Android Layouts: Difference between revisions
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
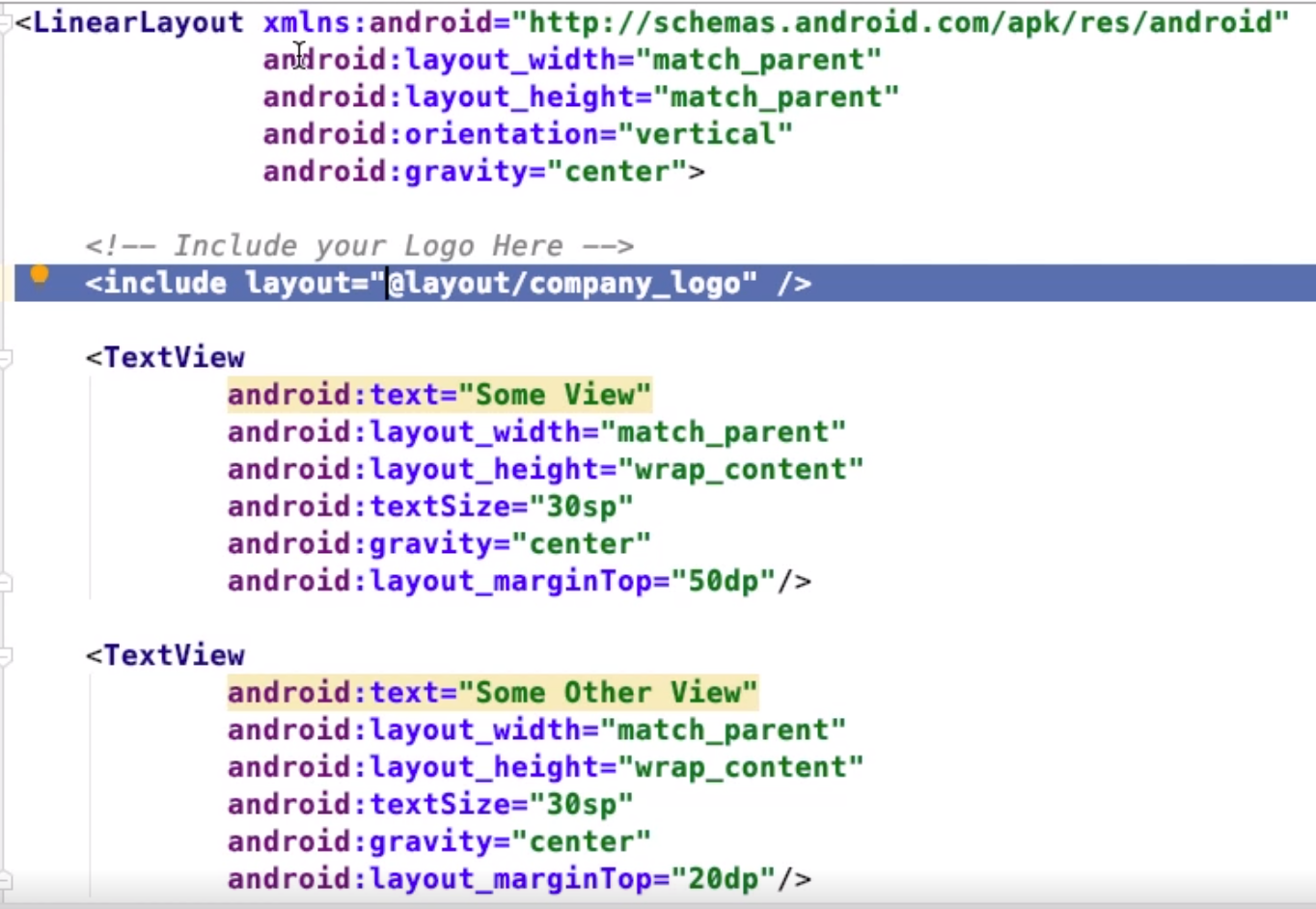
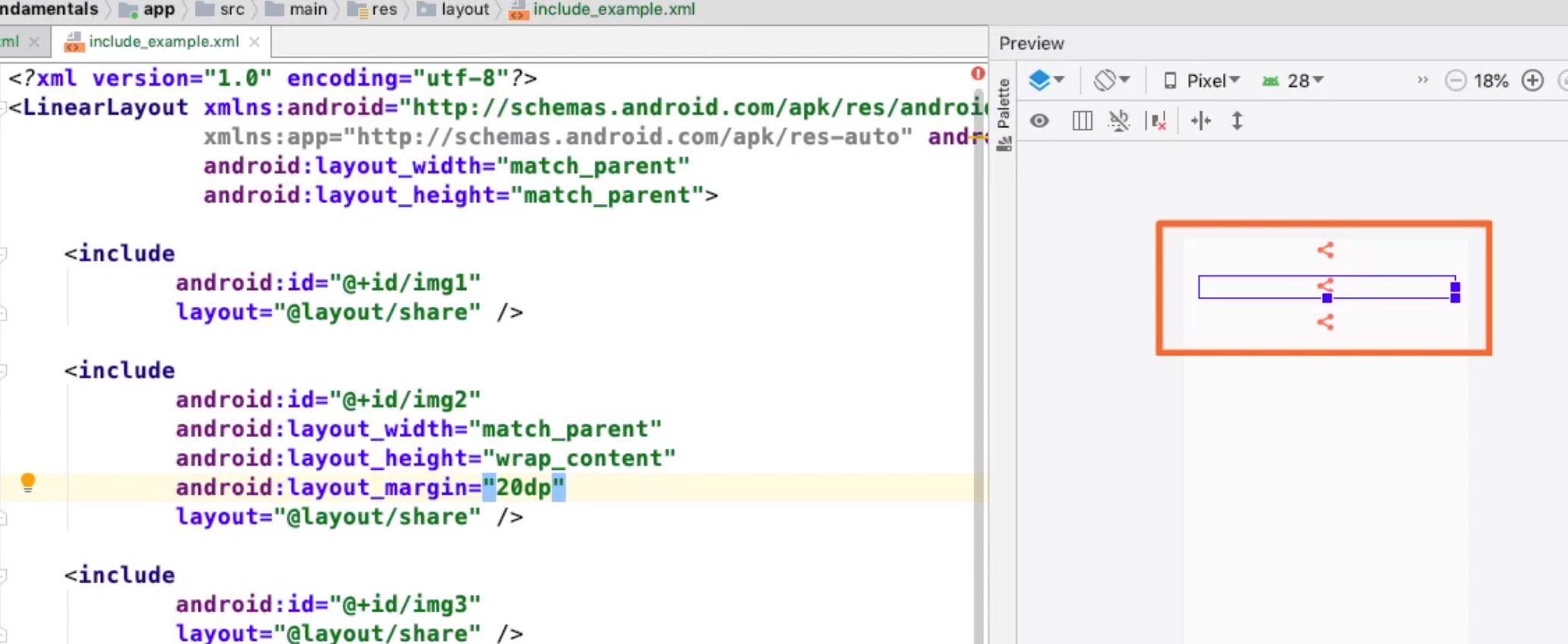
If you want to repeat layouts you can use include. This will get the layout specified in the layout attribute. Note you can override attributes but you must remember to specify the layout_width and layout_height.Note only properties with '''layout_''' can be override. | If you want to repeat layouts you can use include. This will get the layout specified in the layout attribute. Note you can override attributes but you must remember to specify the layout_width and layout_height.Note only properties with '''layout_''' can be override. | ||
[[File:Android Include.png|700px]] | [[File:Android Include.png|700px]] | ||
==Merge== | |||
Sometimes when we include files they already have a layout as a parent. We can use the Merge tag to combine the layout instead. This makes the children become child of the parent layout rather than the LinearLayout (in this case) be embedded. | |||
[[File:Android Merge.png|700px]] | |||
Revision as of 11:46, 5 January 2021
Introduction
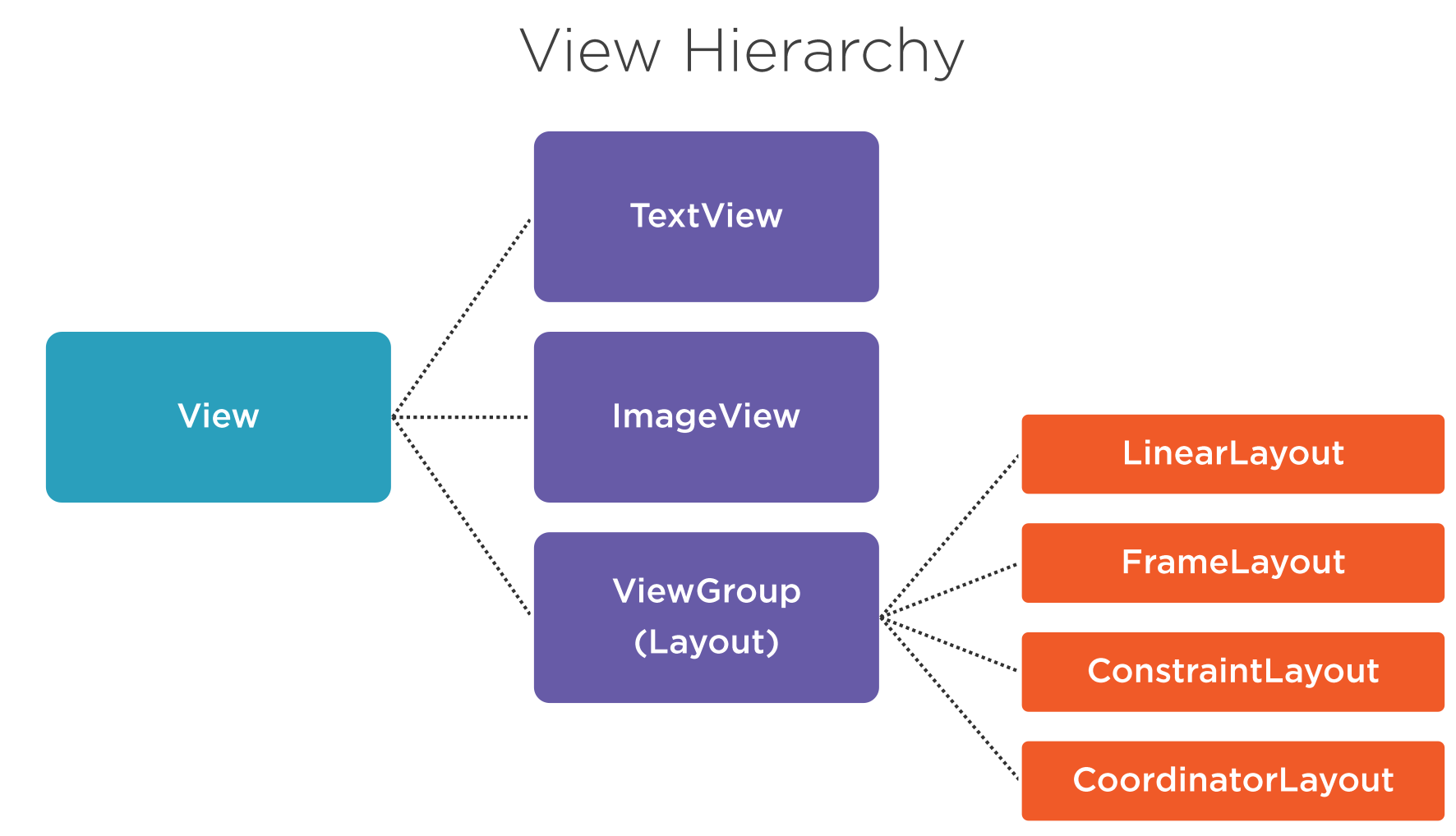
View Hierarchy can be split into types types
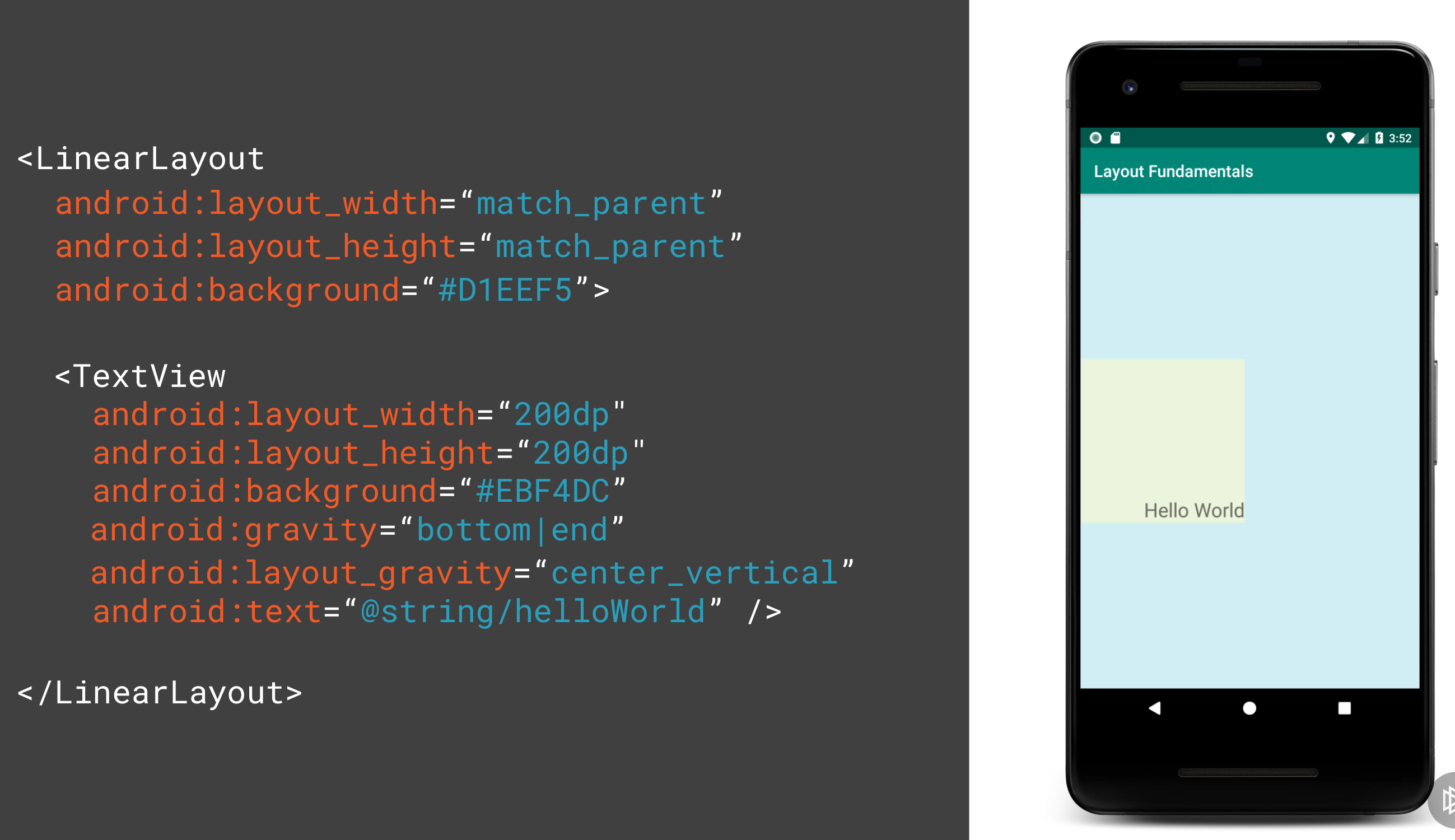
- Margin is the space around the widget
- Padding is the space within the widget
- Gravity is the position of the widget within the widget its self
- Layout Gravity is the position of the widget within its parent
Here shows the difference between layout_gravity and gravity.
Layouts
Linear Layout
These are like rows and columns in flex box. Items are wapped.
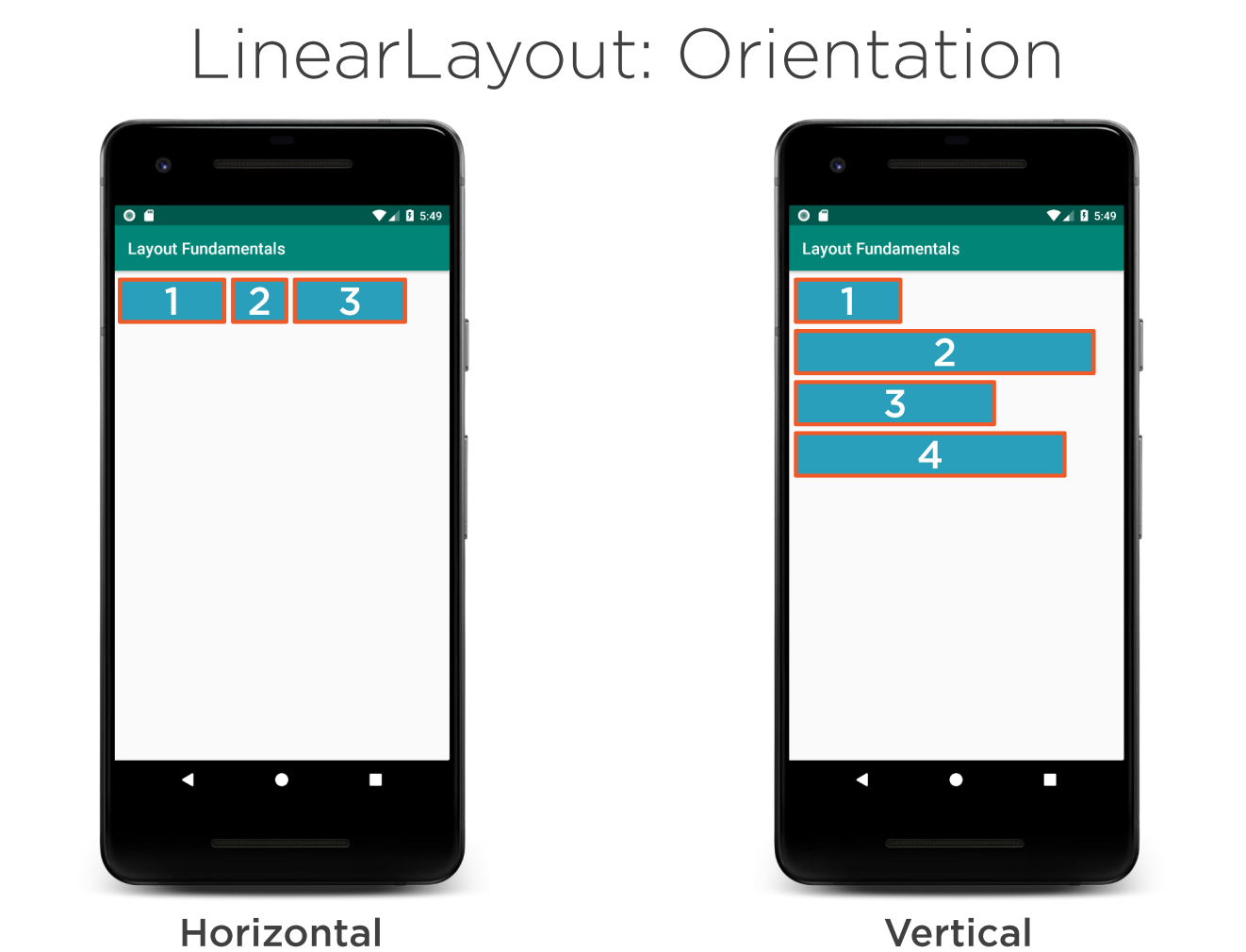
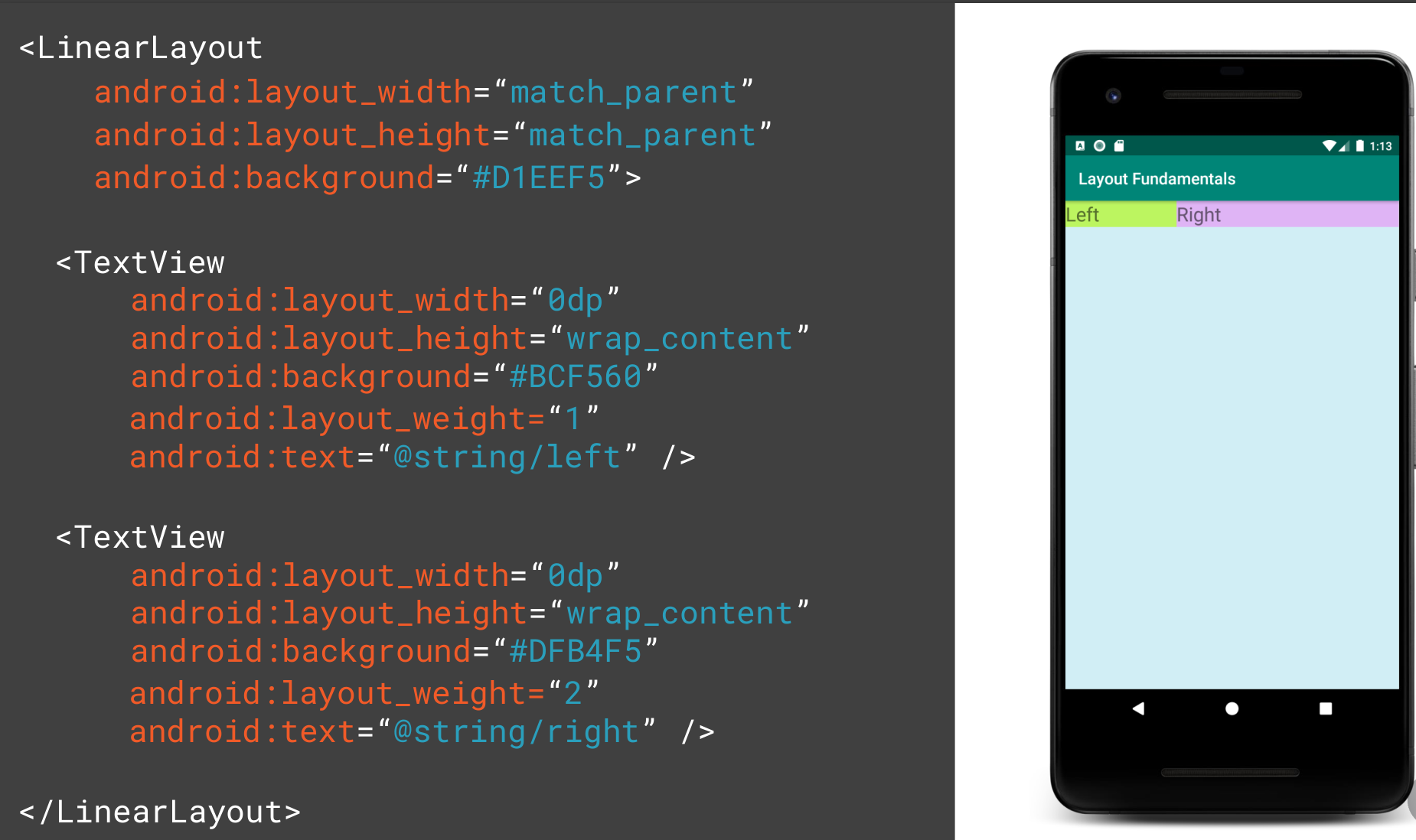
Weight
Weight determines the distribution of the widgets when no width or height is provided. Here the weight adds up to 3 and therefore the ratio is 1:2
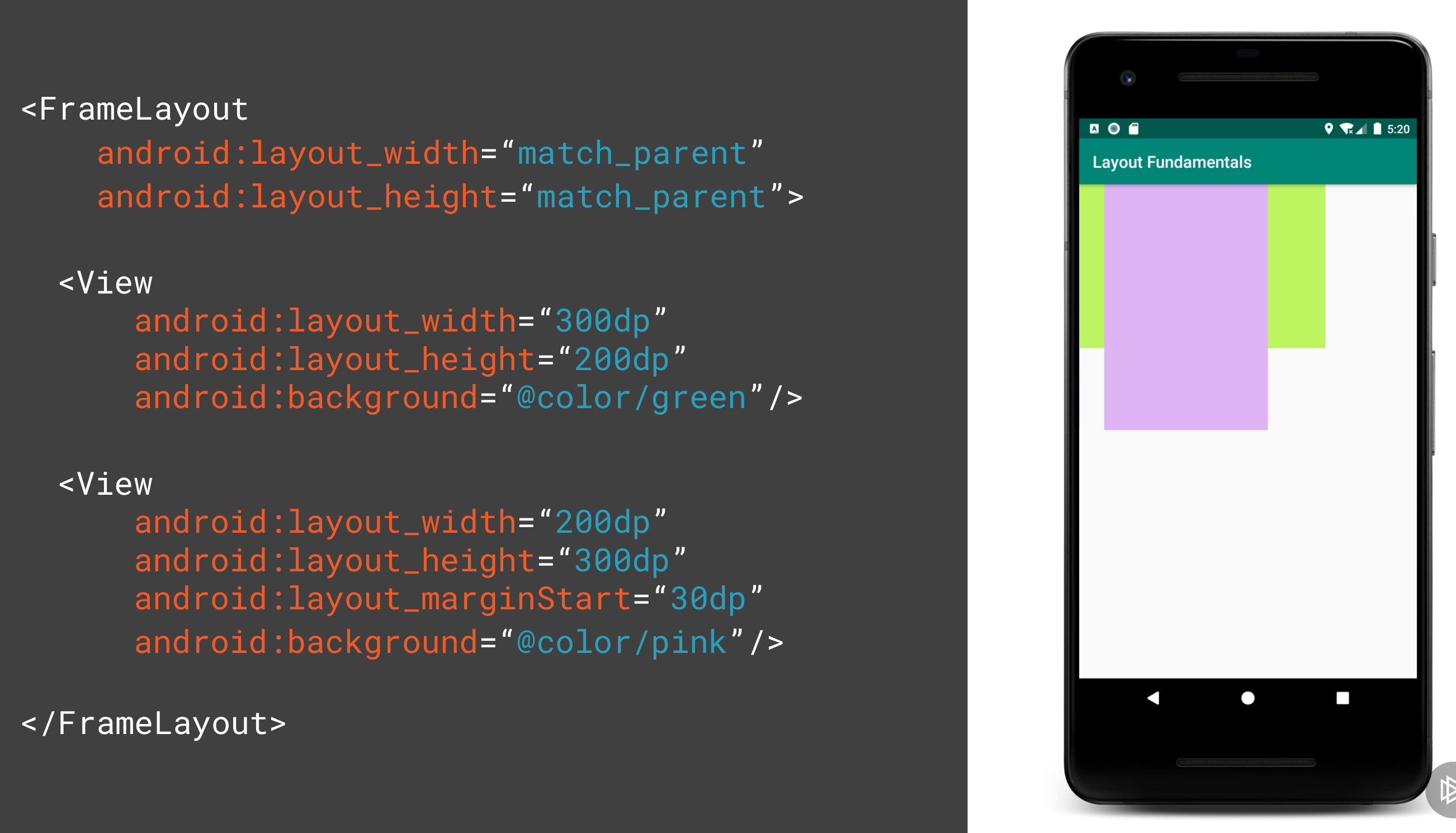
FrameLayout
This allows you to put a layout on top of another. E.g. you want of put text on top of a picture.
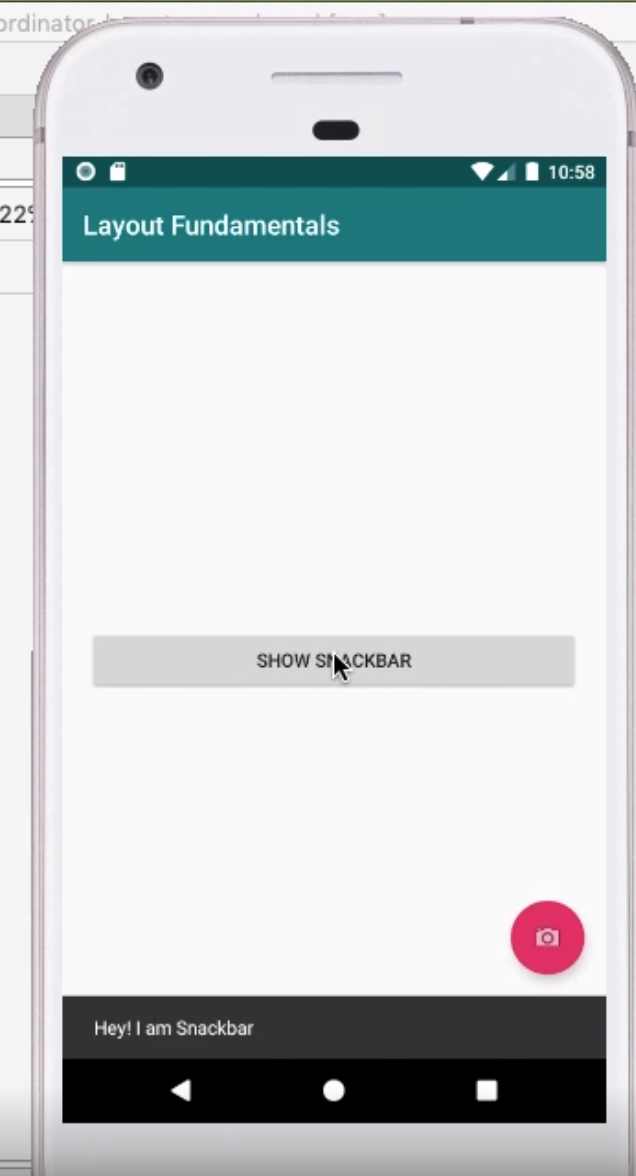
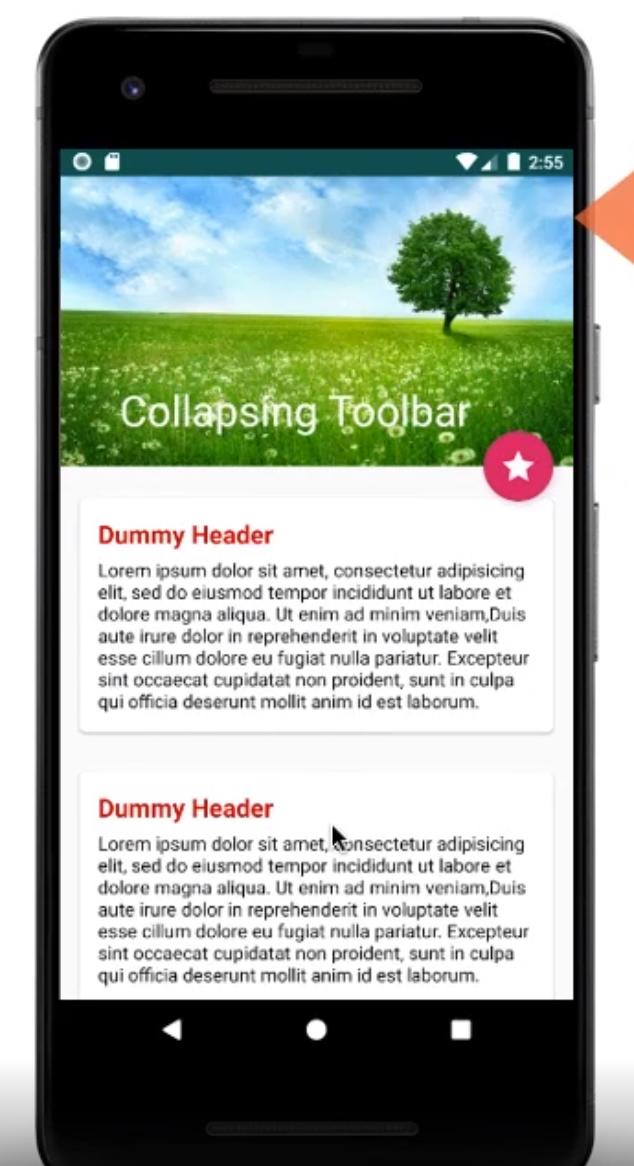
Coordinated Layout
Intended for two primary use cases
- As a top level application decor or chrome-layout
- As a container for a specific interaction
- With its child views
- Between its child views
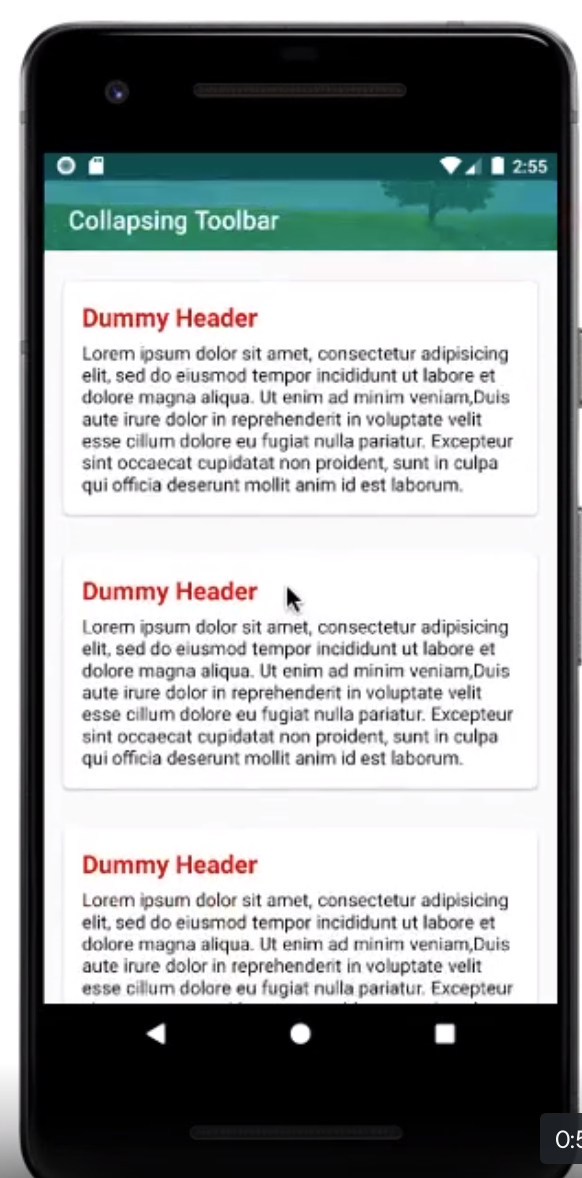
This can be used as parent which will allow other components such as the FAB button to move when the SnackBar appears. The example of collapsing toolbar was very impressive.
Constraint Layout
- Released in 2016
- Compatible with API 9+
- Can be used for animations
- Flat hierarchy so no nested layouts (better performance)
- Provides relative positioning
- You can use drag and drop in Visual Studio
When you use android studio you can convert existing layouts in the component tree by right clicking. This does not always work but is an option
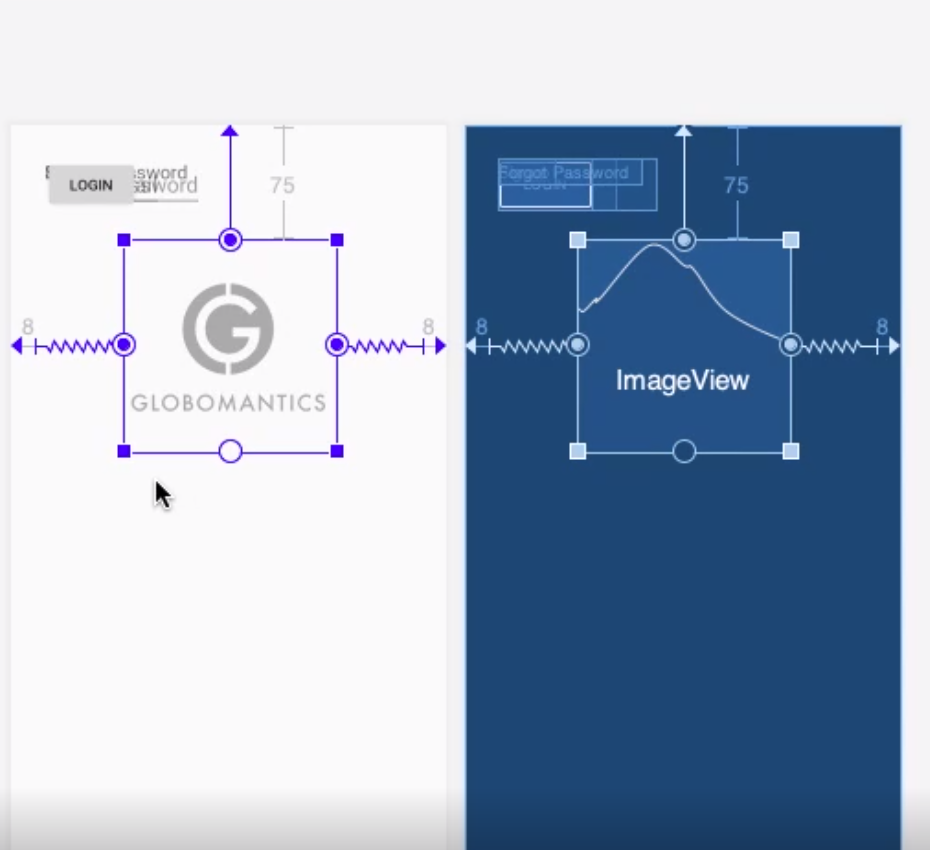
By using the Android Studio Editor you can drag the constraints to the sides so constrain the widget.
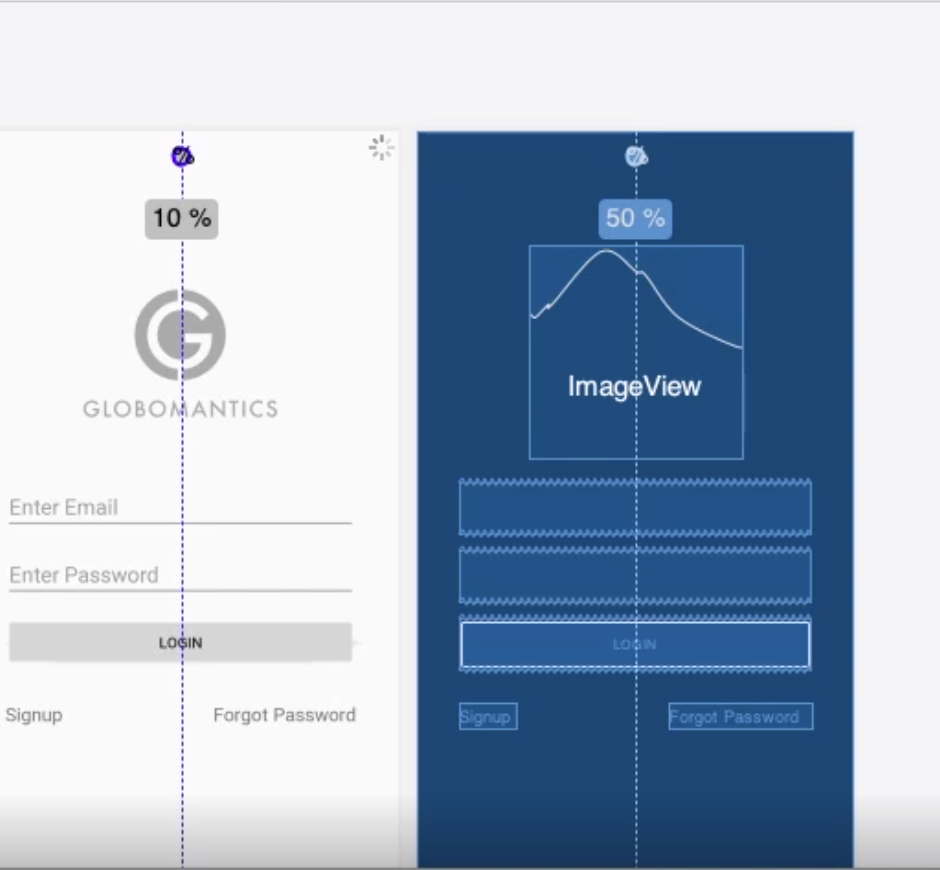
You can add Guidelines to attach to for extra constraints. e.g. for dividing a layout by 50%. These do not show to the user.
Layout Inspector
This is the equivalent of DevTools for the web. You can view the details at runtime of the layout. The main use case would be for non static (dynamic) layouts, fragments etc.
Include Files
If you want to repeat layouts you can use include. This will get the layout specified in the layout attribute. Note you can override attributes but you must remember to specify the layout_width and layout_height.Note only properties with layout_ can be override.
Merge
Sometimes when we include files they already have a layout as a parent. We can use the Merge tag to combine the layout instead. This makes the children become child of the parent layout rather than the LinearLayout (in this case) be embedded.