Distributed Applications with GO: Difference between revisions
| Line 447: | Line 447: | ||
*Notifying services or either addition or removal of registration | *Notifying services or either addition or removal of registration | ||
*Provides the heartbeat method | *Provides the heartbeat method | ||
The heartbeat function demonstrates the use of a WaitGroup where registrations are iterated over. | The heartbeat function demonstrates the use of a WaitGroup where registrations are iterated over and they are checked. Like the mutex it is essential to have the defer to ensure it is released in the event of an error. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="go"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="go"> | ||
package registry | package registry | ||
Revision as of 05:14, 25 August 2021
Elements of a Distributed System
Characteristic
Four aspects might be
- Service Discovery
- Load Balancing
- Distributed tracing and logging
- Service Monitoring
Type of Distributed System
- Hub and Spoke (Satélite approach)
- Advantages Good for load balancing and logging
- Disadvantages Bad to single point of failure. Hub is complex due to responsibilities
- Peer to Peer where each communicate directly
- Advantages No Single point of failure. Highly decoupled
- Disadvantages Service discovery and Load Balancing hard
- Message Queue System where services get work from the queue
- Advantages Easy to scale, Persistence for disaster
- Disadvantages Single Point of failure (message queue), hard to configure
- Hybrid system (none of the above)
- This might will have advantages and disadvantage of both
Architectural Element
These are the aspect you may want to consider
- Languages
- Frameworks (Recommended Go-Kit and Go-Micro)
- Transports
- Protocol
Sample App
The sample app is a hybrid app using GO
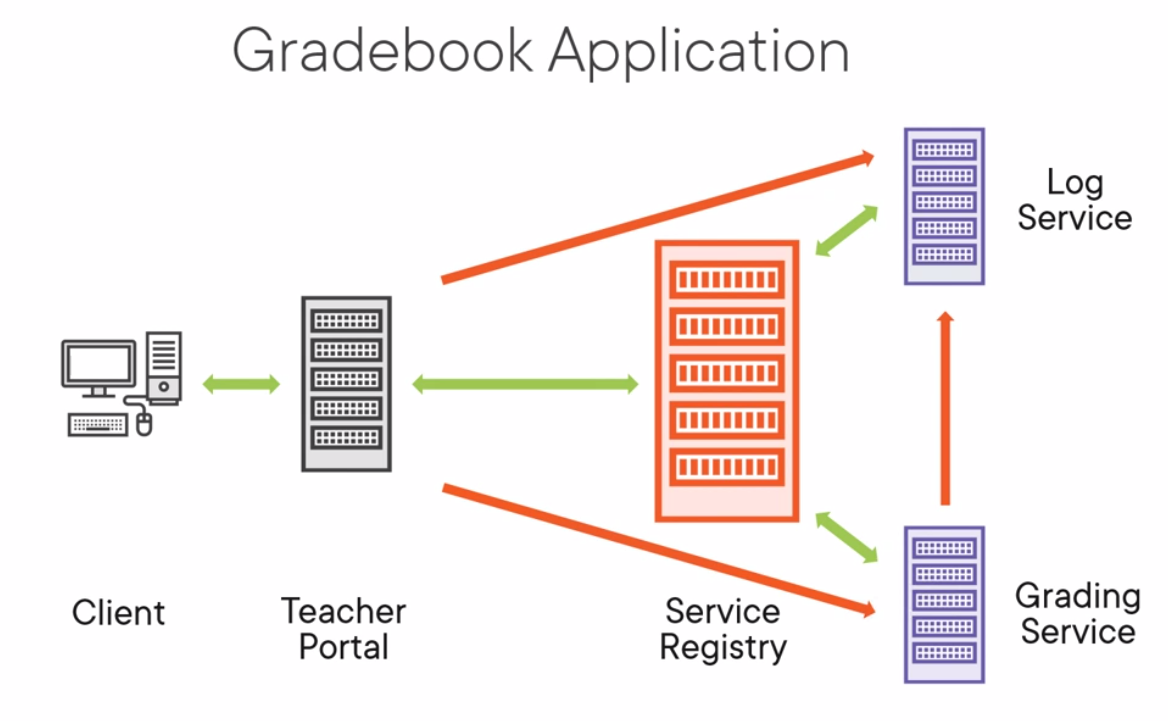
This is the components to build

Introduction
I do not usually go through large portions of code but I thought it might be useful to look at the sample code and comment on the topic and the relationship with GO as a language.
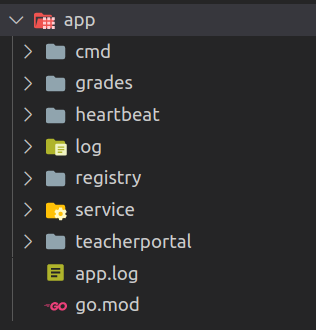
Project Structure
The project structure was basically a root folder with a cmd directory holding the main.go code for each binary. From there there is one folder for each component.
Log Service
Client
- SetClientLogger - Sets the attribute for the standard log package
- Write - Writes data to server
package log
import (
"app/registry"
"bytes"
"fmt"
stlog "log"
"net/http"
)
func SetClientLogger(serviceURL string, clientService registry.ServiceName) {
stlog.SetPrefix(fmt.Sprintf("[%v] - ", clientService))
stlog.SetFlags(0)
stlog.SetOutput(&clientLogger{url: serviceURL})
}
type clientLogger struct {
url string
}
func (cl clientLogger) Write(data []byte) (int, error) {
b := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte(data))
res, err := http.Post(cl.url+"/log", "text/plain", b)
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
if res.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("Failed to send log message. Service responded with %v - %v", res.StatusCode, res.Status)
}
return len(data), nil
}
Server (Endpoints)
This creates an instance of a custom log type, a handler and a function to write to the file.
- Run - Creates a custom log file using the standard log package
- Write - Writes data to the stream
- RegisterHandlers - Registers the "/log", reads the data and writes the message
package log
import (
"io/ioutil"
stlog "log"
"net/http"
"os"
)
var log *stlog.Logger
type fileLog string
func (fl fileLog) Write(data []byte) (int, error) {
f, err := os.OpenFile(string(fl), os.O_CREATE|os.O_WRONLY|os.O_APPEND, 0600)
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
defer f.Close()
return f.Write(data)
}
func Run(destination string) {
log = stlog.New(fileLog(destination), "", stlog.LstdFlags)
}
func RegisterHandlers() {
http.HandleFunc("/log", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
msg, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
if err != nil || len(msg) == 0 {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
write(string(msg))
})
}
func write(message string) {
log.Printf("%v\n", message)
}
Grades Service
This service has three aspects
- Mock data
- Grade Business Logic
- EndPoints
Mock Data
There is nothing special about this data but handy to remind yourself how to do this in GO
package grades
func init() {
students = []Student{
Student{
ID: 1,
FirstName: "Averill",
LastName: "Simen",
Grades: []Grade{
Grade{
Title: "Quiz 1",
Type: GradeQuiz,
Score: 85,
},
Grade{
Title: "Week 1 Homework",
Type: GradeHomework,
Score: 94,
},
Grade{
Title: "Quiz 2",
Type: GradeQuiz,
Score: 88,
},
},
},
Student{
ID: 2,
FirstName: "Marge",
LastName: "Garrard",
Grades: []Grade{
Grade{
Title: "Quiz 1",
Type: GradeQuiz,
Score: 100,
},
Grade{
Title: "Week 1 Homework",
Type: GradeHomework,
Score: 100,
},
Grade{
Title: "Quiz 2",
Type: GradeQuiz,
Score: 88,
},
},
},
Student{
ID: 3,
FirstName: "Sydnie",
LastName: "Barber",
Grades: []Grade{
Grade{
Title: "Quiz 1",
Type: GradeQuiz,
Score: 77,
},
Grade{
Title: "Week 1 Homework",
Type: GradeHomework,
Score: 0,
},
Grade{
Title: "Quiz 2",
Type: GradeQuiz,
Score: 65,
},
},
},
Student{
ID: 4,
FirstName: "Louie",
LastName: "Easton",
Grades: []Grade{
Grade{
Title: "Quiz 1",
Type: GradeQuiz,
Score: 88,
},
Grade{
Title: "Week 1 Homework",
Type: GradeHomework,
Score: 93,
},
Grade{
Title: "Quiz 2",
Type: GradeQuiz,
Score: 84,
},
},
},
Student{
ID: 5,
FirstName: "Kylee",
LastName: "Attwood",
Grades: []Grade{
Grade{
Title: "Quiz 1",
Type: GradeQuiz,
Score: 95,
},
Grade{
Title: "Week 1 Homework",
Type: GradeHomework,
Score: 100,
},
Grade{
Title: "Quiz 2",
Type: GradeQuiz,
Score: 97,
},
},
},
}
}
Grade Business Logic
This is just business logic and useful for examples in GO.
package grades
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
)
type Student struct {
ID int
FirstName string
LastName string
Grades []Grade
}
func (s Student) Average() float32 {
var result float32
for _, grade := range s.Grades {
result += grade.Score
}
return result / float32(len(s.Grades))
}
type Students []Student
var (
students Students
studentsMutex sync.Mutex
)
func (s Students) GetByID(id int) (*Student, error) {
for i := range s {
if s[i].ID == id {
return &s[i], nil
}
}
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Student with ID '%v' not found", id)
}
type GradeType string
const (
GradeTest = GradeType("Test")
GradeHomework = GradeType("Homework")
GradeQuiz = GradeType("Quiz")
)
type Grade struct {
Title string
Type GradeType
Score float32
}
Server (EndPoints)
This has some interest parts
- toJSON which takes and interface and encodes whatever is provider.
- Uses split of the r.URL.Path to determine which was called
- Uses mutex to ensure thread safety
package grades
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
func RegisterHandlers() {
handler := new(studentsHandler)
http.Handle("/students", handler)
http.Handle("/students/", handler)
}
type studentsHandler struct{}
func (sh studentsHandler) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
pathSegments := strings.Split(r.URL.Path, "/")
switch len(pathSegments) {
case 2: // /students
sh.getAll(w, r)
case 3: // /students/{:id}
id, err := strconv.Atoi(pathSegments[2])
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
return
}
sh.getOne(w, r, id)
case 4: // /students/{:id}/grades
id, err := strconv.Atoi(pathSegments[2])
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
return
}
if strings.ToLower(pathSegments[3]) != "grades" {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
return
}
sh.addGrade(w, r, id)
default:
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
}
}
func (sh studentsHandler) getAll(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
studentsMutex.Lock()
defer studentsMutex.Unlock()
data, err := sh.toJSON(students)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
log.Println(err)
return
}
w.Header().Add("content-type", "application/json")
w.Write(data)
}
func (sh studentsHandler) getOne(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, id int) {
studentsMutex.Lock()
defer studentsMutex.Unlock()
student, err := students.GetByID(id)
if err != nil {
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
log.Println(err)
return
}
}
data, err := sh.toJSON(student)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
log.Println(fmt.Errorf("Failed to serialize students: %q", err))
return
}
w.Header().Add("content-type", "application/json")
w.Write(data)
}
func (studentsHandler) toJSON(obj interface{}) ([]byte, error) {
var b bytes.Buffer
enc := json.NewEncoder(&b)
err := enc.Encode(obj)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to serialize students: %q", err)
}
return b.Bytes(), nil
}
func (sh studentsHandler) addGrade(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, id int) {
studentsMutex.Lock()
defer studentsMutex.Unlock()
student, err := students.GetByID(id)
if err != nil {
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
log.Println(err)
return
}
}
var g Grade
dec := json.NewDecoder(r.Body)
err = dec.Decode(&g)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusBadRequest)
log.Println(err)
return
}
student.Grades = append(student.Grades, g)
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusCreated)
data, err := sh.toJSON(g)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
}
w.Header().Add("content-type", "application/json")
w.Write(data)
}
Registry
Server (Endpoints)
This is responsible for
- Adding and Removing registrations
- Notifying services or either addition or removal of registration
- Provides the heartbeat method
The heartbeat function demonstrates the use of a WaitGroup where registrations are iterated over and they are checked. Like the mutex it is essential to have the defer to ensure it is released in the event of an error.
package registry
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"sync"
"time"
)
const ServerPort = ":3000"
const ServicesURL = "http://localhost" + ServerPort + "/services"
type registry struct {
registrations []Registration
mutex *sync.RWMutex
}
func (r *registry) add(reg Registration) error {
r.mutex.Lock()
r.registrations = append(r.registrations, reg)
r.mutex.Unlock()
err := r.sendRequiredServices(reg)
r.notify(patch{
Added: []patchEntry{
patchEntry{Name: reg.ServiceName, URL: reg.ServiceURL},
},
})
return err
}
func (r *registry) remove(url string) error {
for i := range r.registrations {
if r.registrations[i].ServiceURL == url {
r.notify(patch{
Removed: []patchEntry{
patchEntry{Name: r.registrations[i].ServiceName, URL: r.registrations[i].ServiceURL},
},
})
r.mutex.Lock()
r.registrations = append(r.registrations[:i], r.registrations[i+1:]...)
r.mutex.Unlock()
return nil
}
}
return fmt.Errorf("Service at URL %v not found", url)
}
func (r registry) notify(p patch) {
r.mutex.RLock()
defer r.mutex.RUnlock()
for _, reg := range r.registrations {
go func(reg Registration) {
for _, reqService := range reg.RequiredServices {
p := patch{Added: []patchEntry{}, Removed: []patchEntry{}}
sendUpdate := false
for _, added := range p.Added {
if added.Name == reqService {
p.Added = append(p.Added, added)
sendUpdate = true
}
}
for _, removed := range p.Removed {
if removed.Name == reqService {
p.Removed = append(p.Removed, removed)
sendUpdate = true
}
}
if sendUpdate {
err := r.sendPatch(p, reg.ServiceUpdateURL)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return
}
}
}
}(reg)
}
}
func (r registry) sendPatch(p patch, url string) error {
d, err := json.Marshal(p)
if err != nil {
return err
}
_, err = http.Post(url, "application/json", bytes.NewBuffer(d))
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
func (r registry) sendRequiredServices(reg Registration) error {
r.mutex.RLock()
defer r.mutex.RUnlock()
var p patch
for _, serviceReg := range r.registrations {
for _, reqService := range reg.RequiredServices {
if serviceReg.ServiceName == reqService {
p.Added = append(p.Added, patchEntry{
Name: serviceReg.ServiceName,
URL: serviceReg.ServiceURL,
})
}
}
}
err := r.sendPatch(p, reg.ServiceUpdateURL)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
func (r *registry) heartbeat(freq time.Duration) {
for {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for _, reg := range r.registrations {
wg.Add(1)
go func(reg Registration) {
defer wg.Done()
r.checkService(reg)
}(reg)
}
wg.Wait()
time.Sleep(freq)
}
}
func (r *registry) checkService(reg Registration) {
success := true
for attempts := 0; attempts < 3; attempts++ {
res, err := http.Get(reg.HeartbeatURL)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
} else if res.StatusCode == http.StatusOK {
log.Printf("Heartbeat check passed for %v", reg.ServiceName)
if !success {
r.add(reg)
}
break
}
log.Printf("Heartbeat check failed for %v", reg.ServiceName)
if success {
success = false
r.remove(reg.ServiceURL)
}
time.Sleep(3 * time.Second) // wait to try again
}
}
var reg = registry{registrations: make([]Registration, 0),
mutex: new(sync.RWMutex),
}
var once sync.Once
func SetupRegistryService() {
once.Do(func() {
go reg.heartbeat(3 * time.Second)
})
}
type RegistryService struct{}
func (s RegistryService) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
log.Println("Request received")
switch req.Method {
case http.MethodPost:
dec := json.NewDecoder(req.Body)
var r Registration
err := dec.Decode(&r)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
log.Printf("Adding service: %v with URL: %v", r.ServiceName, r.ServiceURL)
err = reg.add(r)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
case http.MethodDelete:
payload, err := ioutil.ReadAll(req.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
url := string(payload)
log.Printf("Removing service at URL: %v", url)
err = reg.remove(url)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
default:
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusMethodNotAllowed)
}
}
Service Registration
- Create Web Service
- Create Register Service
- Register Web Service
- Deregister Web Service
Service Discovery
- Create Grading Service
- Request Required Service On Startup
- Notify when Service Starts
- Notify when Service Shutdown