Dotnet api linux
Set up with VS Code
Create Project
To create a webapi using .net core 3.1 simply type
dotnet new webapi
Restore Nuget Packages
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore
Install Migration Tool
Exercise called for using Add-Migration on windows. In Linux this translates to
# Install Tool
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools.Dotnet
# Install dotnet-ef
dotnet tool install --global dotnet-ef
# Run Migration Creation
dotnet ef migrations add InitialCreate
Install SQL Server
wget -qO- https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add -
# Add to /etc/apt/source.list
# deb [arch=amd64,arm64,armhf] https://packages.microsoft.com/ubuntu/18.04/mssql-server-2019 bionic main
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y mssql-server
sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf setup
# Show working
systemctl status mssql-server --no-pager
Create user
CREATE DATABASE test;
GO
CREATE LOGIN test with PASSWORD = 'guess!';
GO
EXEC master..sp_addsrvrolemember @loginame = N'test', @rolename = N'dbcreator'
GO
Running Query
List tables in DB
select schema_name(t.schema_id) as schema_name,
t.name as table_name,
t.create_date,
t.modify_date
from sys.tables t
order by schema_name,
table_name;
sqlcmd -S localhost -U test -d CourseLibraryDB -Q list_tables.sql
Structuring and Implementing
Interacting with Resources through HTTP Methods
Below is a table which shows the methods and how they work with the Authors and Courses demo app along with suggested naming. Note the use of nouns
Content Negotiation
We also need to ensure that we configure what type of media we support. In ASP .net this can be done by setting the setupAction. This will stop the default of json being returned.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers(setupAction => {
setupAction.ReturnHttpNotAcceptable = true;
}).AddXmlDataContractSerializerFormatters();
...
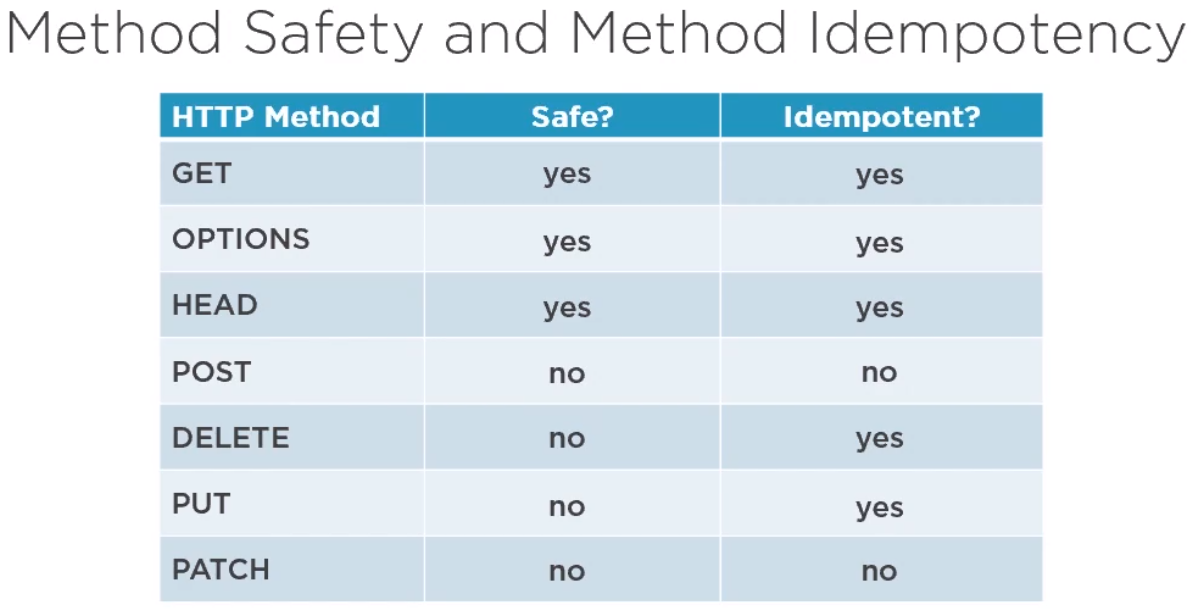
Method Safety and Method Idempotency
Method safety and idempotency help decide which method to use for which use case.
Getting Resources
Intro
When we get resources we generally expect business objects rather than entities. These are known as DTOs (Data Transfer Objects). For C# there are other options but automapper product seems to be the product of choice for ASP .NET.
Adding Automapper
To add automapper
dotnet add package AutoMapper.Extensions.Microsoft.DependencyInjection
Configure Automapper
And configure the service in the code
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services.AddAutoMapper(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.GetAssemblies());
...
Create a DTO Class
public class AuthorDto
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string MainCategory { get; set; }
}
Create a Profile Class
This class performs the mapping from the Entity to the DTO
public class AuthorsProfile : Profile
{
public AuthorsProfile()
{
CreateMap<Entities.Author, Models.AuthorDto>()
.ForMember(
dest => dest.Name,
opt => opt.MapFrom(src => $"{src.FirstName} {src.LastName}"))
.ForMember(
dest => dest.Age,
opt => opt.MapFrom(src => src.DateOfBirth.GetCurrentAge()));
}
}
}
Implement the Get of collection and instance on the controller
...
[HttpGet()]
public ActionResult<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>> GetAuthors()
{
var authorsFromRepo = _courseLibraryRepository.GetAuthors();
return Ok(_mapper.Map<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>>(authorsFromRepo));
}
[HttpGet("{authorId}")]
public IActionResult GetAuthor(Guid authorId)
{
var authorsFromRepo = _courseLibraryRepository.GetAuthor(authorId);
if (authorsFromRepo == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(_mapper.Map<AuthorDto>(authorsFromRepo));
}
Overriding Exception Errors
To control the error the consumer sees in the case of an exception, configure an exception handler in Startup.cs
...
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler(appBuilder => {
appBuilder.Run(async context => {
context.Response.StatusCode = 500;
await context.Response.WriteAsync("An unexpected fault occurred. Please try again");
});
});
}
Supporting HEAD
To support just sending the result without the body simply add HttpHead to the getters.
[HttpGet()]
[HttpHead]
public ActionResult<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>> GetAuthors()
{
var authorsFromRepo = _courseLibraryRepository.GetAuthors();
return Ok(_mapper.Map<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>>(authorsFromRepo));
}
Filtering And Searching
Bindings
To get the arguments for filtering and search ASP .NET uses the following
- [FromQuery] - Gets values from the query string.
- [FromRoute] - Gets values from route data.
- [FromForm] - Gets values from posted form fields.
- [FromBody] - Gets values from the request body.
- [FromHeader] - Gets values from HTTP headers.
Filtering
Basically add an argument to the get method and implement it on the data repository checking for an argument and returning appropriately. Note the default [FromQuery] argument is the key to this being passed. E.g. mainCategory=Rum on the URI
# In the controller
[HttpGet()]
[HttpHead]
public ActionResult<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>> GetAuthors(string mainCategory)
{
var authorsFromRepo = _courseLibraryRepository.GetAuthors(mainCategory);
return Ok(_mapper.Map<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>>(authorsFromRepo));
}
# In the Repository
public IEnumerable<Author> GetAuthors(string mainCategory)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(mainCategory)) return _context.Authors.ToList<Author>();
return _context.Authors.Where(x => x.MainCategory == mainCategory.Trim()).ToList();
}
Searching
To implement this just add a parameter for the searching as you did for filtering and implement appropriately
public IEnumerable<Author> GetAuthors(string mainCategory, string searchQuery)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(mainCategory) && string.IsNullOrEmpty(searchQuery)) return _context.Authors.ToList<Author>();
var collection = _context.Authors as IQueryable<Author>;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(mainCategory))
{
collection = collection.Where(x => x.MainCategory == mainCategory.Trim());
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(searchQuery))
{
collection = collection.Where(
x => x.MainCategory.Contains(searchQuery.Trim()) ||
x.FirstName.Contains(searchQuery.Trim()) ||
x.LastName.Contains(searchQuery.Trim()));
}
return collection.ToList();
}
Combining Parameters
Make a class to contain these and pass them to the repository.
public class AuthorsResourceParameters
{
public string MainCategory { get; set; }
public string SearchQuery { get; set; }
}
You will need to tell the controller where to find them as it is not the default. i.e.
[HttpGet()]
[HttpHead]
public ActionResult<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>> GetAuthors([FromQuery] AuthorsResourceParameters authorsResourceParameters)
{
var authorsFromRepo = _courseLibraryRepository.GetAuthors(authorsResourceParameters);
return Ok(_mapper.Map<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>>(authorsFromRepo));
}
Creating Resources
Create a DTO for creations
public class AuthorForCreationDto
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public DateTimeOffset DateOfBirth { get; set; }
public string MainCategory { get; set; }
}
Create a profile
This converts the DTO to an entity
public class AuthorsProfile : Profile
{
CreateMap<Models.AuthorForCreationDto, API.Entities.Author>();
}
Implement Post
Add a name to your GET for your entity
[HttpGet("{authorId}", Name="GetAuthor")]
public IActionResult GetAuthor(Guid authorId)
{
...
}
Most of the code is simple except for the CreateAtRoute. This is used to add a Location header to the response. The Location header specifies the URI of the newly created item.
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult<AuthorDto> CreateAuthor(AuthorForCreationDto author)
{
var authorEntity = _mapper.Map<Author>(author);
_courseLibraryRepository.AddAuthor(authorEntity);
_courseLibraryRepository.Save();
var authorToReturn = _mapper.Map<AuthorDto>(authorEntity);
return CreatedAtRoute("GetAuthor", // the name of the route
new { authorId = authorToReturn.Id }, // the parameters of the route
authorToReturn); // the DTO to create the DTO from
}
Creating Resources For a Collection
This is the same as above with the exception of the Location header. If you are creating a collection then the location header will need to support the retrieval of the collection post creation.
Creating the Post Collection Request
This is identical to the single request but using an array.
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>> CreateAuthorCollections(IEnumerable<AuthorForCreationDto> authorCollection)
{
var authorEntities = _mapper.Map<IEnumerable<Author>>(authorCollection);
foreach (var author in authorEntities)
{
_courseLibraryRepository.AddAuthor(author);
}
_courseLibraryRepository.Save();
var authorCollectionToReturn = _mapper.Map<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>>(authorEntities);
return CreatedAtRoute("GetAuthorCollection",
new { authorId = string.Join(",", authorCollectionToReturn.Select(x => x.Id)) },
authorCollectionToReturn);
}
Creating the Get Collection Request
Everything is the same except you need a [FromRoute] and a ModelBinder. The model binder needs to create and array of composite keys so that all of the items can be retrieved.
[HttpGet("({authorIds})", Name = "GetAuthorCollection")]
public IActionResult GetAuthorCollection(
[FromRoute]
[ModelBinder(BinderType = typeof(ArrayModelBinder))] IEnumerable<Guid> authorIds)
{
if (authorIds == null)
{
return BadRequest();
}
var authorsFromRepo = _courseLibraryRepository.GetAuthors(authorIds);
if (authorIds.Count() != authorsFromRepo.Count())
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(_mapper.Map<IEnumerable<AuthorDto>>(authorsFromRepo));
}
Creating Array Model Binder
What is Model Binding
What is Model binding Controllers and Razor pages work with data that comes from HTTP requests. For example, route data may provide a record key, and posted form fields may provide values for the properties of the model. Writing code to retrieve each of these values and convert them from strings to .NET types would be tedious and error-prone. Model binding automates this process. The model binding system:
Retrieves data from various sources such as route data, form fields, and query strings. Provides the data to controllers and Razor pages in method parameters and public properties. Converts string data to .NET types. Updates properties of complex types.
My Example of Model Binding
Tried to provide explanation in the comments but basically if checks if sane and then returns an appropriate array of composite keys.
public class ArrayModelBinder : IModelBinder
{
public Task BindModelAsync(ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
// Our binder only works on enumerable types
if(!bindingContext.ModelMetadata.IsEnumerableType)
{
bindingContext.Result = ModelBindingResult.Failed();
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
// Get Inputted value from the value provided
var value = bindingContext.ValueProvider.GetValue(bindingContext.ModelName).ToString();
// If the value is null or whitespace, we return null
if(string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value))
{
bindingContext.Result = ModelBindingResult.Success(null);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
// If the model is enumerable and
// the value isn't null or whitespace
// Get the enumerable types and a converter
var elementType = bindingContext.ModelMetadata.ModelType.GetTypeInfo().GetGenericArguments()[0];
var elementTypeConvertor = TypeDescriptor.GetConverter(elementType);
// Convert each item in the value list to the enumerable type
var valuesAsStringArray = value.Split( new[] {","}, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
var values = valuesAsStringArray.Select(x=> elementTypeConvertor.ConvertFrom(x.Trim())).ToArray();
// Create an array of the same length received and the element type in the binding context
var typedValues = Array.CreateInstance(elementType, values.Length);
// Copy the string values to to the typed values
values.CopyTo(typedValues,0);
// Set the model
bindingContext.Model = typedValues;
// Return the result
bindingContext.Result = ModelBindingResult.Success(bindingContext.Model);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
