Distributed Applications with GO: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
*Transports | *Transports | ||
*Protocol | *Protocol | ||
=Sample App= | |||
The sample app is a hybrid app using GO | The sample app is a hybrid app using GO | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 11:05, 24 August 2021
Elements of a Distributed System
Characteristic
Four aspects might be
- Service Discovery
- Load Balancing
- Distributed tracing and logging
- Service Monitoring
Type of Distributed System
- Hub and Spoke (Satélite approach)
- Advantages Good for load balancing and logging
- Disadvantages Bad to single point of failure. Hub is complex due to responsibilities
- Peer to Peer where each communicate directly
- Advantages No Single point of failure. Highly decoupled
- Disadvantages Service discovery and Load Balancing hard
- Message Queue System where services get work from the queue
- Advantages Easy to scale, Persistence for disaster
- Disadvantages Single Point of failure (message queue), hard to configure
- Hybrid system (none of the above)
- This might will have advantages and disadvantage of both
Architectural Element
These are the aspect you may want to consider
- Languages
- Frameworks (Recommended Go-Kit and Go-Micro)
- Transports
- Protocol
Sample App
The sample app is a hybrid app using GO
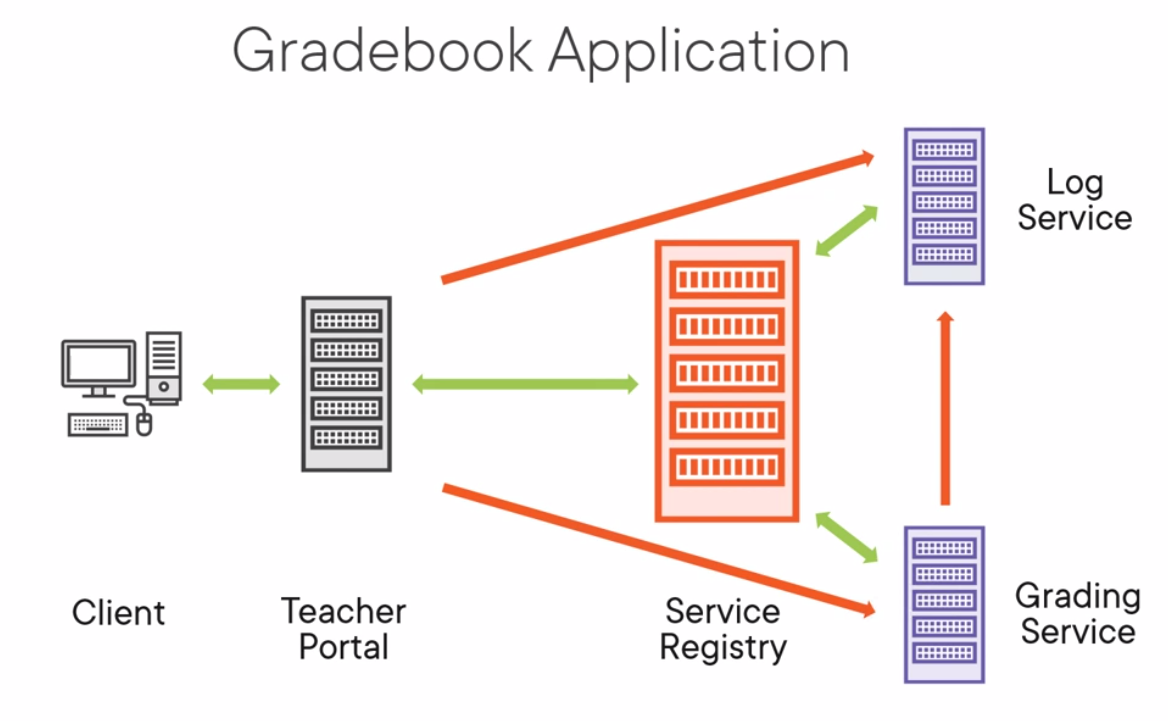
This is the components to build

Service Registration
- Create Web Service
- Create Register Service
- Register Web Service
- Deregister Web Service
Service Discovery
- Create Grading Service
- Request Required Service On Startup
- Notify when Service Starts
- Notify when Service Shutdown