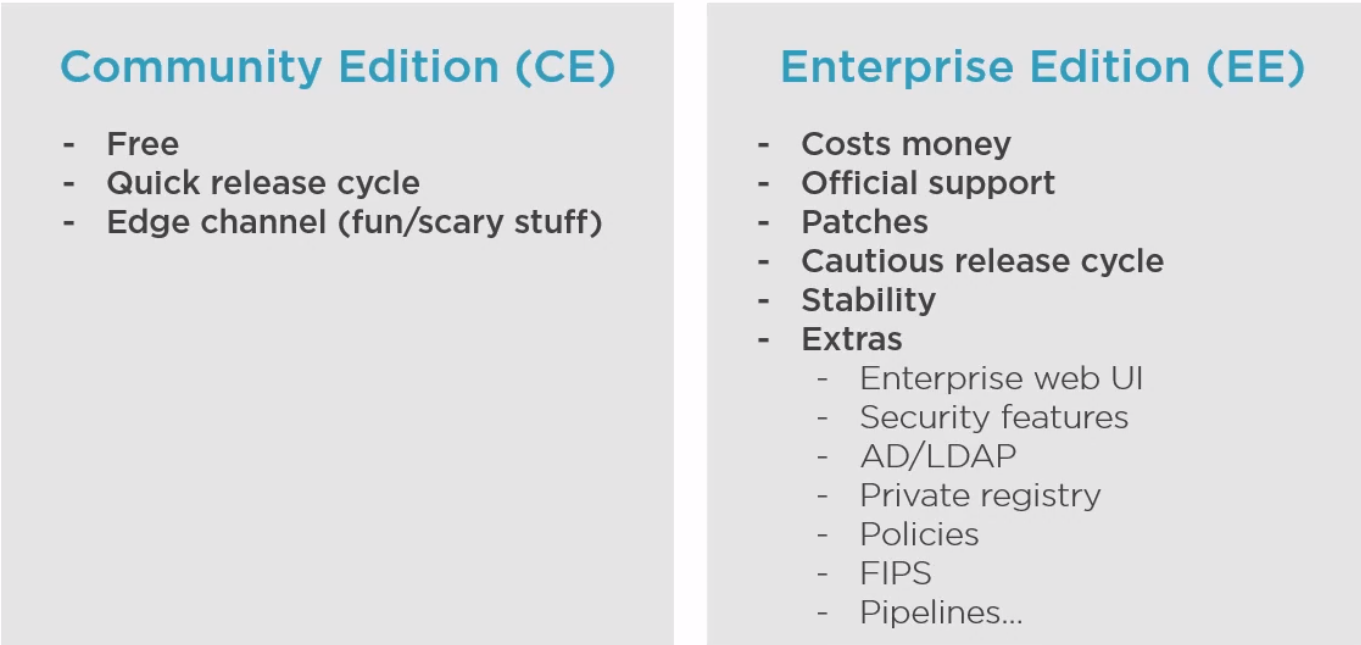
Docker is Open source and known as Community Edition (CE). The company Docker releases an Enterprise Edition (EE).
The general approach is to
- Create an image (docker build)
- Store it in a registry (docker image push)
- Start a container from it (docker container run)
The differences between EE and CE are shown below
Architecture
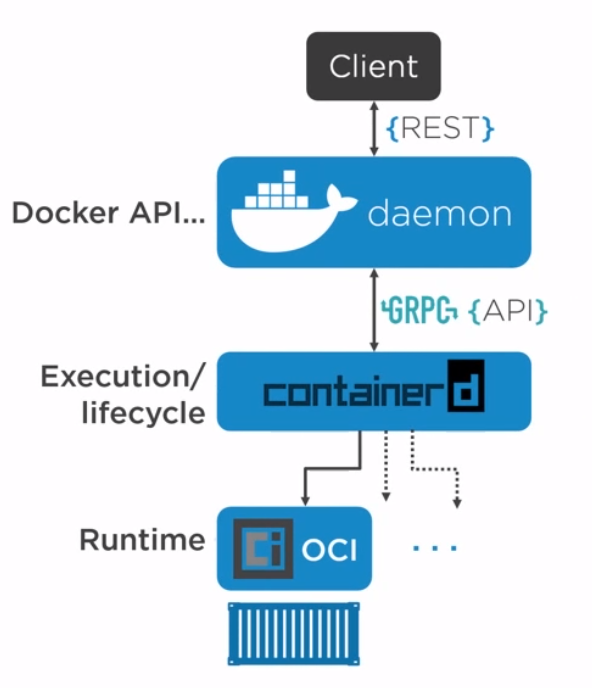
Docker is made up of a docker engine and containers which are comprised of namespaces and control groups. Wiki defines namespaces as Namespaces are a feature of the Linux kernel that partitions kernel resources such that one set of processes sees one set of resources while another set of processes sees a different set of resources.
Docker Engine
Here are the core elements of the docker engine.
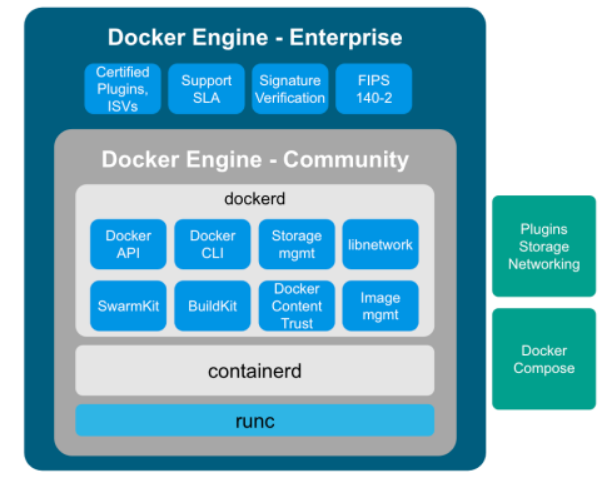
- dockerd: The Docker daemon is where all of your Docker communications take place. It manages the state of your containers and images, as well as connections with the outside world, and controls access to Docker on your machine.
- containerd: This is a daemon process that manages and runs containers. It pushes and pulls images, manages storage and networking, and supervises the running of containers.
- runc: This is the low-level container runtime (the thing that actually creates and runs containers). It includes libcontainer, a native Go-based implementation for creating containers
When we create a container, this is the workflow. It is the runc which actually the part which creates the container. The components containerd and runc standardized and it is easily possible to swap runc out for any oci compliant runtime.
Namespace Types
Within the Linux kernel, there are different types of namespaces. Each namespace has its own unique properties:
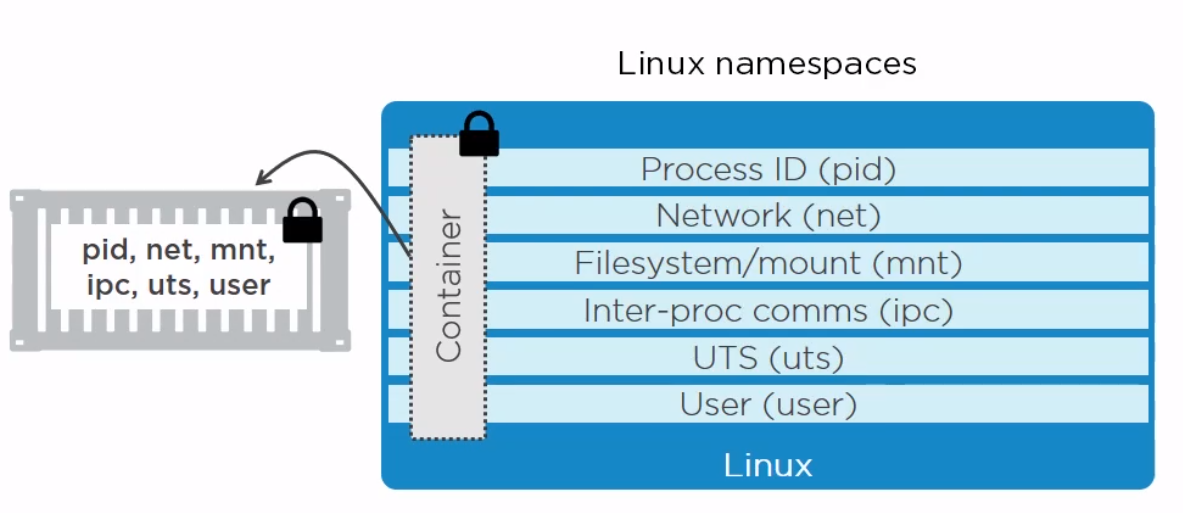
- A user namespace has its own set of user IDs and group IDs for assignment to processes. In particular, this means that a process can have root privilege within its user namespace without having it in other user namespaces.
- A process ID (PID) namespace assigns a set of PIDs to processes that are independent from the set of PIDs in other namespaces. The first process created in a new namespace has PID 1 and child processes are assigned subsequent PIDs. If a child process is created with its own PID namespace, it has PID 1 in that namespace as well as its PID in the parent process’ namespace. See below for an example.
- A network namespace has an independent network stack: its own private routing table, set of IP addresses, socket listing, connection tracking table, firewall, and other network‑related resources.
- A mount namespace has an independent list of mount points seen by the processes in the namespace. This means that you can mount and unmount filesystems in a mount namespace without affecting the host filesystem.
- An interprocess communication (IPC) namespace has its own IPC resources, for example POSIX message queues.
- A UNIX Time‑Sharing (UTS) namespace allows a single system to appear to have different host and domain names to different processes.
Control Groups
A control group (cgroup) is a Linux kernel feature that limits, accounts for, and isolates the resource usage (CPU, memory, disk I/O, network, and so on) of a collection of processes.
Now we have namespace we need a way to control the resources across the namespaces. This is where cgroups come in.
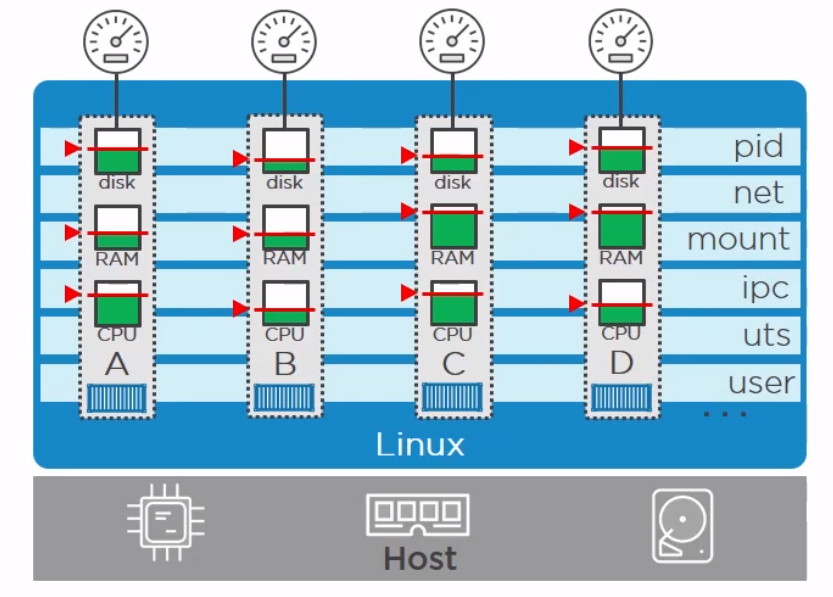
- Resource limits – You can configure a cgroup to limit how much of a particular resource (memory or CPU, for example) a process can use.
- Prioritization – You can control how much of a resource (CPU, disk, or network) a process can use compared to processes in another cgroup when there is resource contention.
- Accounting – Resource limits are monitored and reported at the cgroup level.
- Control – You can change the status (frozen, stopped, or restarted) of all processes in a cgroup with a single command.
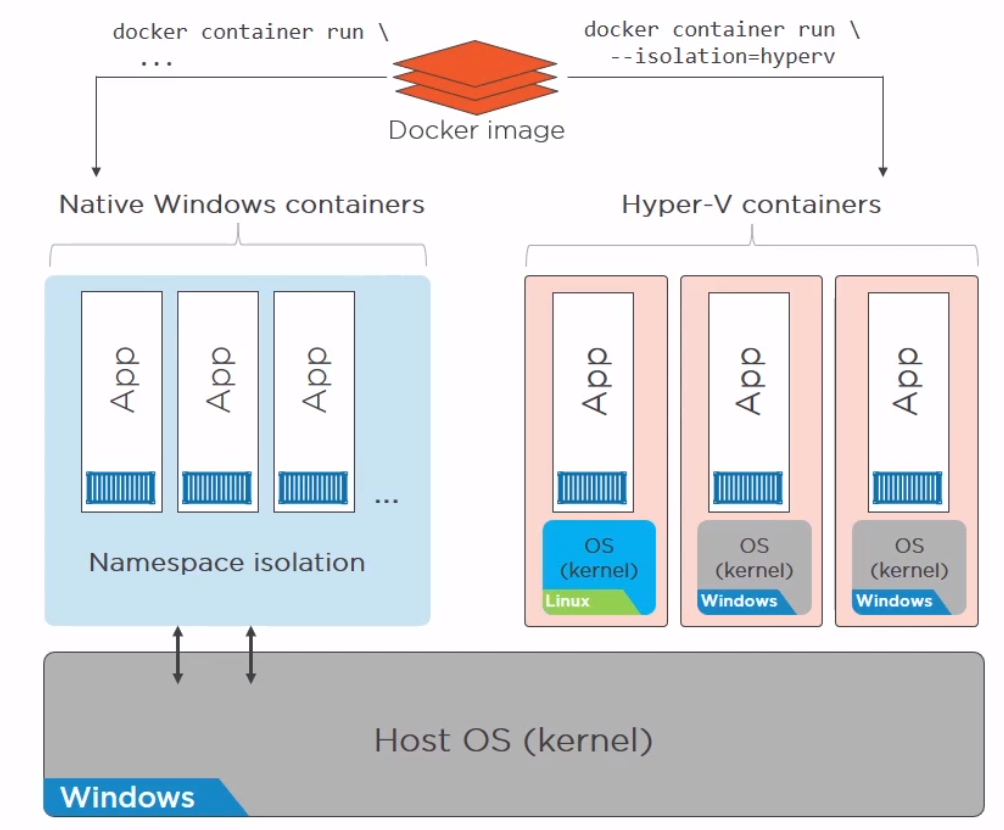
Docker on Windwos
Finally a quick image to demonstrate the difference between native and hyper-v containers on windows. They made me do it gov.
Images
Image a made up of a manifest and layers.
Getting Images
We can get images using the pull command. The command is two step. It reads the manifests and then pulls the layers checking that the hashes pulled match the manifest hashes.
docker image pull redis
>Using default tag: latest
>latest: Pulling from library/redis
>33847f680f63: Pull complete
>26a746039521: Pull complete
>18d87da94363: Pull complete
>5e118a708802: Pull complete
>ecf0dbe7c357: Pull complete
>46f280ba52da: Pull complete
>Digest: sha256:cd0c68c5479f2db4b9e2c5fbfdb7a8acb77625322dd5b474578515422d3ddb59
>Status: Downloaded newer image for redis:latest
>docker.io/library/redis:latest
#To get the digest
docker image ls --digests
REPOSITORY TAG DIGEST IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
redis latest sha256:cd0c68c5479f2db4b9e2c5fbfdb7a8acb77625322dd5b474578515422d3ddb59 aa4d65e670d6 3 weeks ago 105MB
The Layers
We can find where our layers are by using
docker system info
>Client:
> Context: default
> Debug Mode: false
>
>Server:
> Containers: 2
> Running: 0
> Paused: 0
> Stopped: 2
> Images: 3
> Server Version: 20.10.7
> Storage Driver: overlay2
> Backing Filesystem: extfs
> Supports d_type: true
> Native Overlay Diff: true
> userxattr: false
> Logging Driver: json-file
> Cgroup Driver: cgroupfs
> Cgroup Version: 1
...
> Docker Root Dir: /var/lib/docker
> Debug Mode: false
> Registry: https://index.docker.io/v1/
> Labels:
> Experimental: false
> Insecure Registries:
> 127.0.0.0/8
> Live Restore Enabled: false
We can see it is using overlay2 storage driver and the root is /var/lib/docker so the layers are stored in /var/lib/docker/overlay2.
We can look at the history of the image and the commands used to make it with
docker history redis
>IMAGE CREATED CREATED BY SIZE >COMMENT
>aa4d65e670d6 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) CMD ["redis-server"] 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) EXPOSE 6379 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) ENTRYPOINT ["docker-entry… 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) COPY file:df205a0ef6e6df89… 374B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) WORKDIR /data 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) VOLUME [/data] 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c mkdir /data && chown redis:redis … 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c set -eux; savedAptMark="$(apt-m… 31.7MB
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) ENV REDIS_DOWNLOAD_SHA=4b… 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) ENV REDIS_DOWNLOAD_URL=ht… 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) ENV REDIS_VERSION=6.2.5 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c set -eux; savedAptMark="$(apt-ma… 4.15MB
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) ENV GOSU_VERSION=1.12 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c groupadd -r -g 999 redis && usera… 329kB
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) CMD ["bash"] 0B
><missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) ADD file:45f5dfa135c848a34… 69.3MB
The non-zero size changes are generally a layer.
For even more information run inspect
docker image inspect redis
Registries
Where images live. By default Docker uses docker hub but you can use your own or other peoples. Docker divides registries between official and unofficial. Official images live at top of the namespace e.g docker.io/redis docker.lo/mysql. It is important to understand when pulling an image there are three components.
- Registry - e.g. dockerio
- Repo - e.g. redis
- Image (or Tag) - e.g. latest
It is just that Docker has defaults for registry and image so docker pull redis works but it is really doing docker pull docker.io/redis/latest
It was mentioned that the hashes on the file system for an image are referred to as content hashes and when images are pushed to the registry, before sending the layers are compressed and these hashes are referred to as distribution hashes.
Best Practice
- Use Official images
- Use Small images
- Be explicit referencing images (:latest noooo!)
Containers Detail
Copy on Write
As we know the container is a bunch of layers and the images are read-only. Only the read/write layer is writeable. When we change values in a running container we actually copy the original file and put it in the read/write layer. This is known as copy on write

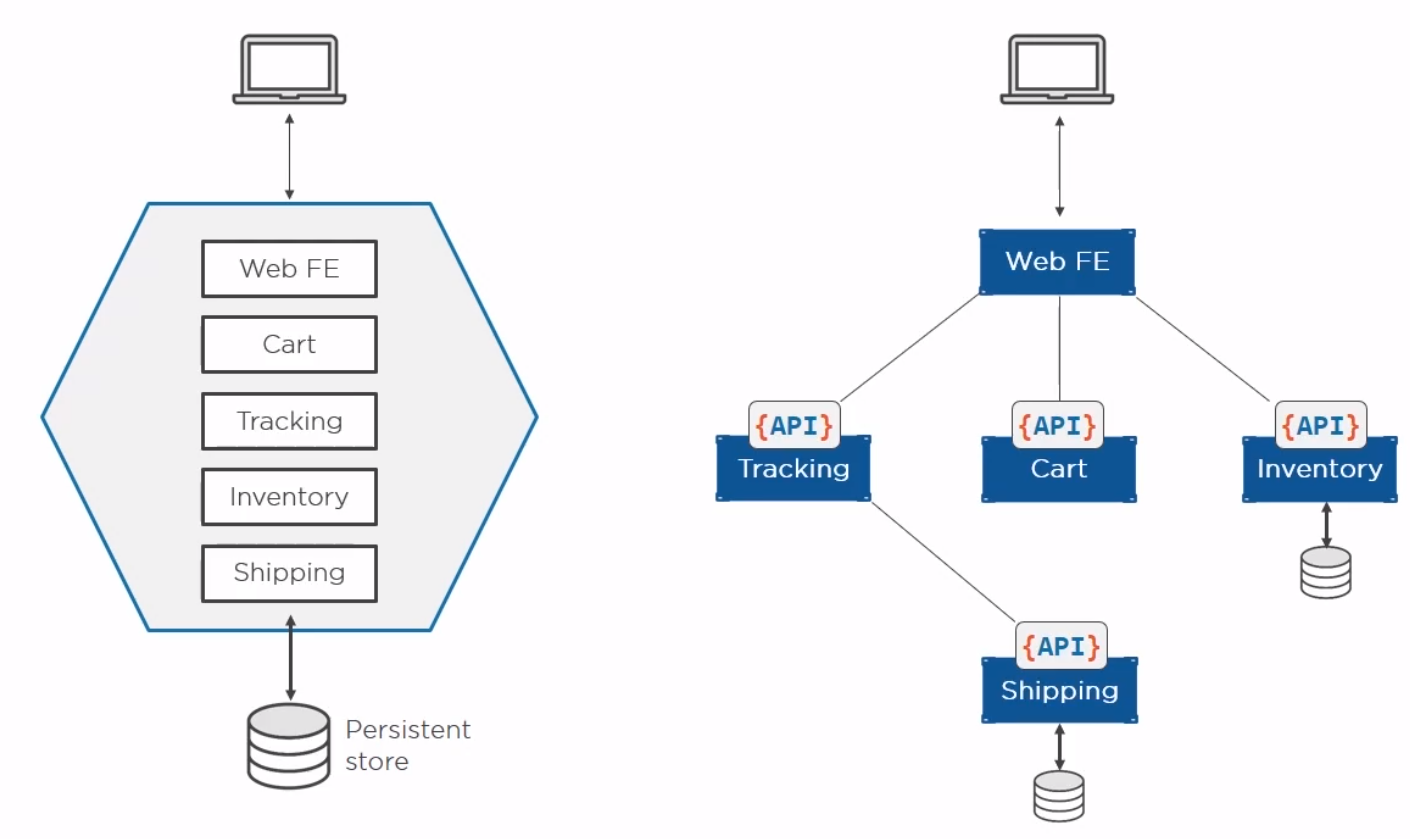
Microservices
Perhaps the current buzz-word. Previously we built our apps to have all of the components on one server. With containers we can break these down into individual containers. The old way is referred to as a monolith. The new way is to separate services and connect them with well documented APIs.
Helpful Commands
Some useful bits
# You only need the best match for container in commands
docker container ls
>49978c1c8547 redis "docker-entrypoint.s…" 19 seconds ago Up 18 seconds 6379/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8088->8088/tcp, :::8088->8088/tcp test
# Get the ports using part of the container name
docker port 499
>8088/tcp -> 0.0.0.0:8088
>8088/tcp -> :::8088
# Get IP of container
docker inspect -f "{{ .NetworkSettings.Networks.bridge.IPAddress }}" 499
# This works the same as inspect where you get all of the setting. the .NetowrkSettings is a filter
# Clean up containers
docker container rm $(docker container ls -aq) -f
Container Logging
We can set the logging driver in daemon.json (alternatives Gelf, Splunk, Fluentd...) and override for a container by passing --log-driver and --log-opts.
The standard way to view the logs is
docker logs <container>
Docker Swarm
Introduction
Swarm has two parts, the orchestrator and the secure cluster. The orchestrator does the start stop elements of running containers, the secure cluster is a way to run a group of containers with mutual authentication and encryption between them.
Swarm mode
With docker you can run containers as Single-engine mode or in something called Swarm mode. Whilst there a some notes on the options here I will leave detail for another day. This is just for awareness.
# To create a swarm
docker swarm init
When we do this
- The first node becomes the manager/leader
- They becomes the root CA (overrideable)
- They get a client certificate
- It builds a secure cluster store (which is etcd)
- This is distributed to every manager in store automatically
- Create cryptographic tokens, one for managers and one for workers
To join a new manager we pass the manager token and
docker swarm join-token manager
docker swarm join --token blarblarblar
To join a new worker we pass the worker token and
docker swarm join-token manager
docker swarm join --token blarblarblar
You can see the nodes with
docker node ls
We can rotate the worker token with
docker swarm join-token --rotate worker
We can lock/unlock swarms so they cannot be restarted without authentication with.
docker swarm lock
docker swarm unlock
Docker Networking
OSI Layers
Just a brief reminder of the OSI Layers
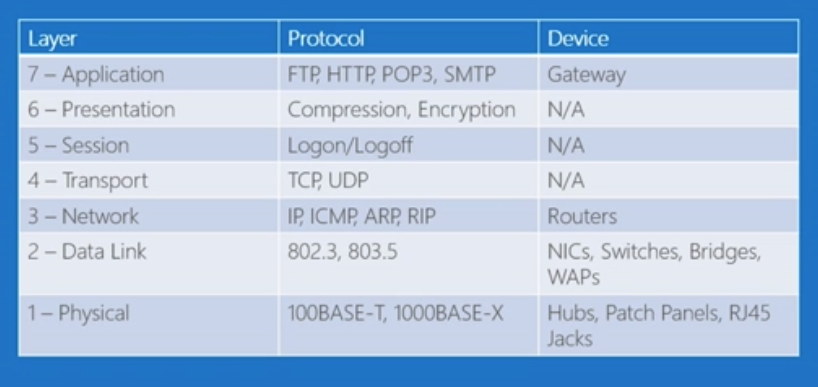
- Physical Layer
The lowest layer of the OSI Model is concerned with electrically or optically transmitting raw unstructured data bits across the network from the physical layer of the sending device to the physical layer of the receiving device. It can include specifications such as voltages, pin layout, cabling, and radio frequencies. At the physical layer, one might find “physical” resources such as network hubs, cabling, repeaters, network adapters or modems.
- Data Link Layer
At the data link layer, directly connected nodes are used to perform node-to-node data transfer where data is packaged into frames. The data link layer also corrects errors that may have occurred at the physical layer.
The data link layer encompasses two sub-layers of its own. The first, media access control (MAC), provides flow control and multiplexing for device transmissions over a network. The second, the logical link control (LLC), provides flow and error control over the physical medium as well as identifies line protocols.
- Network Layer
The network layer is responsible for receiving frames from the data link layer, and delivering them to their intended destinations among based on the addresses contained inside the frame. The network layer finds the destination by using logical addresses, such as IP (internet protocol). At this layer, routers are a crucial component used to quite literally route information where it needs to go between networks.
- Transport Layer
The transport layer manages the delivery and error checking of data packets. It regulates the size, sequencing, and ultimately the transfer of data between systems and hosts. One of the most common examples of the transport layer is TCP or the Transmission Control Protocol.
- Session Layer
The session layer controls the conversations between different computers. A session or connection between machines is set up, managed, and termined at layer 5. Session layer services also include authentication and reconnections.
- Presentation Layer
The presentation layer formats or translates data for the application layer based on the syntax or semantics that the application accepts. Because of this, it at times also called the syntax layer. This layer can also handle the encryption and decryption required by the application layer.
- Application Layer
At this layer, both the end user and the application layer interact directly with the software application. This layer sees network services provided to end-user applications such as a web browser or Office 365. The application layer identifies communication partners, resource availability, and synchronizes communication.
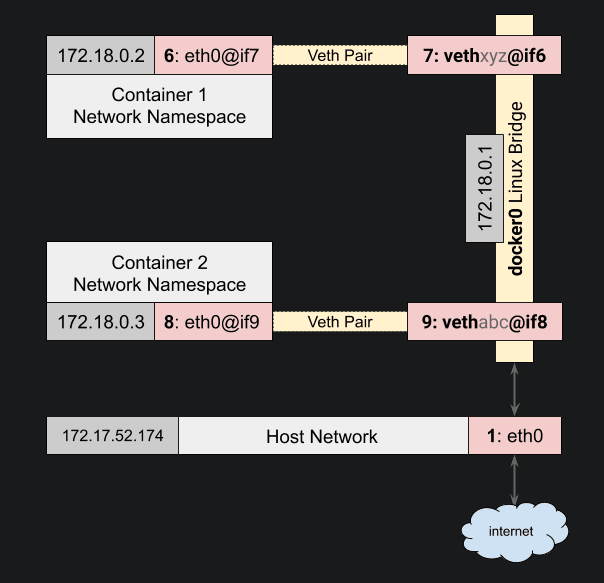
Bridge Network
There are four importance concepts about bridged networking:
- Docker0 Bridge
- Network Namespace
- Veth Pair
- External Communication
When we create a container a veth pair is created. Here is a diagram to help
This is the network which docker uses by default. We can see this with the command ls or inspect.
docker network ls
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
6960786ad2f8 bridge bridge local
d40bd7769843 host host local
e9a4e7e98aa1 none null local
docker network inspect bridge
>[
> {
> "Name": "bridge",
> "Id": "6960786ad2f80a1a309e8b9bf773ad73b5bc7c2f68ee36f545fd464619969461",
> "Created": "2021-08-15T17:27:07.794617822+12:00",
> "Scope": "local",
> "Driver": "bridge",
> "EnableIPv6": false,
> "IPAM": {
> "Driver": "default",
> "Options": null,
> "Config": [
> {
> "Subnet": "172.17.0.0/16",
> "Gateway": "172.17.0.1"
> }
> ]
> },
> "Internal": false,
> "Attachable": false,
> "Ingress": false,
> "ConfigFrom": {
> "Network": ""
> },
> "ConfigOnly": false,
> "Containers": {},
> "Options": {
> "com.docker.network.bridge.default_bridge": "true",
> "com.docker.network.bridge.enable_icc": "true",
> "com.docker.network.bridge.enable_ip_masquerade": "true",
> "com.docker.network.bridge.host_binding_ipv4": "0.0.0.0",
> "com.docker.network.bridge.name": "docker0",
> "com.docker.network.driver.mtu": "1500"
> },
> "Labels": {}
> }
>]
The only way to talk to other containers on a different bridge network is IP/Port to IP/Port.
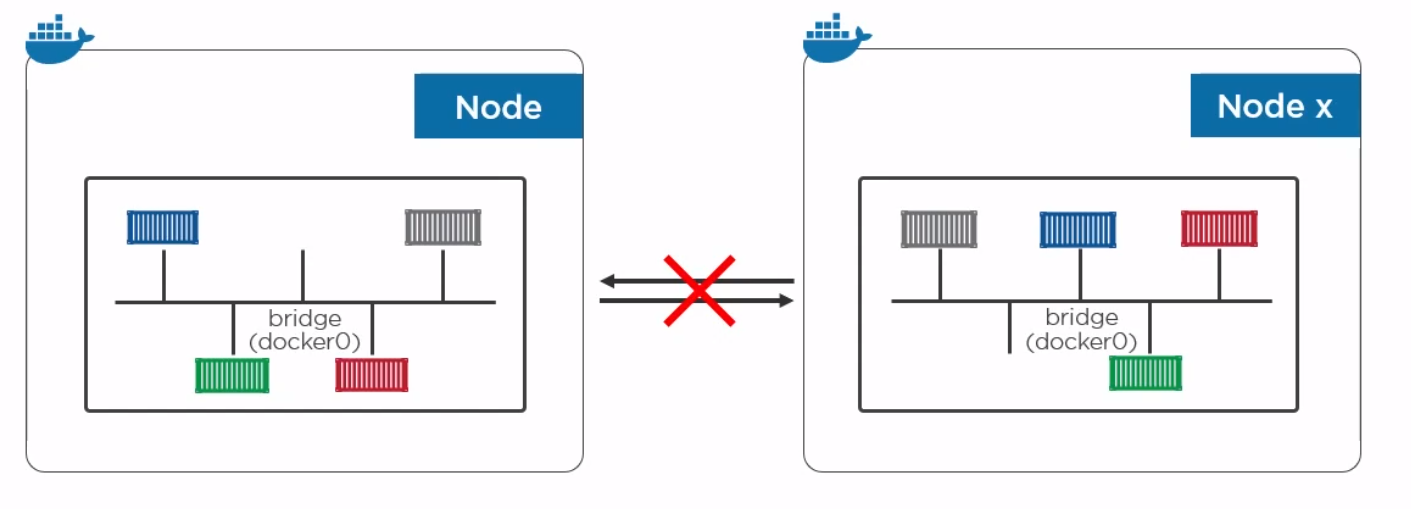
To create a network and add a container
docker network create -d bridge too-far
docker container run --rm -d --network toofar alpine sleep 1d
Overlay Network
With an overlay network containers can talk to each other on the same network and on different machines. This can be created with a single command on docker along with encryption. With built in overlay is container only. Note overlay is multiple host so any device on the network will be available.
docker network create overlay overnet -o encrypted
docker service create -d -name pinger --replicas 2 --network overnet alpine sleep 1d
If you want to talk to physical boxes or vlans you can use MACVLAN.
Network Services
- Discovery Make every service in the swarm discoverable via built-in DNS
- Ingress/Internal Load Balancing Every node in the swarm knows about every service
Volumes and Persistent Data
Introduction
Here for completeness
docker volume create myvol
docker volume ls
docker volume inspect
docker volume rm myvol
Using Volumes
This mounts a volume on the container at /vol and creates a volume if it does not exist.
docker container run -dit -name myvol --mount source=ubervol, target=/vol alpine:latest
Docker Secrets
A docker secret is a blob up to 500k. It needs swarm mode with services because it use the security components. We create a secret and send it to the swarm manager with the following command.
docker secret create mysec-v1 .\myfileondisk
docker secret ls
docker secret inspect
#Create a service
docker service create -d --name my-service --secret mysec-v1 alpine sleep 1d
#We can see the secret config
docker service inspect my-server
#On the node we can see /run/secrets
cat /run/secrets
#You cannot delete a secret in use to you need to delete the service first.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes came out of Google and Open Source. Greek for helmsman or k8s (Kates). Kubernetes is an orchestrator and can schedule, scale and update containers. There are alternatives like Docker Swarm
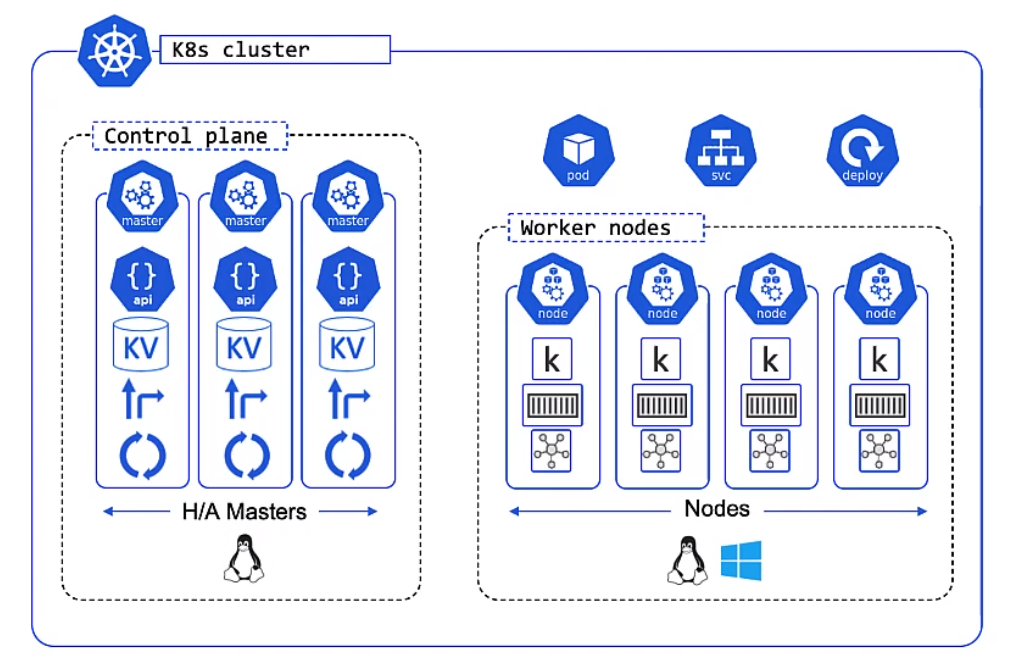
Architecture
Overview
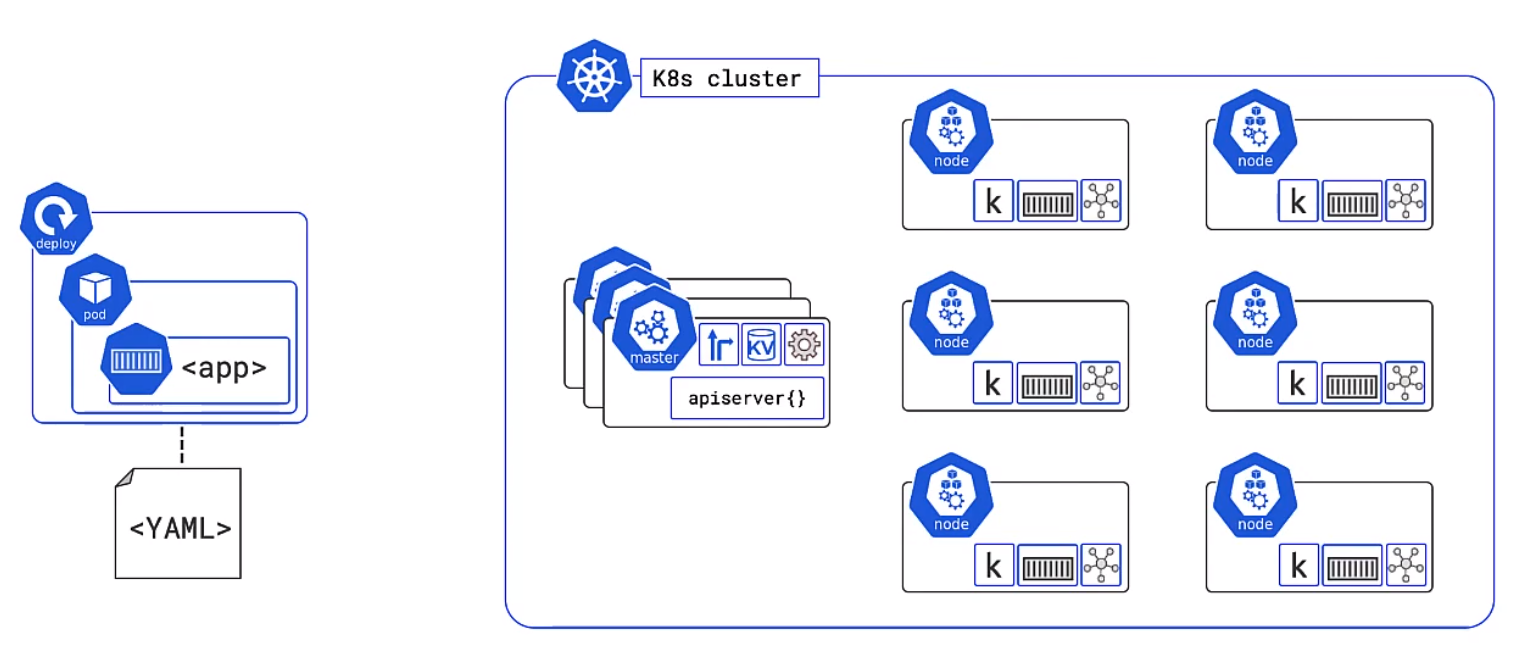
Apps are put in a container, wrapped in a pod and deployment details. They are provisioned on a Node inside a K8s Clustoer
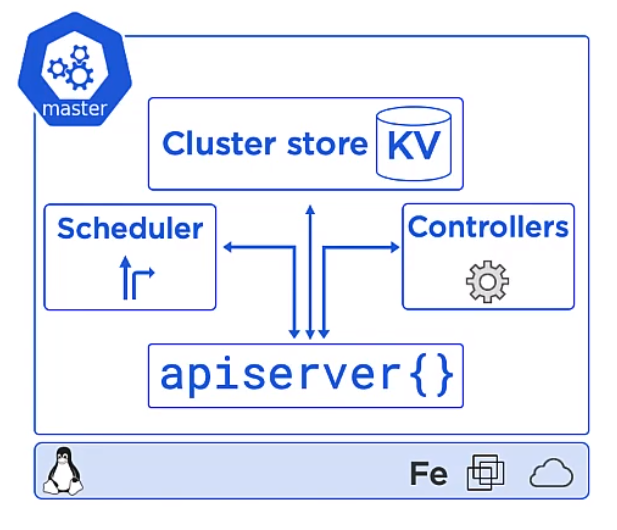
Master
In general these are a hosted services on the cloud but you can run them locally on a linux box.
- This is the front-end to the control plane
- It exposes a RESTFul API consuming JSON and Yaml
- We send manifests describing our apps to this
The Cluster Store for users with large changes often separate this
The controllers controls
- Node Controller
- Deployment controller
- Endpoints/EndpointSlice
The scheduler
- Watches for new work
- Assigns Work to the cluster nodes
Kubernetes Nodes
Now its time for the Nodes. These are made up of three parts, the Kublet, Container runtime and the Kube Proxy
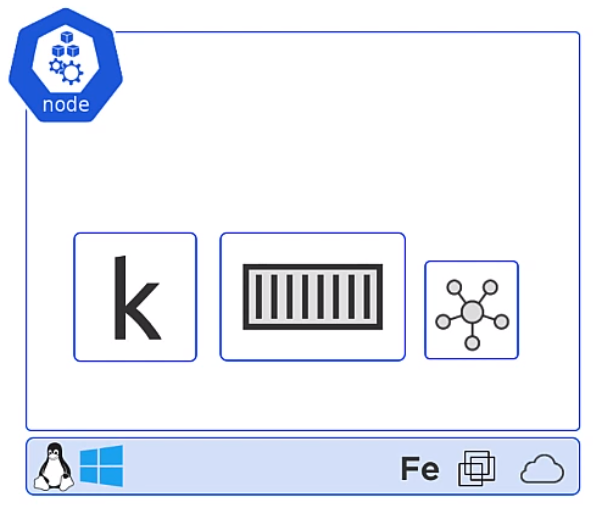
Kubelet
The Kubelet is the Main Kubernetes agent it
- Registers node with the cluster
- Watches API Server for work tasks (Pods)
- Executes Pods
- Reports to the master
Container Runtime
- Can be Docker
- Pluggable via Container Runtime Interface (CRI)
- Generally is Docker or containerd, other like gVisor and katacontainers exist
- Does the stop and starting of containers
Kube Proxy
- The Networking Component
- Does light-weight load balancing
Declarative Model/Desired State
We describe what we want the cluster to look like but we do not care how it happens. Kubernetes constantly checks the desired state matches the observed state.
Pods
A pod is a shared execution environment and can container one or more containers. It is the Pod which has a unique IP. Containers within the same pod must allocate unique ports if they are to talk to each other or the outside world. The same for volumes etc.When scaling you scale Pods not Containers.
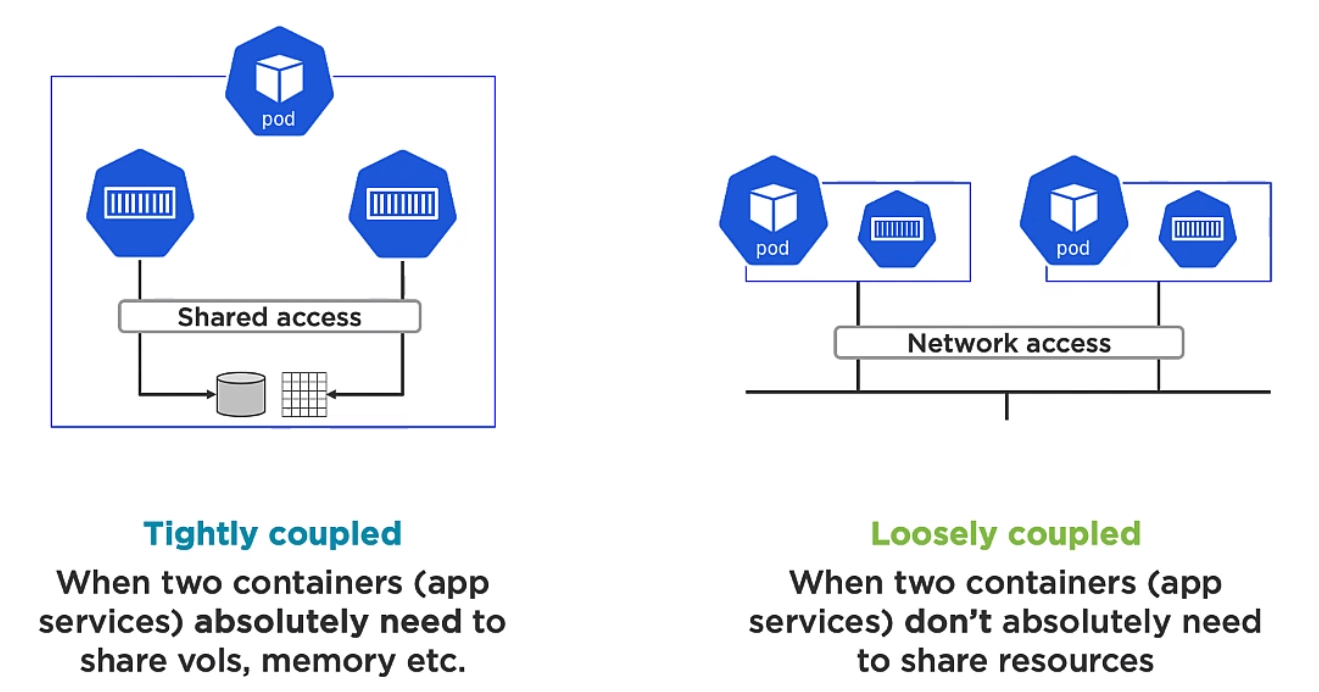
Multi container Pods are for two different but complimentary containers which need to be aligned. An example of this might be a service mesh. For example the mesh container could be responsible for encryption or decryption. Note Deployment of Pods is atomic
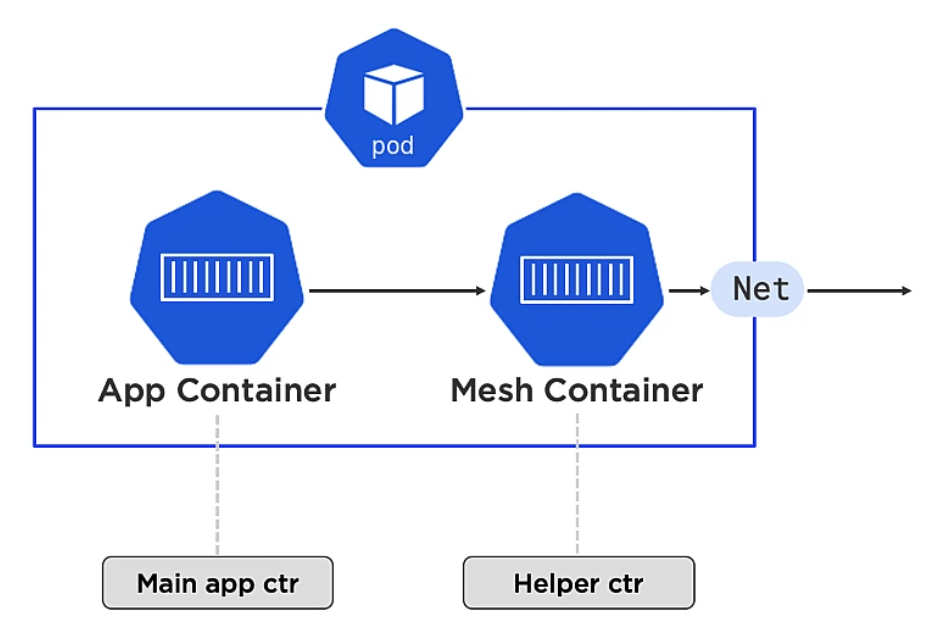
Pods provide
- Annotations
- Labels
- Policies
- Resources
- Co-scheduling of contianers
and other Metadata.
Kubernetes Service Objects
As mentioned the IP address are provided for each Pod. However Pods die, we scales up and down and it would not be practical to use them so Kurbenetes provides the Service object which is describe in the deploymennt. With the use of labels the Service object knows which pods to send traffic to. By either removing labels from the pod the objects can be match generically.
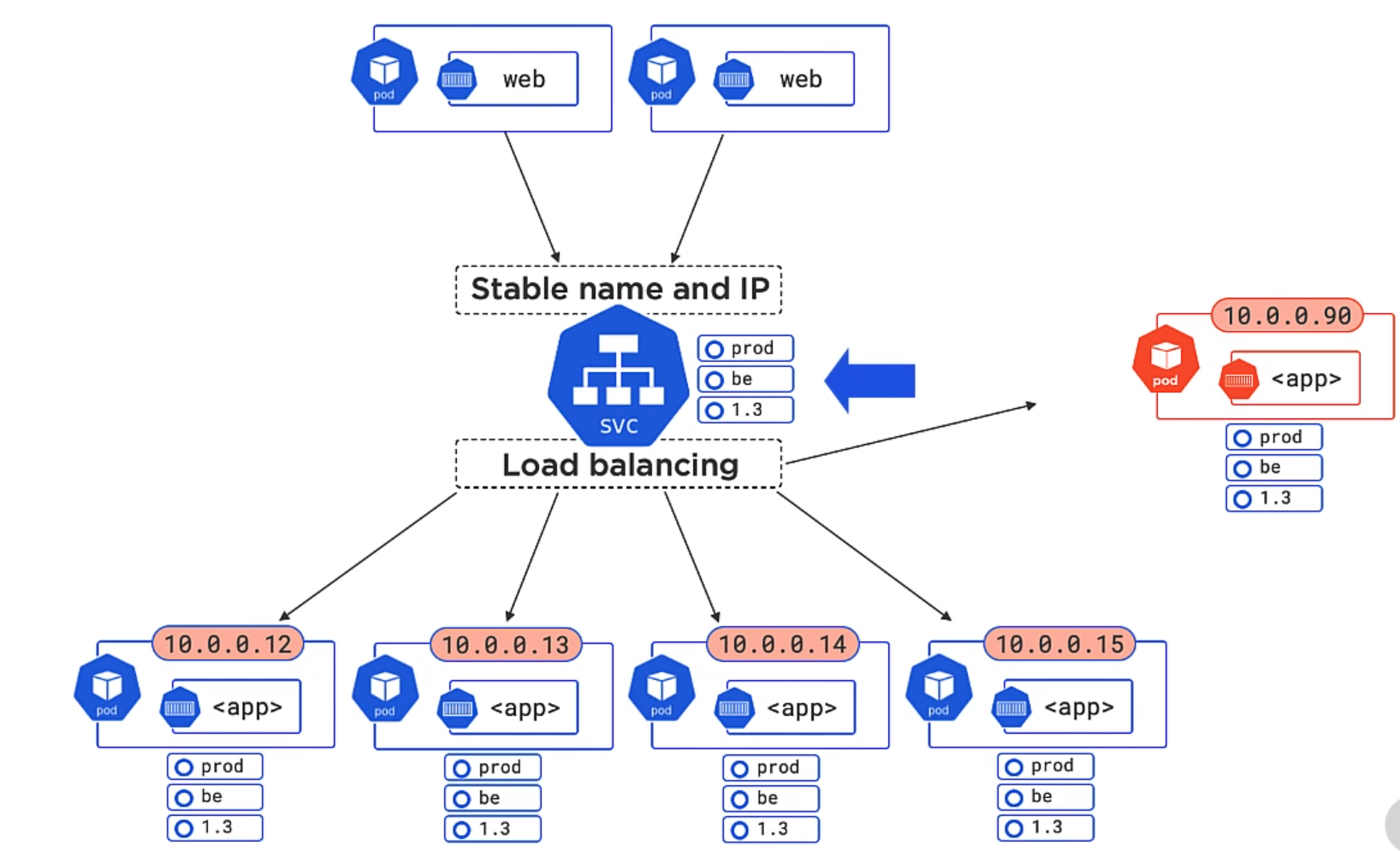
In the example below both 1.3 and 1.4 will be matched of the Pods. Equally we could add a version to the service object and the unmatched version would not be used.
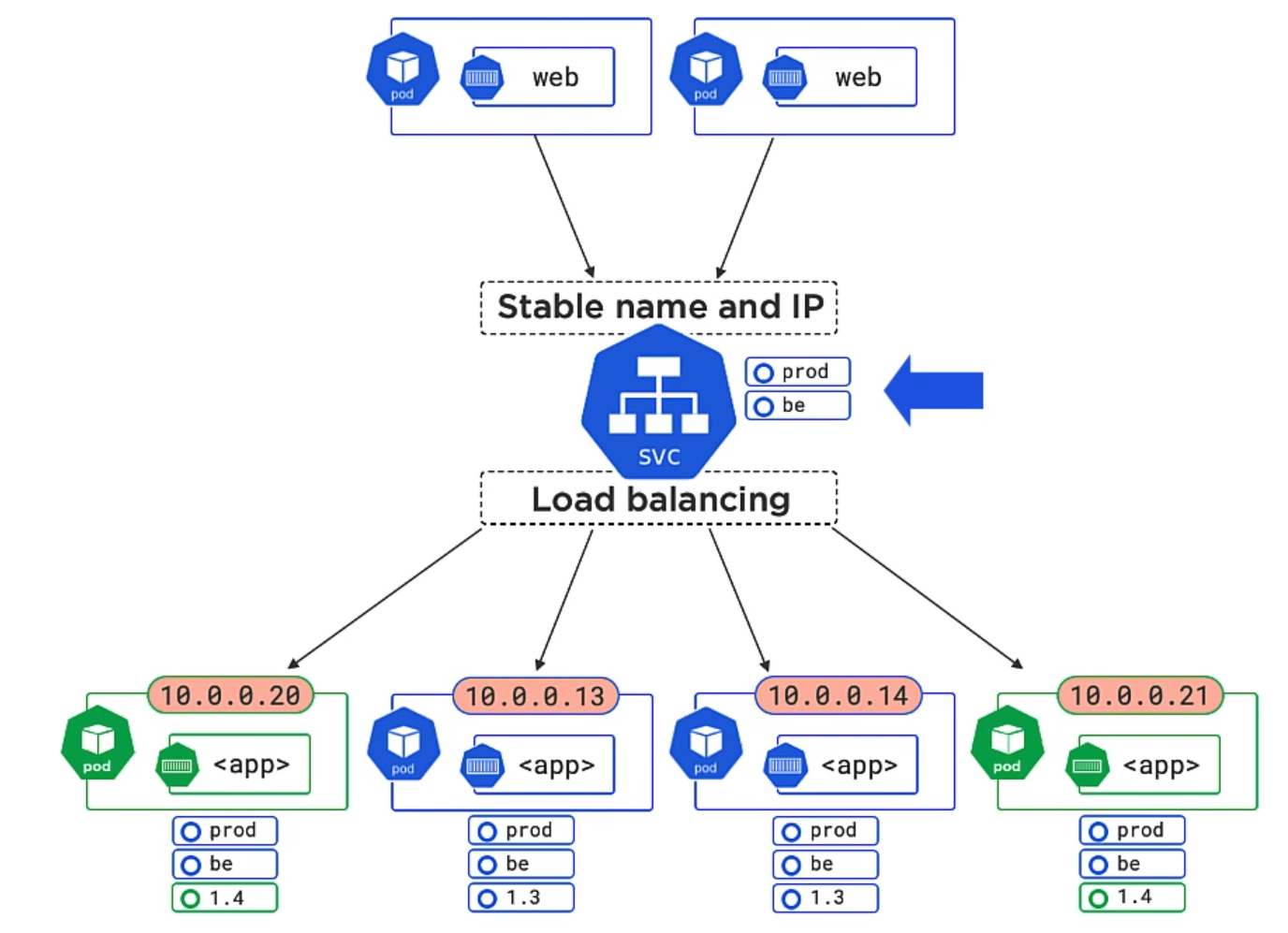 Service objects
Service objects
- Only Send traffic to healthy Pods
- Can do session affinity (Sending of subsequent requests to the same Pod)
- Can send traffic to endpoints outside of the cluster
- Can do TCP and UDP
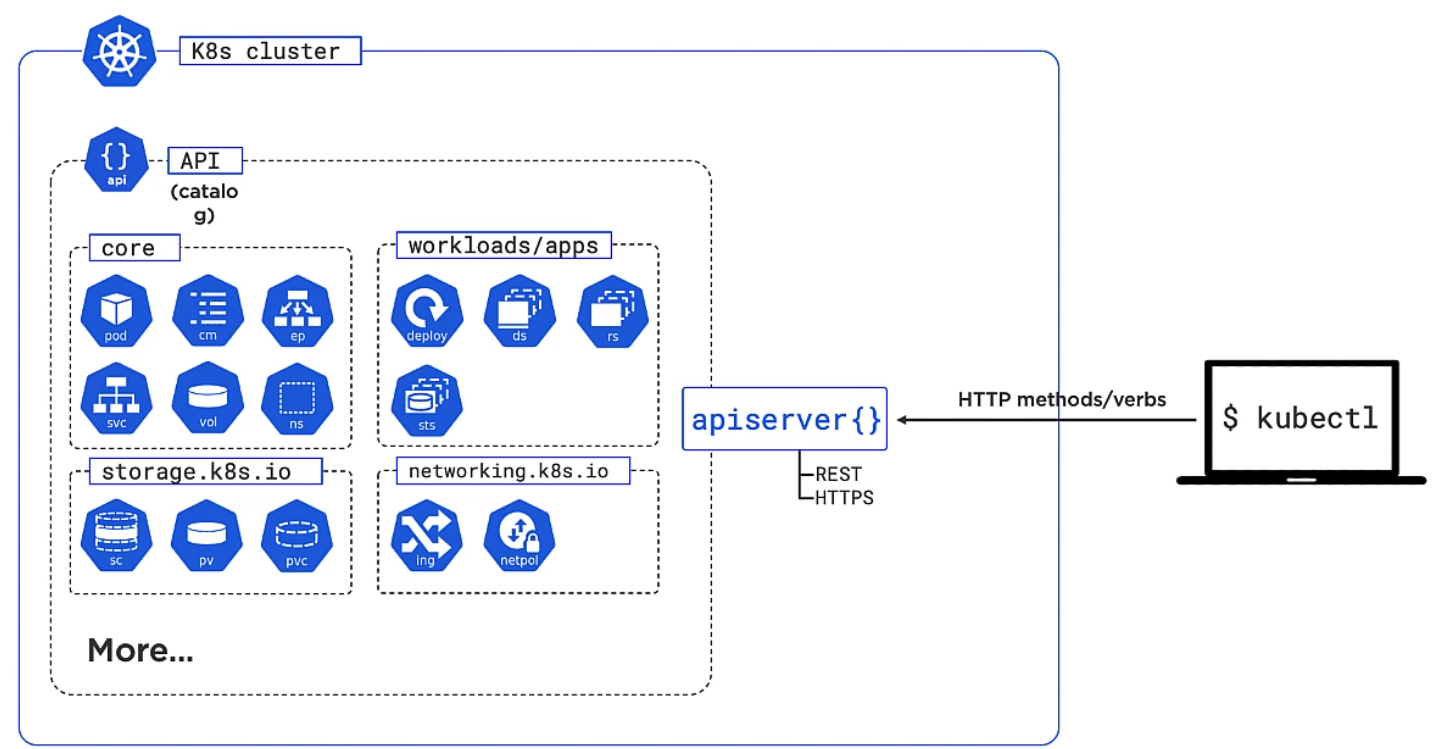
Kubernetes API Server
This is the API which exposes and RESTFul API. It exposes the various objects handles the requests. The objects are broken up into various sub categories. We use the command line kubectl to control this.
Installing Ubuntu
This was really easy. Had to use Firefox to get the dashboard to work on https://127.0.0.1:10443. Need to review how to get it to work on Chrome.
sudo snap install microk8s --classic
sudo usermod -a -G microk8s $USER
sudo chown -f -R $USER ~/.kube
su - $USER
microk8s status --wait-ready
microk8s enable dashboard dns ingress
microk8s kubectl get all --all-namespaces
microk8s dashboard-proxy
To be able to use the dashboard on chrome you need to go to chrome://flags/#allow-insecure-localhost and enable Allow invalid certificates for resources loaded from localhost. Firefox works by default.
Deploying Pods
Introduction
We do this by
- Creating App Code
- Create an image
- Store in a repo
- Define in a manifest
- Post to the API Server
Example
Creating App Code
Clone the App Code
git clone https://github.com/nigelpoulton/getting-started-k8s.git
Create an Image
Easy pezzy lemon squeezy. Where nigelpulton is your own Docker hub account/repository
cd getting-started-k8s/App
docker image build -t nigelpulton/getting-started-k8s:1.0 .
Store in repo
Now push the image to your docker hub account.
docker image push nigelpoulton/getting-started-k8s:1.0
Define in a manifest
We can define this in either Yaml or Json. I used yq eval -j to convert mine but it does say kubectl convert should work. I am using microk8s and it said it did not work.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: hello-pod
labels:
app: web
spec:
containers:
- name: web-ctr
image: nigelpulton/getting-started-k8s:1.0
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
And the json version
{
"apiVersion": "v1",
"kind": "Pod",
"metadata": {
"name": "hello-pod",
"labels": {
"app": "web"
}
},
"spec": {
"containers": [
{
"name": "web-ctr",
"image": "nigelpulton/getting-started-k8s:1.0",
"ports": [
{
"containerPort": 8080
}
]
}
]
}
}
The "Kind" and "apiVersion" refer to the object. The objects you can use are grouped into types. Here is some of the objects in the apps group.
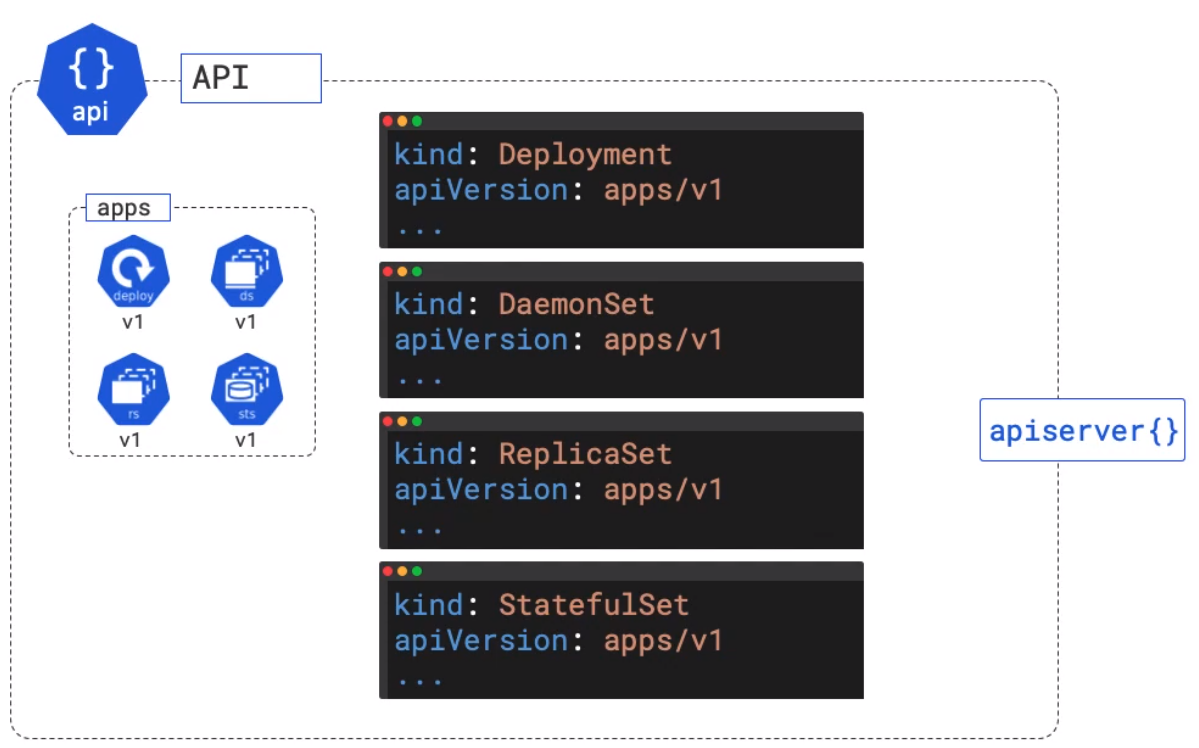 The default image tag by default will use the docker hub. You can add a prefix with the dns name if it is stored somewhere else.
The default image tag by default will use the docker hub. You can add a prefix with the dns name if it is stored somewhere else.
Post to the API Server
You can post the manifest to the cluster with
cd Pods
kubectl apply -f pod.yml
# Get the status
kubectl get pods --watch -o wide
# Get All the Pod information
kubectl describe pods hello-pod
Example Cleanup
To clean up the deployment we can either
# Delete by using delete and the manifest
kubectl delete -f pod.yml
# Or delete using the name
kubectl delete pod hello-pod
Kubernetes Services
The Service has a frontend and a backend.
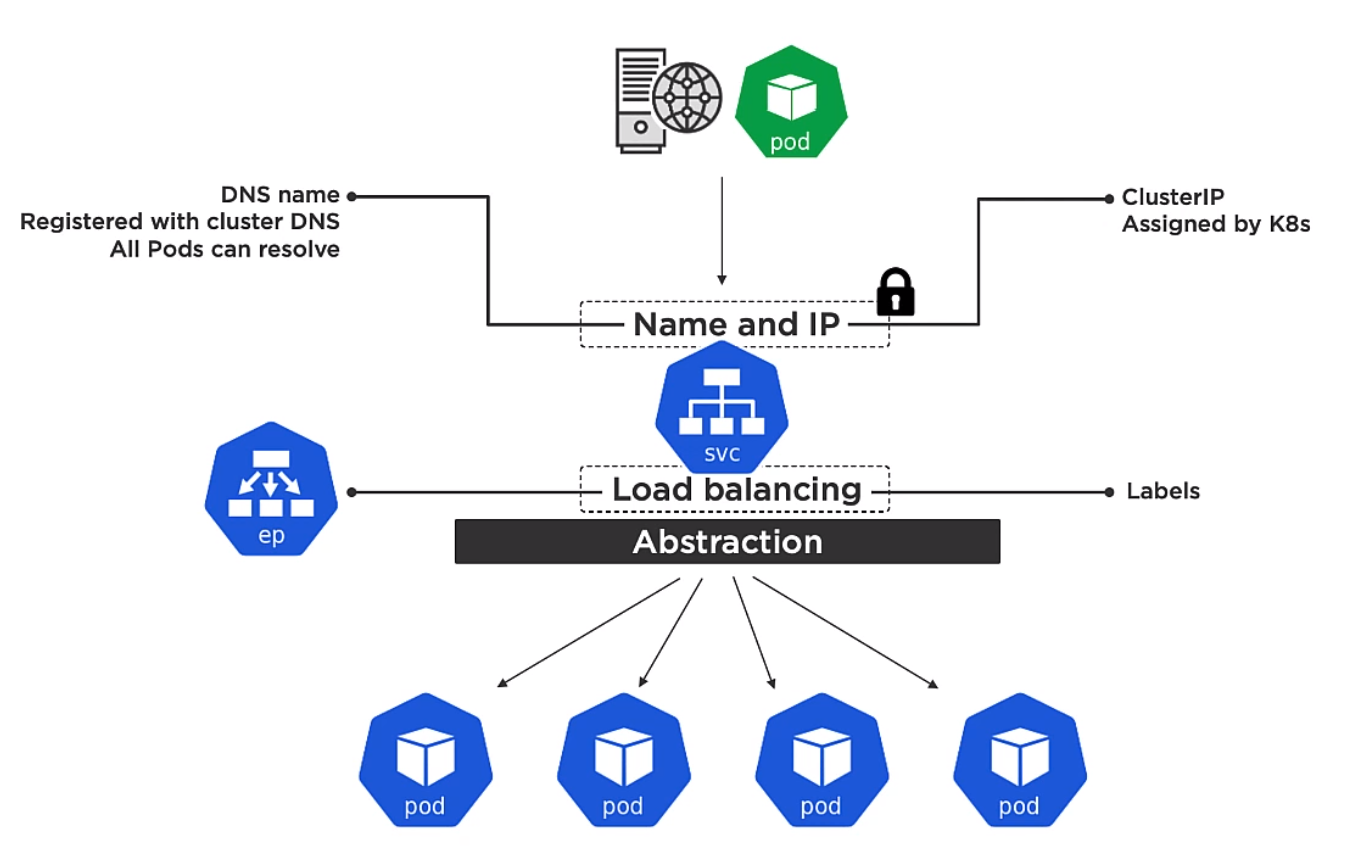
Frontend
The frontend is
- Name
- IP
- Port
The IP on the frontend is called a ClusterIP and is assigned by Kubernetes. It is only for use within the cluster. The name is the name of the service and that is registered with DNS.
Every container in every pod can resolve service names
Backend
Is a way for the service to know which pods to send track on to. The endpoint slice tracks the list of healthy Pod which match the services label selector.
Types of Service
- LoadBalancer External access via cloud load-balancer
- NodePrt External access via nodes
- ClusterIP (default) internal cluster connectivity
Creating a Services
We can create service in two ways
- Imperatively
- Declaratively
Imperatively
With imperative we can simply use the kubectl.
kubectl expose pod hello-pod --name=hello-svc --target-port=8080 --type=NodePort
microk8s kubectl get svc
>NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
>kubernetes ClusterIP 10.152.183.1 <none> 443/TCP 21h
>hello-svc NodePort 10.152.183.147 <none> 8080:30737/TCP 11s
From there we can get to the service using the node port which is the outbound port shown for the service. In our case this is 30737. So going to the ip of the machine and port should show the service. e.g. htttp://192.xxx.xxx.1.70:30737. Node ports are allocated by Kubernetes between 32000 and 32767
Declaratively
Here is the yaml file to create the above service. Note I put the word name inside of app for the selector which resulted in the service having no endpoint.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ps-nodeport
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
nodePort: 31111
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: web
And here is a picture to explain the ports.
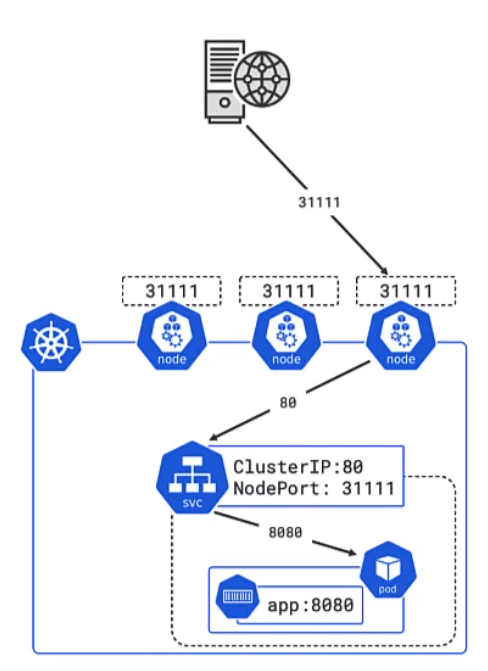
- 31111 is the port for external access
- 80 is the port the cluster is listening on
- 8080 is the port exposed by the pod and the defined in the docker container
We can check we have the right name (label) in the service with the command
kubectl get pods --show-labels
>NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
>hello-pod 1/1 Running 0 79m app=web
Clean up
Deleting service can be done with
kubectl delete svc hello-svc
Deployments
Introduction
To deploy a solution we need
- Deployment (Updates and Rollbacks)
- Replication Set (Scalability, Reliability, Desired State)
- Pod (Scheduling and Execution)
- App (App code)
Rolling Updates and Rollbacks
To update we simply provide a new version of the deployment. We can define how this happens e.g. wait 10 mins before OK. Kubernetes keeps the old pods to allow the user to reverse the deployment by using a previous version of the deployment. Here we see the rollback where the green pods are being replace by the original pods.
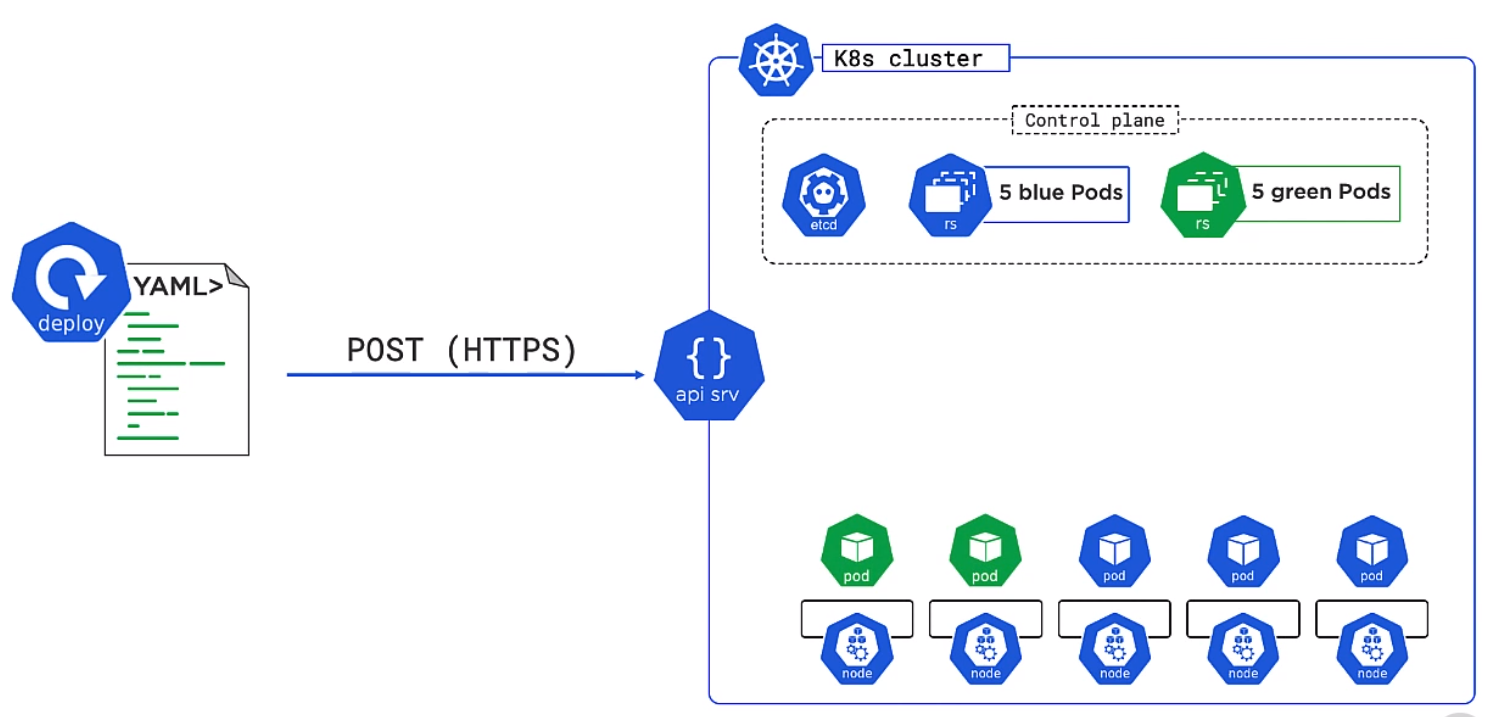
Deployment Section
The example below show a deployment and provides and overview. The labels in the deployment spec must match the label in the Pods spec. The always is for security and ensures the code not the local copy.
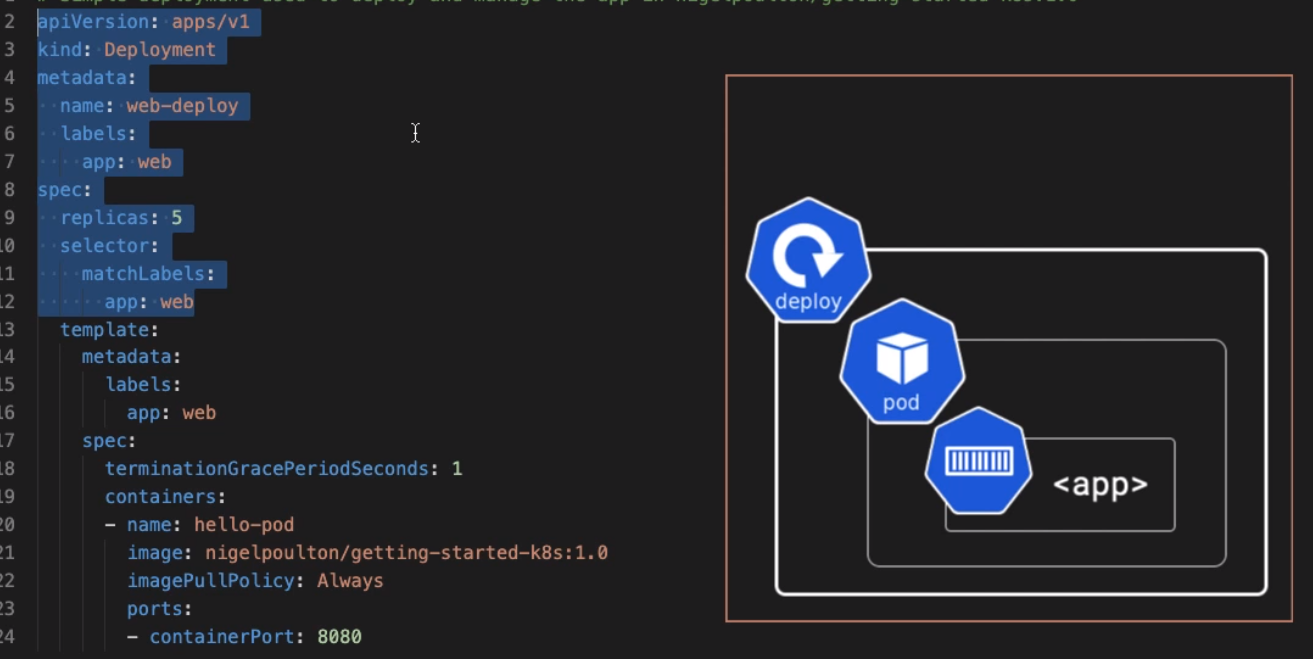
Full Example
Here is a full example. There are many options under the strategy we can configure. In this example we have opted for
- minReadySeconds The amount of time to wait and see if container is working before proceeding
- maxUnavailable Number which should be available during update
- maxSurge The number it can exceed the desired amount by.
So in this example there will be 6 pods during the update and it will wait for 5 seconds and reduce back down to 5.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: web-deploy
labels:
app: web
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: web
replicas: 5
minReadySeconds: 5
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 0
maxSurge: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: web
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 1
containers:
- name: hello-pod
image: nigelpoulton/getting-started-k8s:2.0
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
Doing Update
To perform an update we use the deploy command
#Do Deployment
kubectl apply -f deploy-complete.yml
#Monitor the deploy progress with
kubectl get deploy
#Monitor the replicate sets progress with
kubectl get rs
Reversing the update
As discussed the old replicates still reside with in kubernetes. We can see this by looking as the replication sets. We can reverse the update by
#Get the deployment history
kubectl rollout history deploy web-deploy
>deployment.apps/web-deploy
>REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE
>1 <none>
>2 <none>
#To reverse we just need to provide the revision to rollback to.
kubectl rollout undo deploy web-deploy --to-revision=1
Monitoring Deployment
We can see both the deploy and the replication sets with
kubectl get deploy
kubectl get rs
We can use describe ep to see the endpoints for our configuration.
microk8s kubectl describe ep
>Name: ps-nodeport
>Namespace: default
>Labels: <none>
>Annotations: endpoints.kubernetes.io/last-change-trigger-time: 2021-08->14T17:53:23+12:00
>Subsets:
> Addresses: 10.1.114.202
> NotReadyAddresses: <none>
> Ports:
> Name Port Protocol
> ---- ---- --------
> <unset> 8080 TCP
>
>Events: <none>
iwiseman@OLIVER:
Self Healing and Scaling
We can delete pods and nodes and Kubernetes will fix the problem. This is known as self healing. We can manually deploy with more replicas to scale up and down. There is Horizontal Pod Autoscaler and Cluster Autoscaler as well.