Vue Introduction
Intro
Hello John (No world)
Resource for the tutorial was https://github.com/johnpapa/vue-getting-started
The vue js lives at https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue. Below is a simple example just showing two way binding
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="name">
<p>Hello {{name}}</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
name: "John"
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
Sections
Vue files are comprised of three sections. No prizes for what each bit does
<template>
<a v-bind:href="github" target="_blank">
</a>
<template/>
<script>
</script>
<style>
</style>Displaying Data and Events
Data Model
We can define a data model and use it with standard double curly braces.
</template>
...
<div>{{hero.id}}</div>
...
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Heroes',
data() {
return {
id: 20,
firstName: 'Fred',
lastName: 'Bloggs'
message: ''
}
},
};
</script>
Data Binding
Binding we can use v-bind or the short cut : (full colon). So in the template put the colon and define a data component below
<template>
...
<a
v-bind:="github"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
<i class="fab fa-github fa-2x" aria-hidden="true"></i>
</a>
<a
:href="twitter"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
<i class="fab fa-twitter fa-2x" aria-hidden="true"></i>
</a>
...
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'headerLinks',
data() {
return {
github: 'https://github.com/johnpapa/vue-getting-started',
twitter:'https://twitter.com/john_papa',
}
},
}
</script>Two Way Binding
To bind two-way with v-model with the model and property.
</template>
<input class="input" id="firstName" v-model="hero.firstName"/>
</template>Event Binding
Example
To bind events we use v-on: or @ to bind our methods to an event.
</template>
<button @click="cancelHero">Cancel</button>
<button v-on:click="cancelHero">Cancel 2</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Heroes',
data() {
...
},
methods: {
cancelHero() {
this.message = ''
},
}
};
</script>Keyup
Below is an example of binding to the keyup event. The .esc denotes the escape key. </template> <script>
<select
id="power"
v-model="hero.power"
:class="{ invalid: !hero.power }"
@keyup.esc="clearPower"
>
</script> </syntaxhighlight>
Checkbox, Radio
No surprises here
<template>
<input
type="radio"
id="color-red"
value="red"
v-model="hero.capeColor"
/>
<input
type="checkbox"
class="is-primary"
id="active"
v-model="hero.active"
/>
</template>Styles and Classes
Styles and Classes are trickier because of the object approach of the data
<template>
<select
id="power"
v-model="hero.power"
@keyup.esc="clearPower"
>
<div
class="color-line"
:style="{ 'background-color': hero.capeColor }"
></div>
</template>Displaying List and Conditional Content
Iterating v-for
So just create a key and use the right syntax and the defined model
<template>
<ul class="list is-hoverable">
<li v-for="hero in heroes" :key="hero.id">
<a class="list-item"><span>{{ hero.firstName }}</span></a>
</li>
</ul>
</template>Binding to selection
We can do this by binding to the model on click. Note the conditional class based on if the current hero === selected hero.
<template>
<li v-for="hero in heroes" :key="hero.id">
<a
class="list-item"
@click="selectedHero = hero"
:class="{ 'is-active': selectedHero === hero }"
><span>{{ hero.firstName }}</span></a
>
</li>
</template>Conditional Displaying v-if and v-show
v-if
Same as *ngIf. So if no selection on the list
<template>
<div class="columns" v-if="selectedHero">
<div class="column is-3">
<header class="card-header">
<p class="card-header-title">{{ selectedHero.firstName }}</p>
</header>
<div class="card-content">
<div class="content">
...
</template>v-show
This will put the data in dom.
<template>
<div class="field" v-show="showMore">
<label class="label" for="lastName">last name</label>
<input
class="input"
id="lastName"
v-model="selectedHero.lastName"
/>
</div>
</template>Interacting within a Component
Computed
This is a section in the scripts section which allow you to define function to compute value maybe from existing model data
<script>
computed: {
fullName() {
return `${this.selectedHero.firstName} ${this.selectedHero.lastName}`;
},
},
</script>Component Lifecycle Hooks
Here are the component lifecycle hooks for Vue.
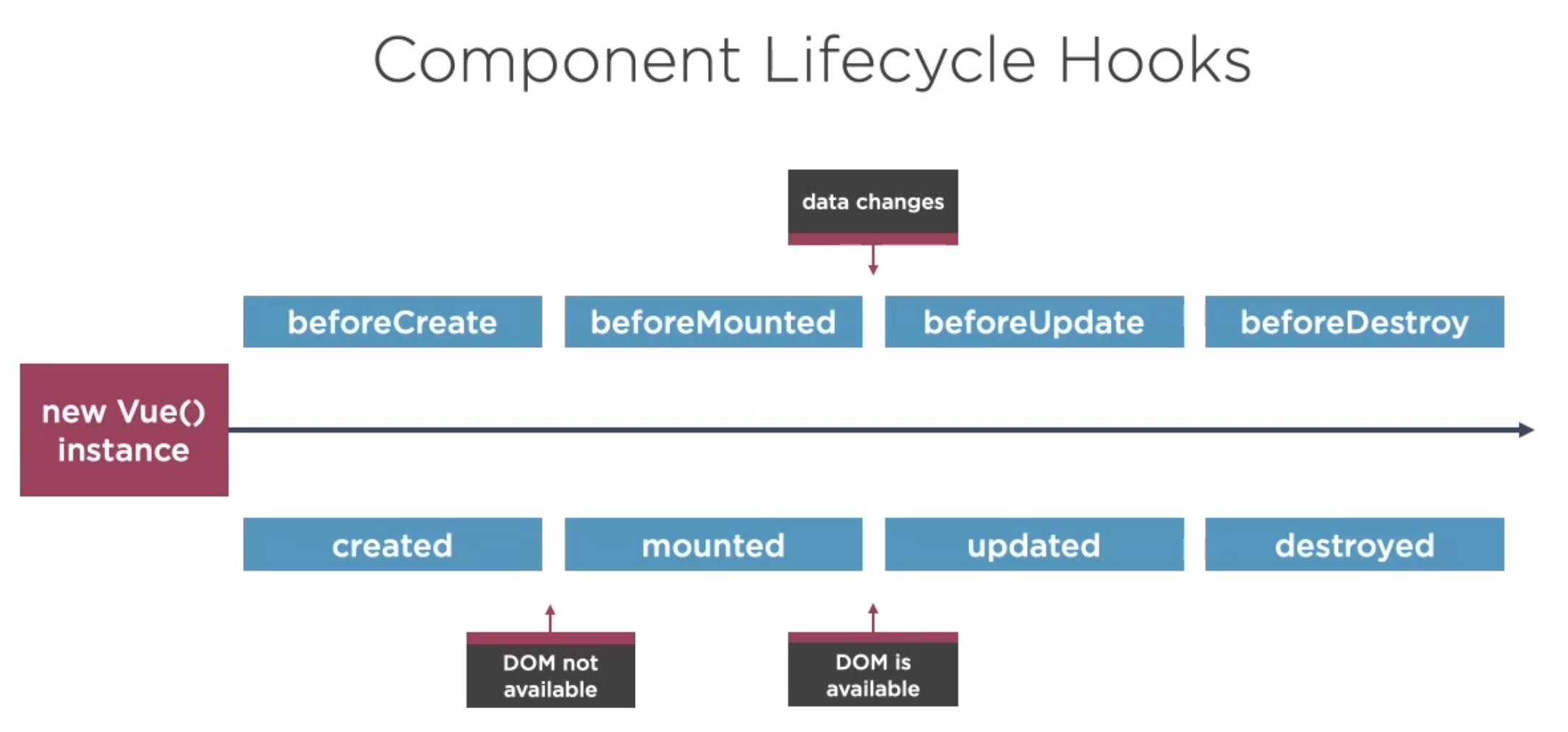
<script>
</script><script>
</script>