Android Architecture: Difference between revisions
| Line 258: | Line 258: | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
The implementation of this interface creates on change methods for each of the live data streams. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
... | |||
private final RemoteDataSource mRemoteDataSource; | |||
private final LocalDataSource mLocalDataSource; | |||
... | |||
MediatorLiveData<List<CoinModel>> mDataMerger = new MediatorLiveData<>(); | |||
MediatorLiveData<String> mErrorMerger = new MediatorLiveData<>(); | |||
private CryptoRepositoryImpl(RemoteDataSource mRemoteDataSource, LocalDataSource mLocalDataSource, CryptoMapper mapper) { | |||
this.mRemoteDataSource = mRemoteDataSource; | |||
this.mLocalDataSource = mLocalDataSource; | |||
mMapper = mapper; | |||
mDataMerger.addSource(this.mRemoteDataSource.getDataStream(), entities -> | |||
mExecutor.execute(new Runnable() { | |||
@Override | |||
public void run() { | |||
mLocalDataSource.writeData(mMapper.mapEntitiesToString(entities)); | |||
List<CoinModel> list = mMapper.mapEntityToModel(entities); | |||
mDataMerger.postValue(list); | |||
} | |||
}) | |||
); | |||
mDataMerger.addSource(this.mLocalDataSource.getDataStream(), json -> | |||
mExecutor.execute(new Runnable() { | |||
@Override | |||
public void run() { | |||
List<CryptoCoinEntity> entities = mMapper.mapJSONToEntity(json.toString()); | |||
List<CoinModel> models = mMapper.mapEntityToModel(entities); | |||
mDataMerger.postValue(models); | |||
} | |||
}) | |||
); | |||
mErrorMerger.addSource(mRemoteDataSource.getErrorStream(), errorStr -> { | |||
mErrorMerger.setValue(errorStr); | |||
Log.d(TAG, "Network error -> fetching from LocalDataSource"); | |||
mLocalDataSource.fetch(); | |||
} | |||
); | |||
mErrorMerger.addSource(mLocalDataSource.getErrorStream(), errorStr -> mErrorMerger.setValue(errorStr)); | |||
} | |||
Revision as of 04:51, 21 December 2020
Architecture
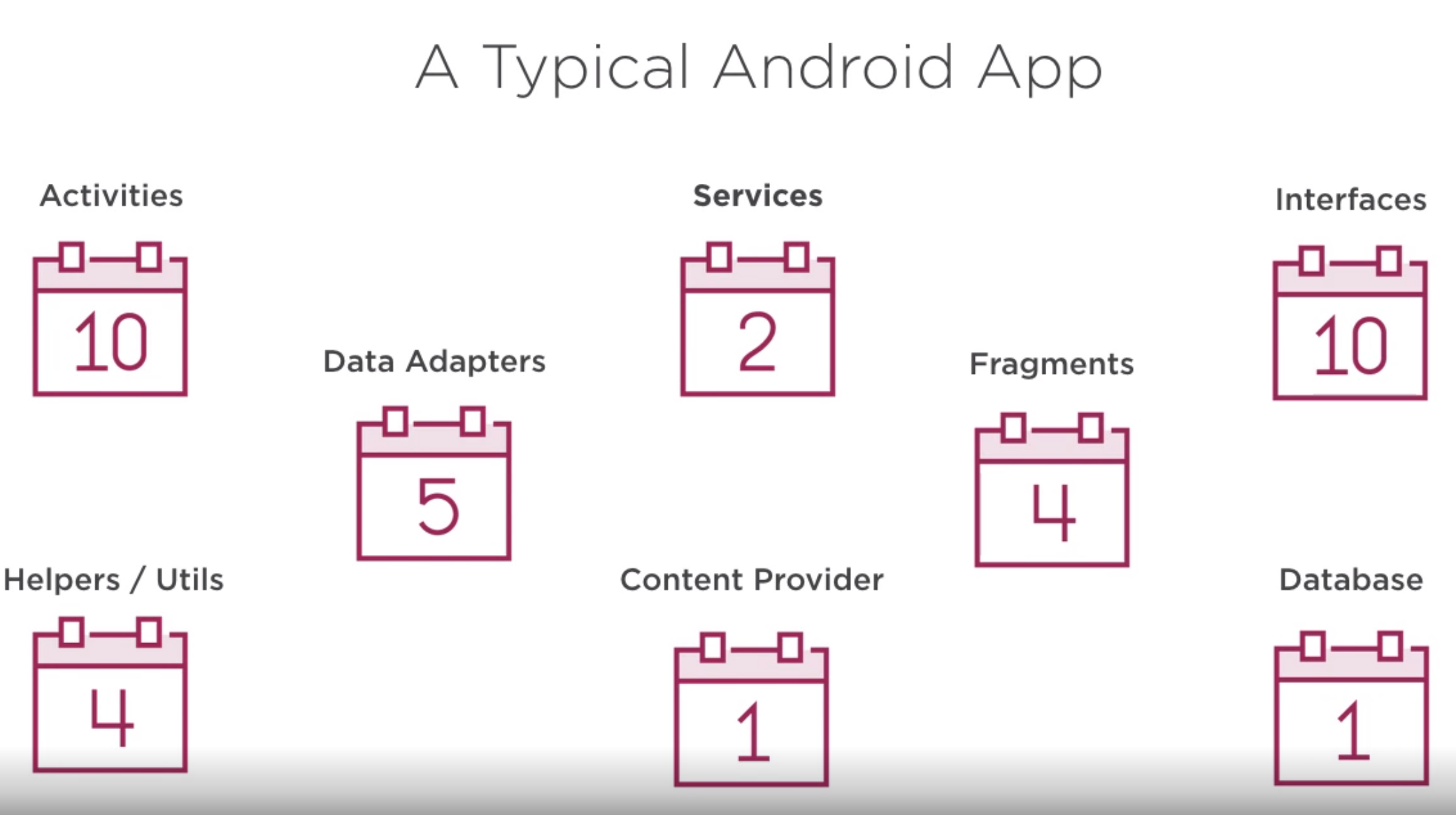
Typical Android apps look like this
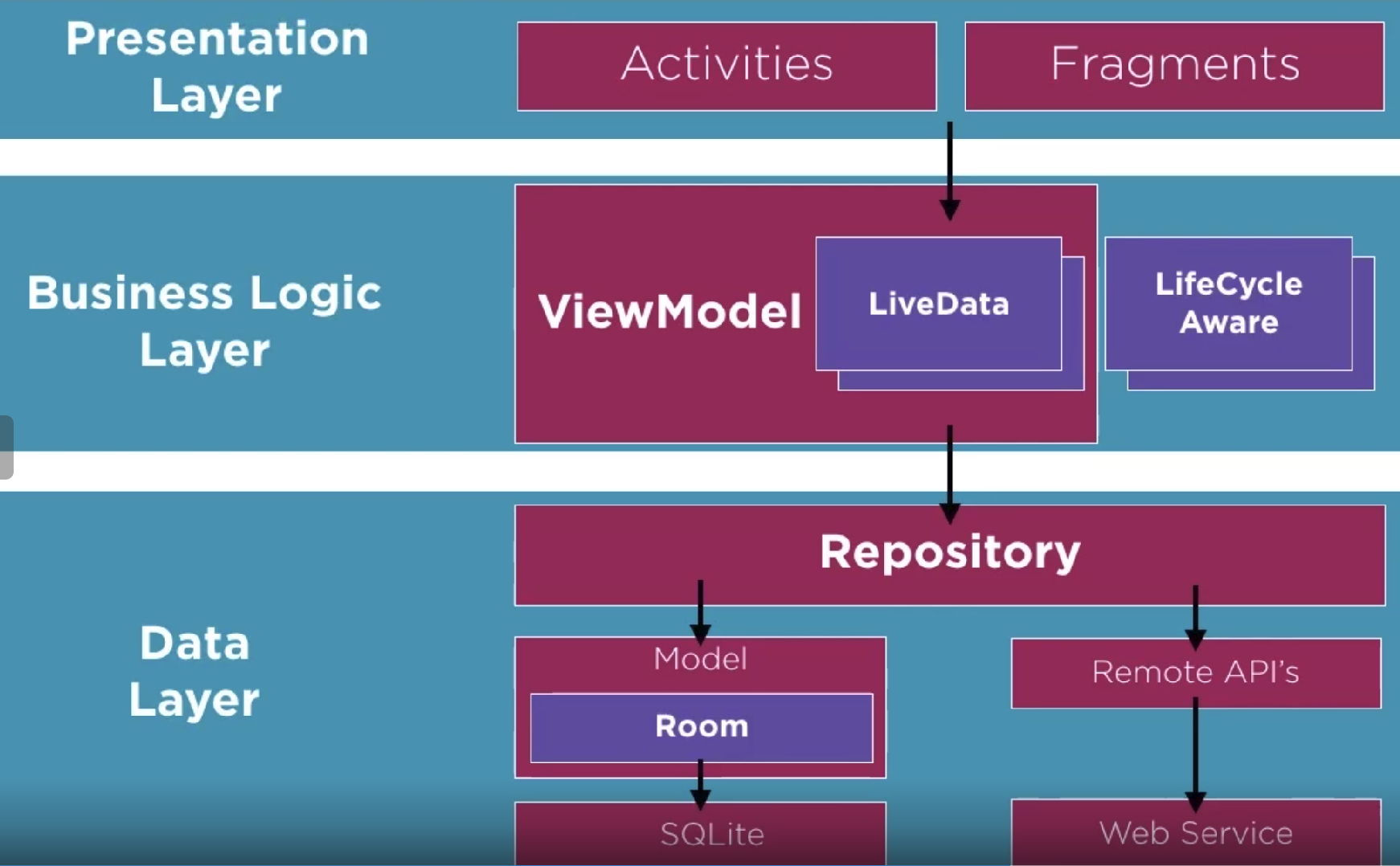
 And this
And this
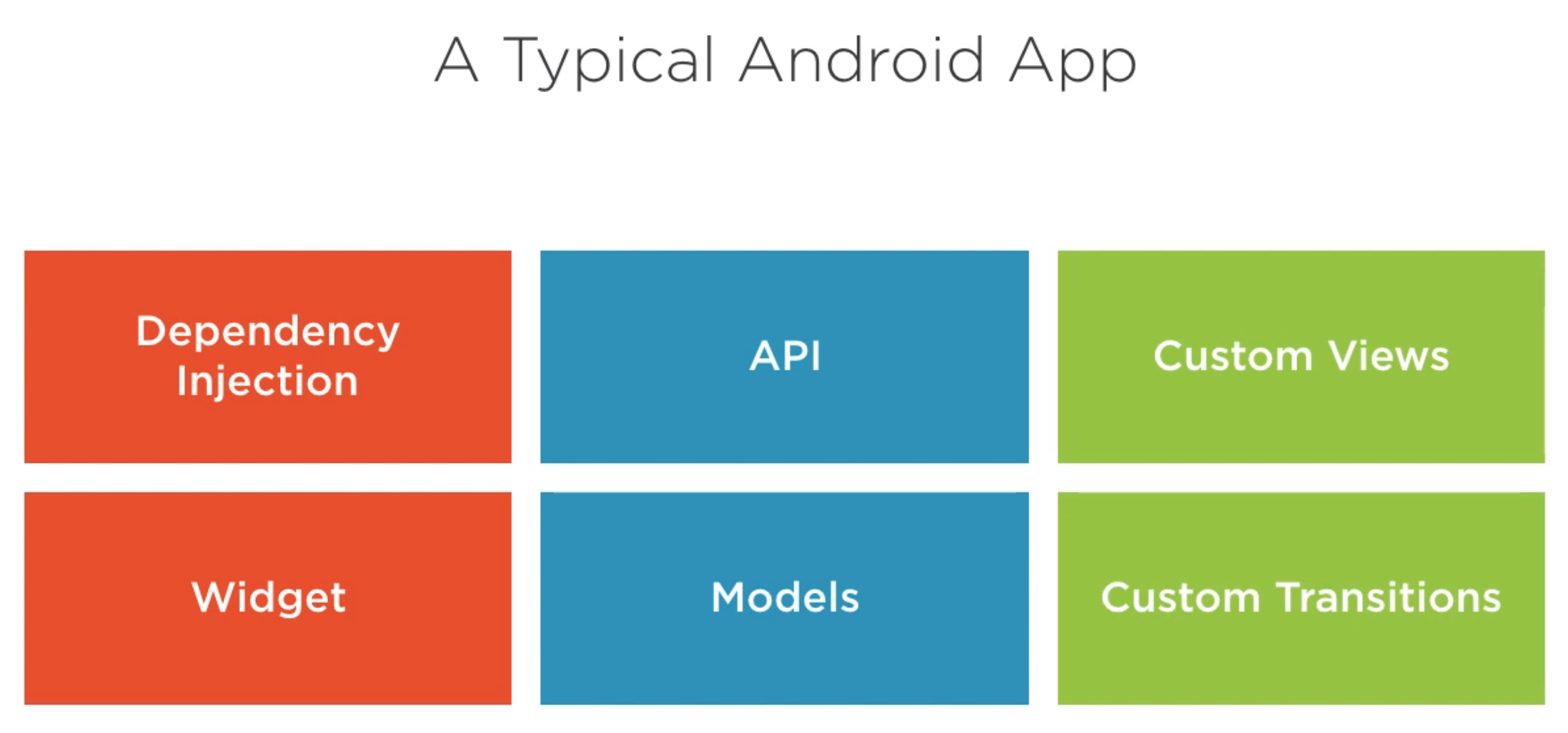 Looking at this I am building an app with the architecture of
Looking at this I am building an app with the architecture of
 The was discussion on god class which I had not heard before
The was discussion on god class which I had not heard before
- Contains a high number of components
- Components are coupled
- Lengthy class
Avoid a all costs or don't cos I like getting rid of them
Design Patterns
Just a reminder of the design patterns but with maybe a more Android flare.
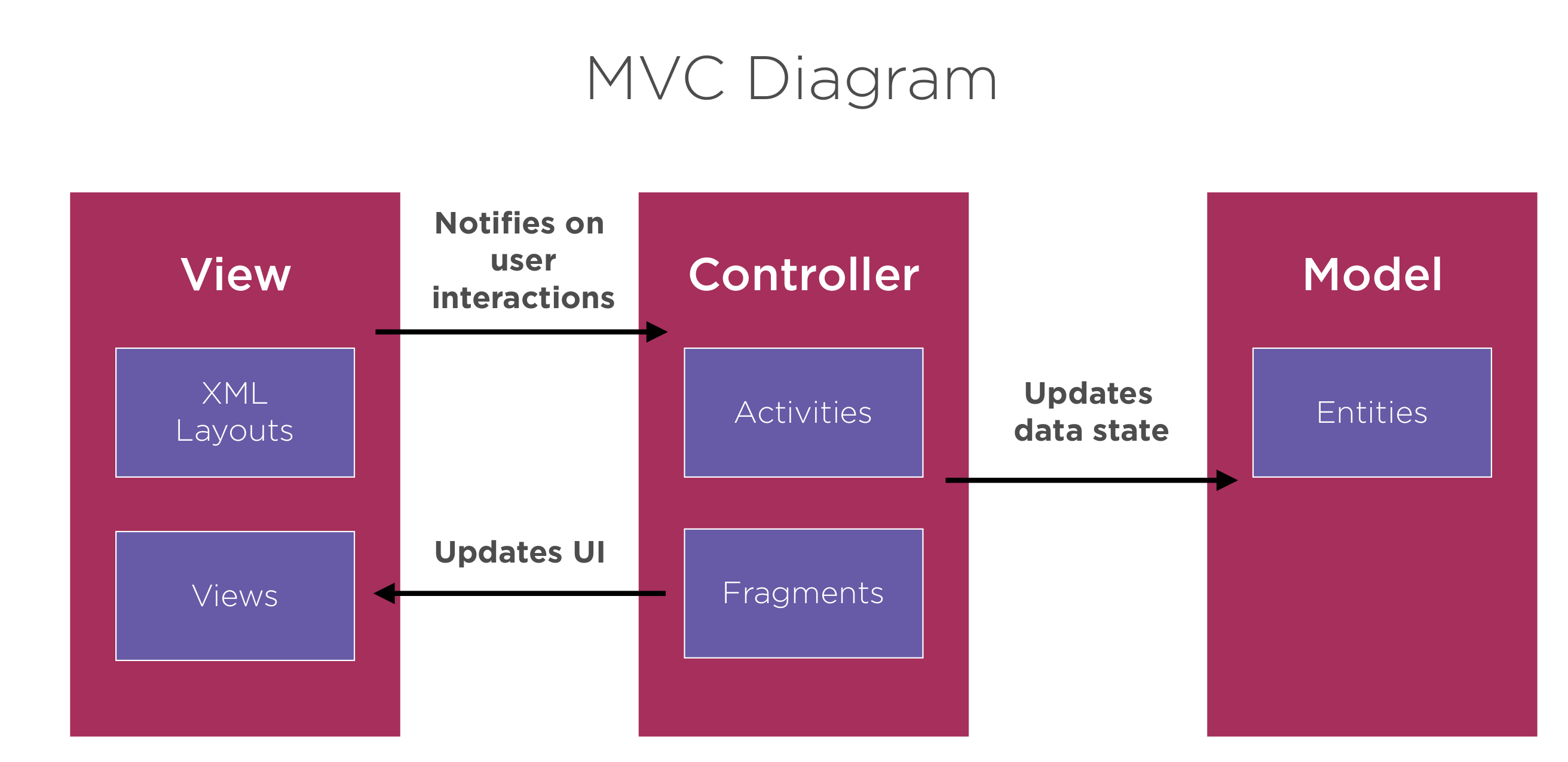
MVC
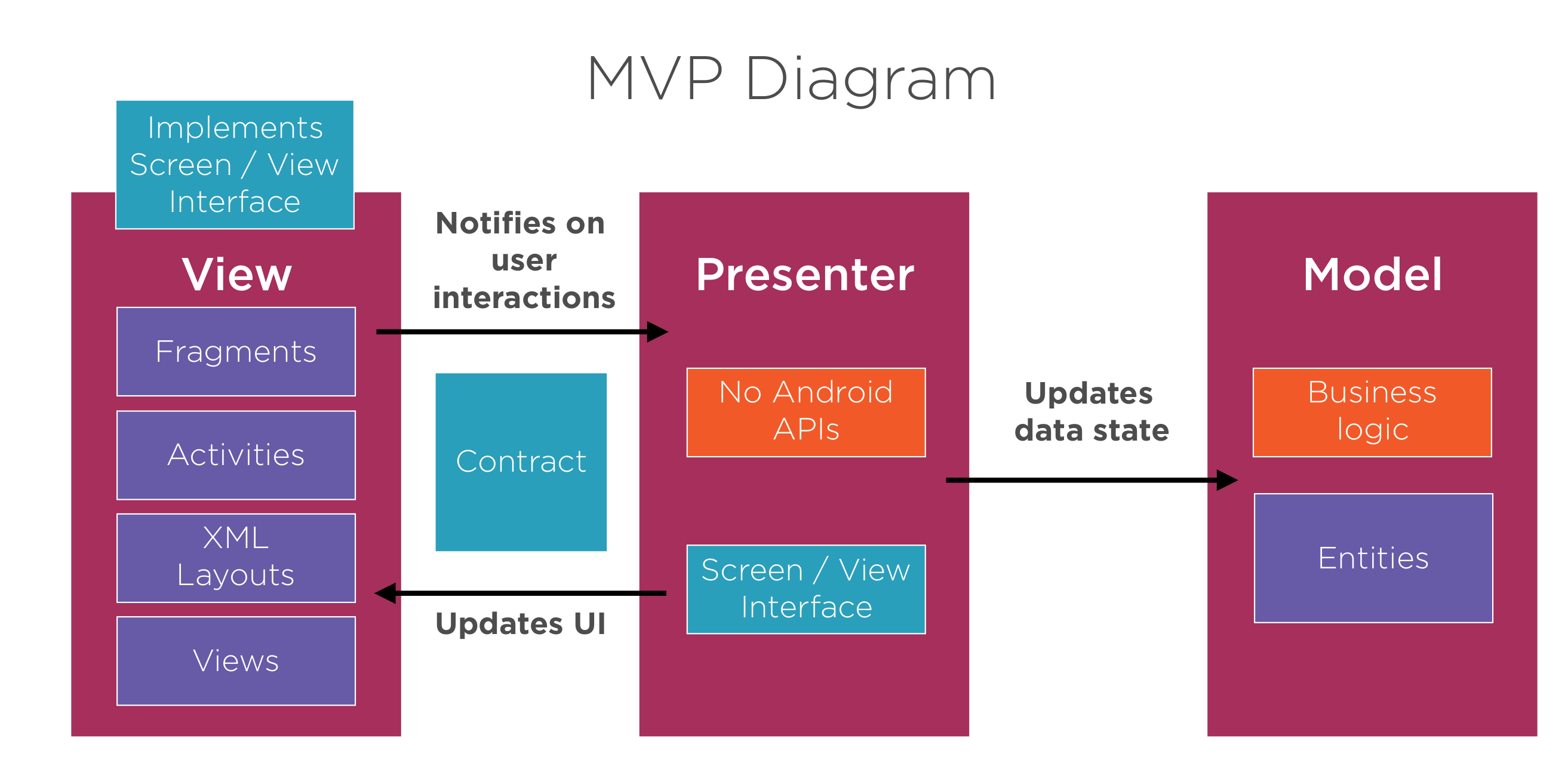
MVP
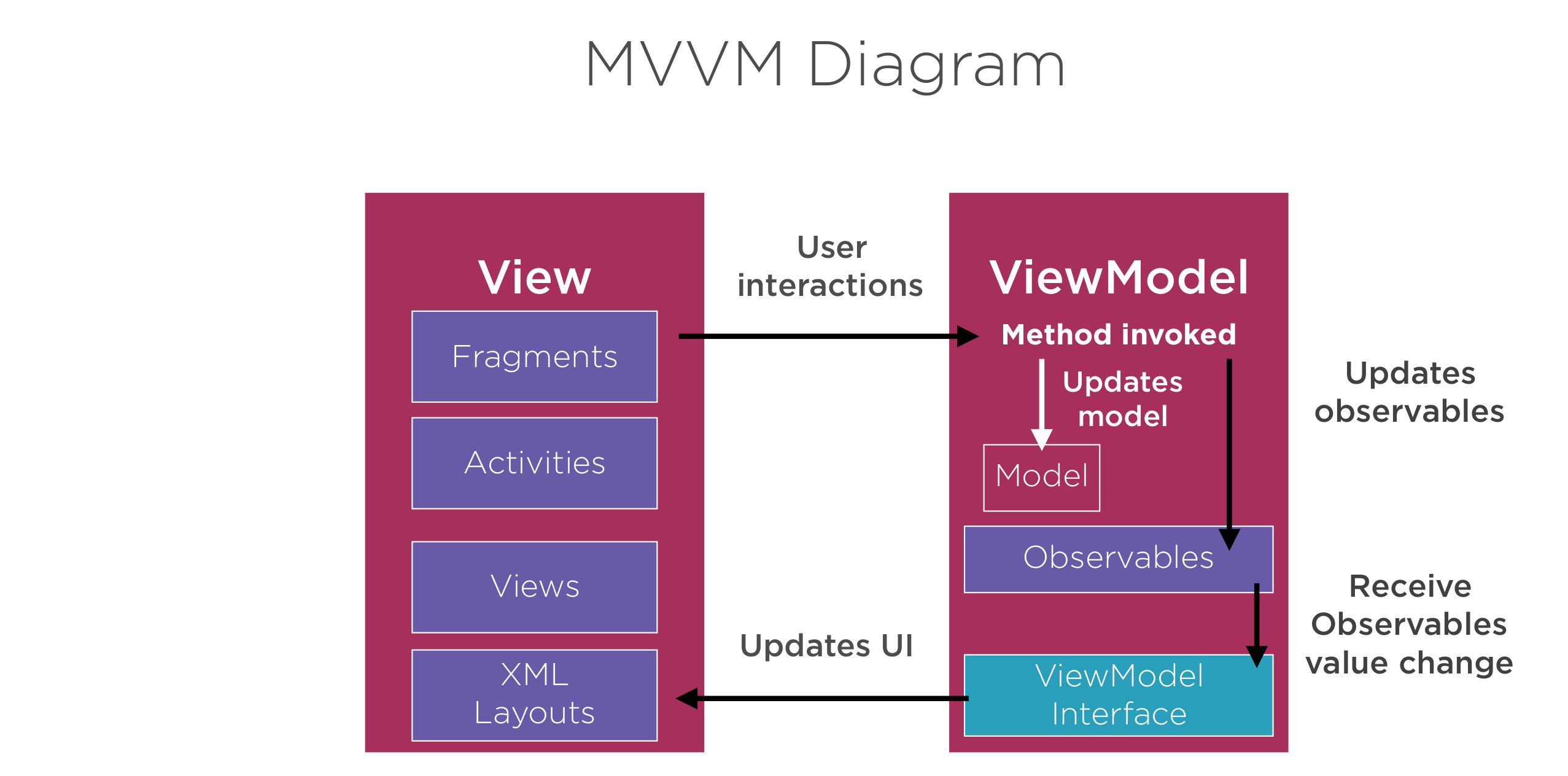
MVVM
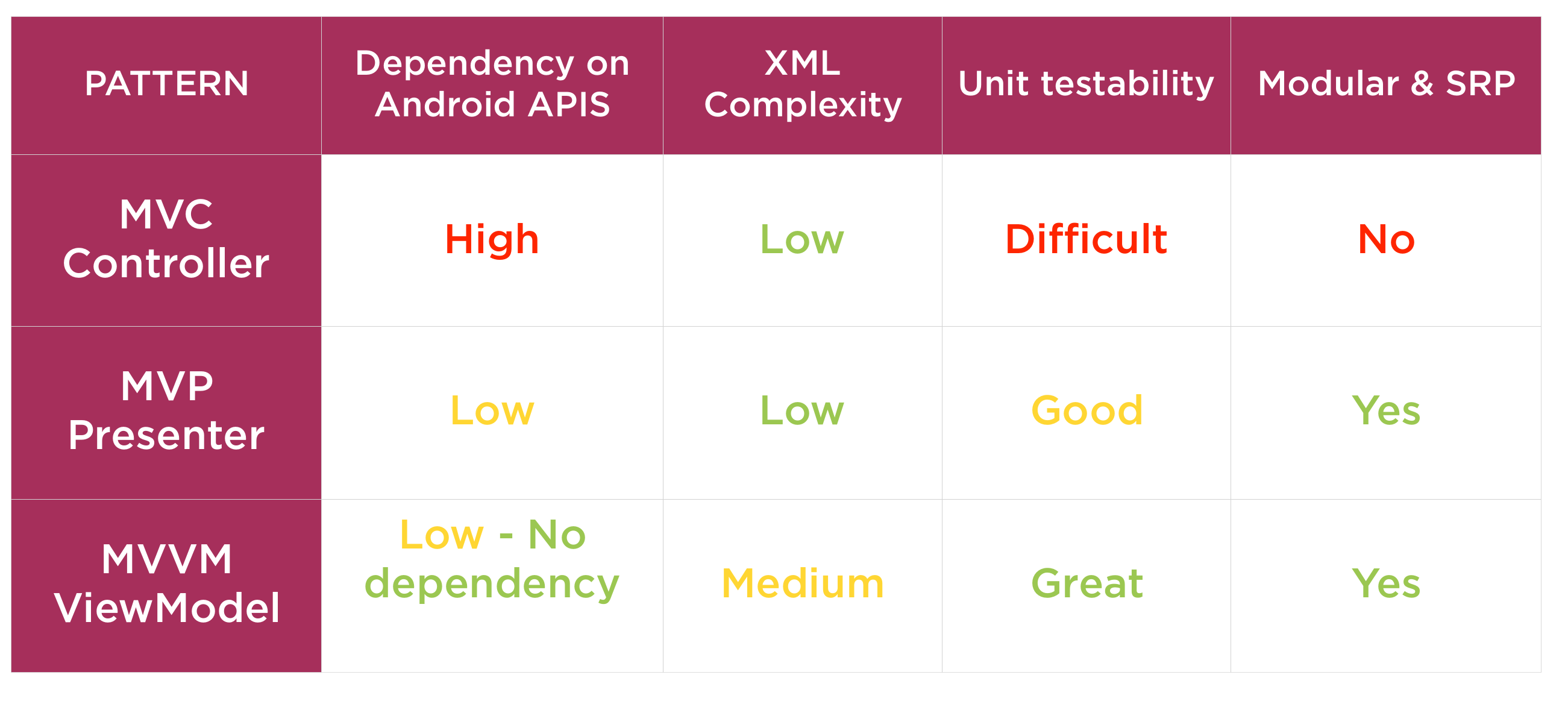
Summary
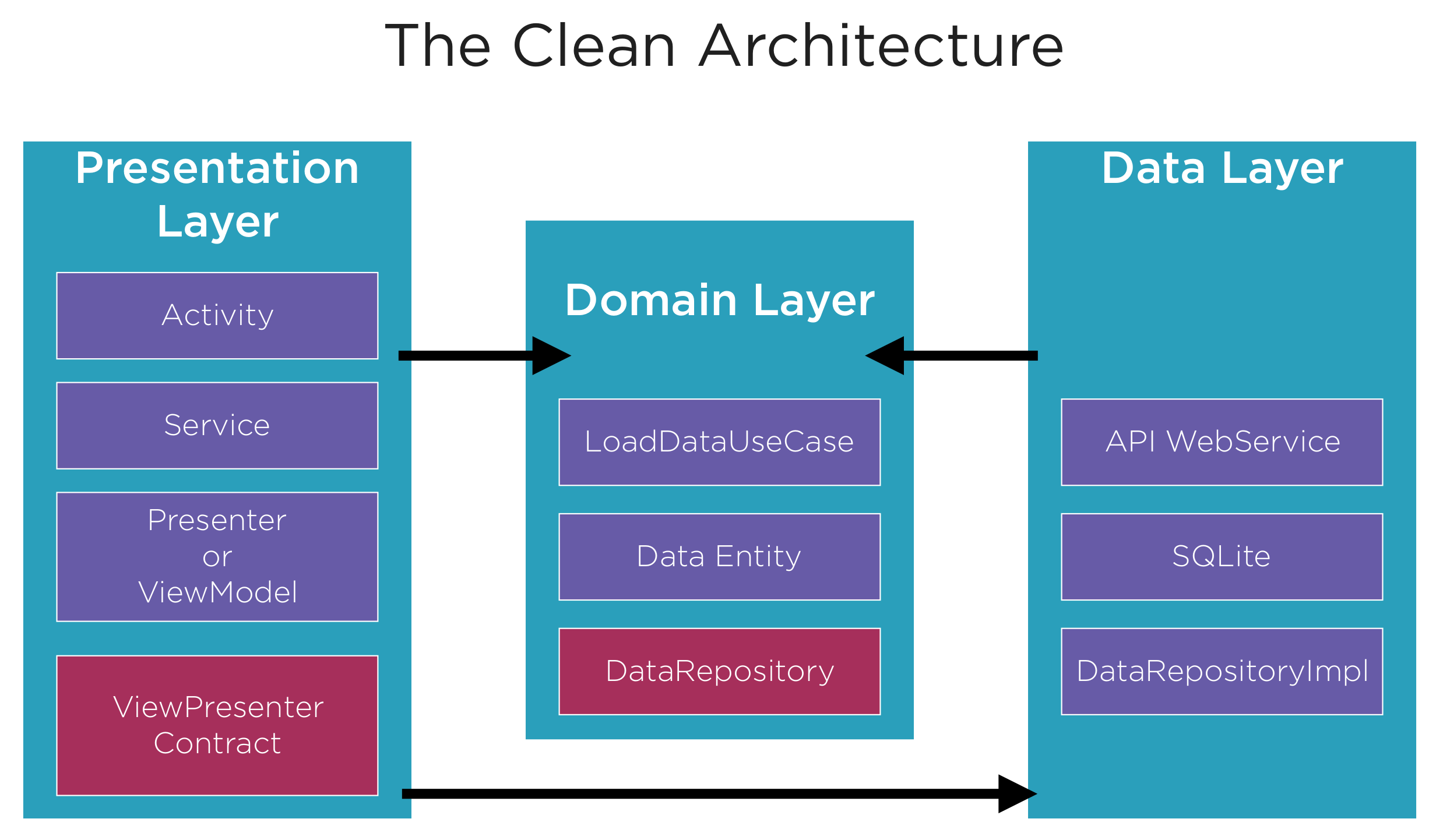
Clean Architecture
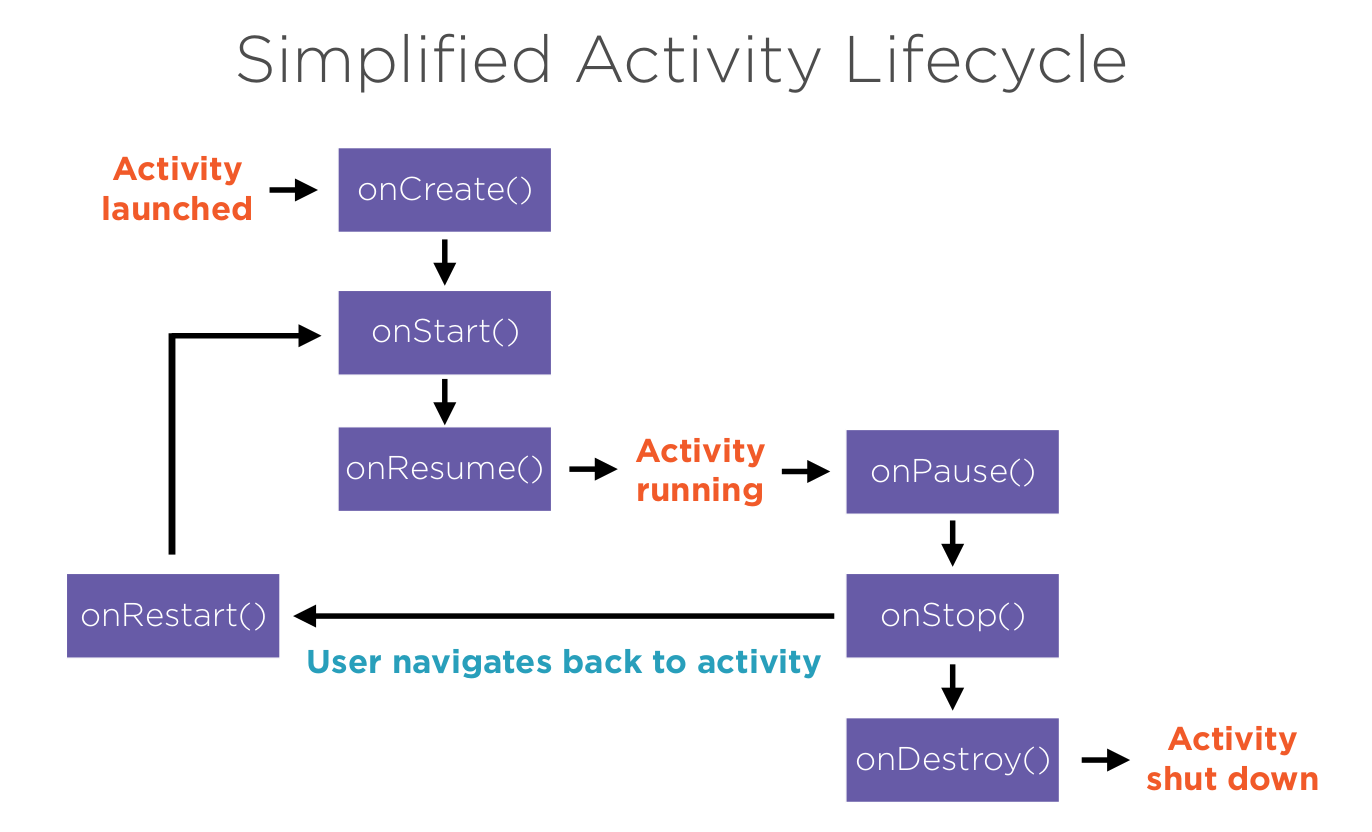
Activity Lifecycle
Here is a simplified version of the lifecycle
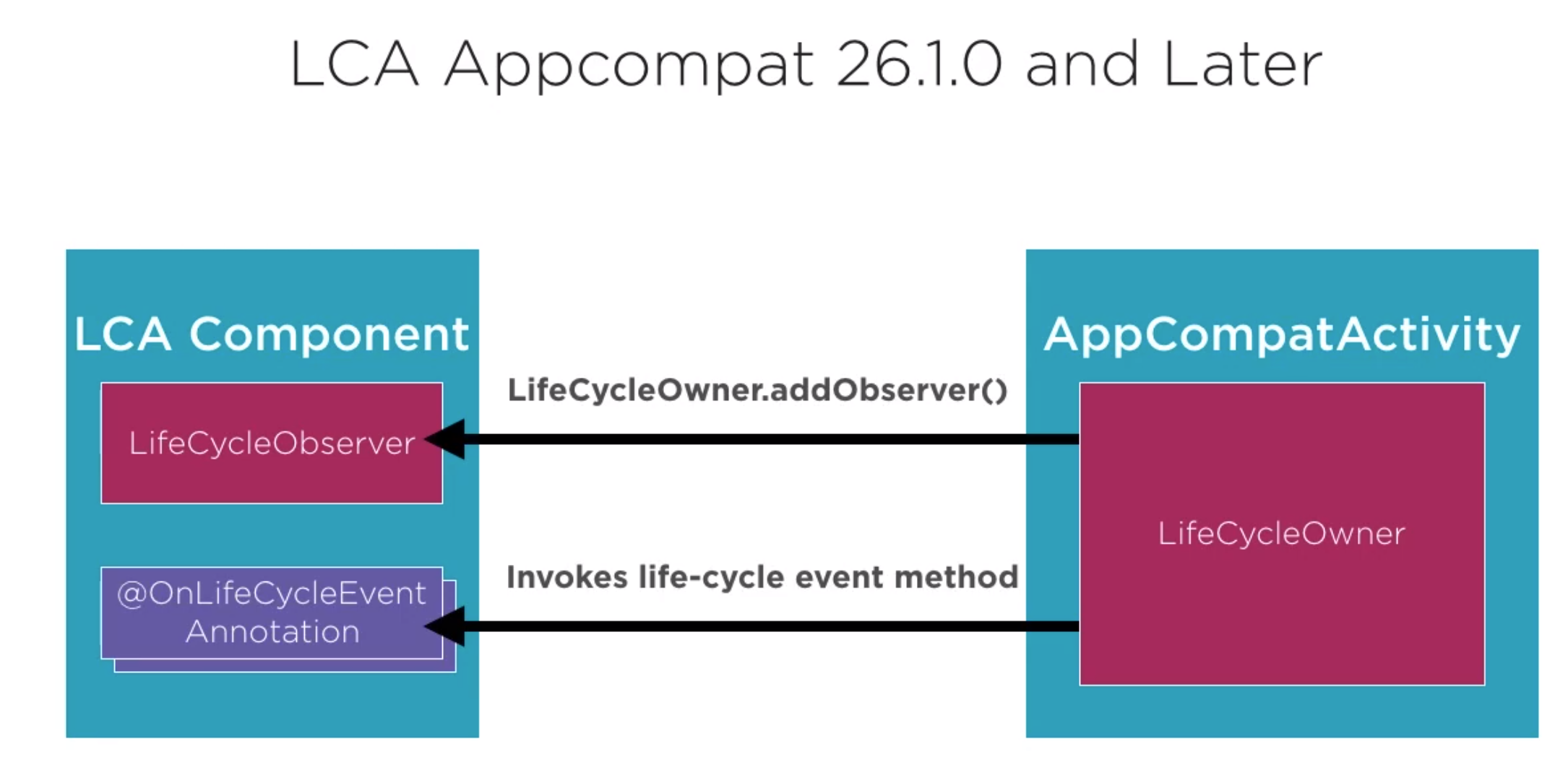
 By implementing the addObserver and don't forget the removeObserver the functions in the component (object instance) are envoked.
By implementing the addObserver and don't forget the removeObserver the functions in the component (object instance) are envoked.
 For example add
For example add
...
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
myLocationManager = new MyLocationManager(this,mTracker);
checkLocationPermission();
getLifecycle().addObserver(myLocationManager);
}
...
And in the Manager Class the clean() function is called when the lifecycle is STOP.
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_STOP)
public void clean() {
Log.d(TAG, "clean() called");
if(mGoogleApiClient !=null) {
mGoogleApiClient.disconnect();
}
final LifecycleOwner lcOwner = (LifecycleOwner)mCon;
lcOwner.getLifecycle().removeObserver(this);
mCon = null;
}
Application Tidy Up
Introduction
Here is an overview of the app prior to looking at it. All of the code is in on Main Activity
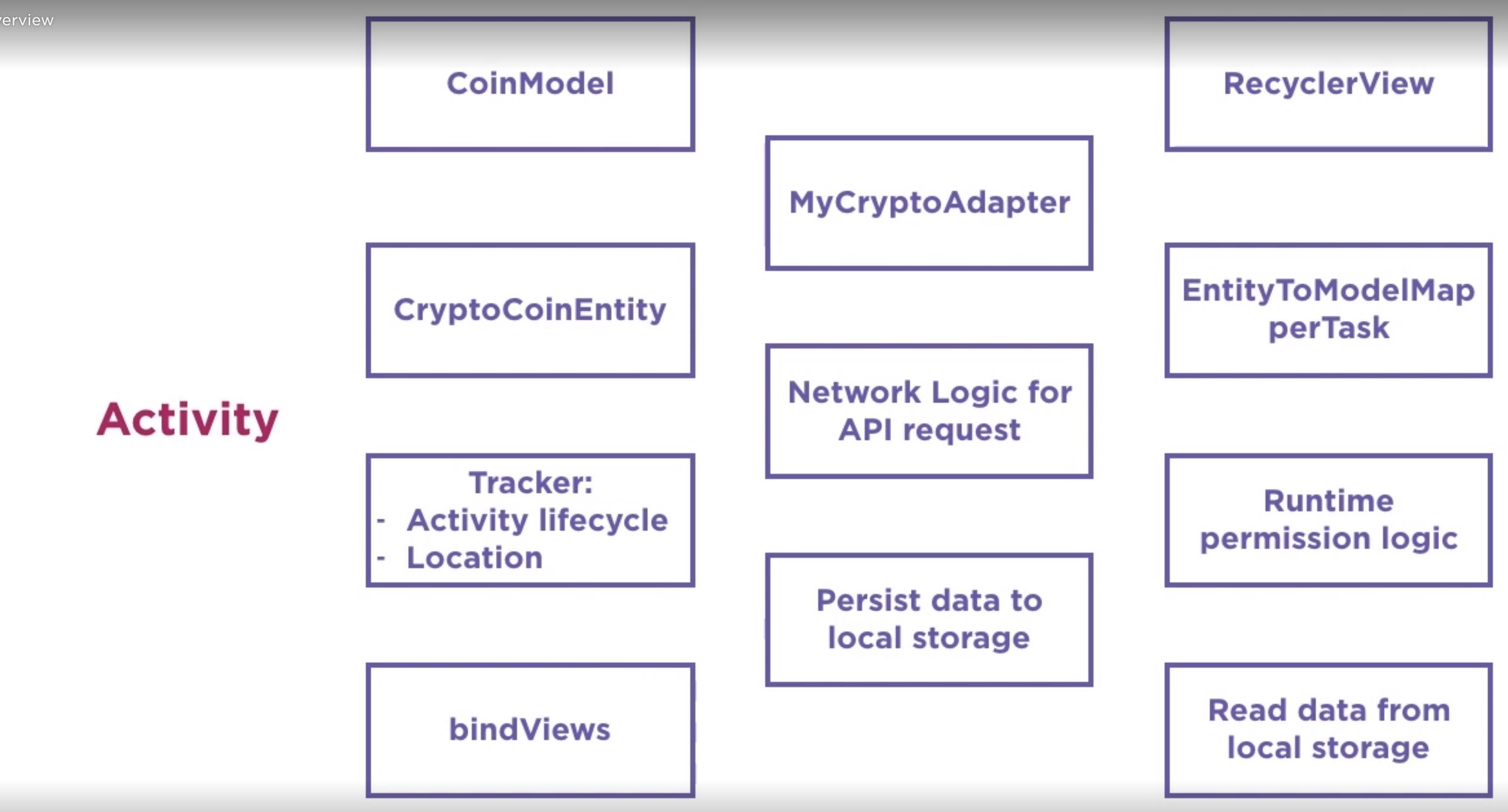
Step 1
- Created TrackerActivity which extends AppCompatActivity and will be now good for other activities
- Move Tracker to its own class and implement the Lifecycle Observer interface
- When using lifecycle observer we need to remote it on destory
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_DESTROY)
public void trackOnDestroy() {
Log.d(TAG, "trackOnDestroy called");
((AppCompatActivity) con).getLifecycle().removeObserver(this);
// mQueue.add(generateTrackingStringRequest("destroy"));
}
Step 2
- Moved CoinModel, Divider and MyCryptoAdapter to their own files in recview package
- Add LocationManager, implemented lifecycle observer
- Added create and destruction of FusedLocationProviderClient in lifecyle
- Added disconnect of GoogleAPiClient and removal of lifecycle observer
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_START)
public void init() {
Log.d(TAG, "init() called");
mFusedLocationClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(mCon);
}
@OnLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.Event.ON_STOP)
public void clean() {
Log.d(TAG, "clean() called");
if(mGoogleApiClient !=null) {
mGoogleApiClient.disconnect();
}
final LifecycleOwner lcOwner = (LifecycleOwner)mCon;
lcOwner.getLifecycle().removeObserver(this);
mCon = null;
}
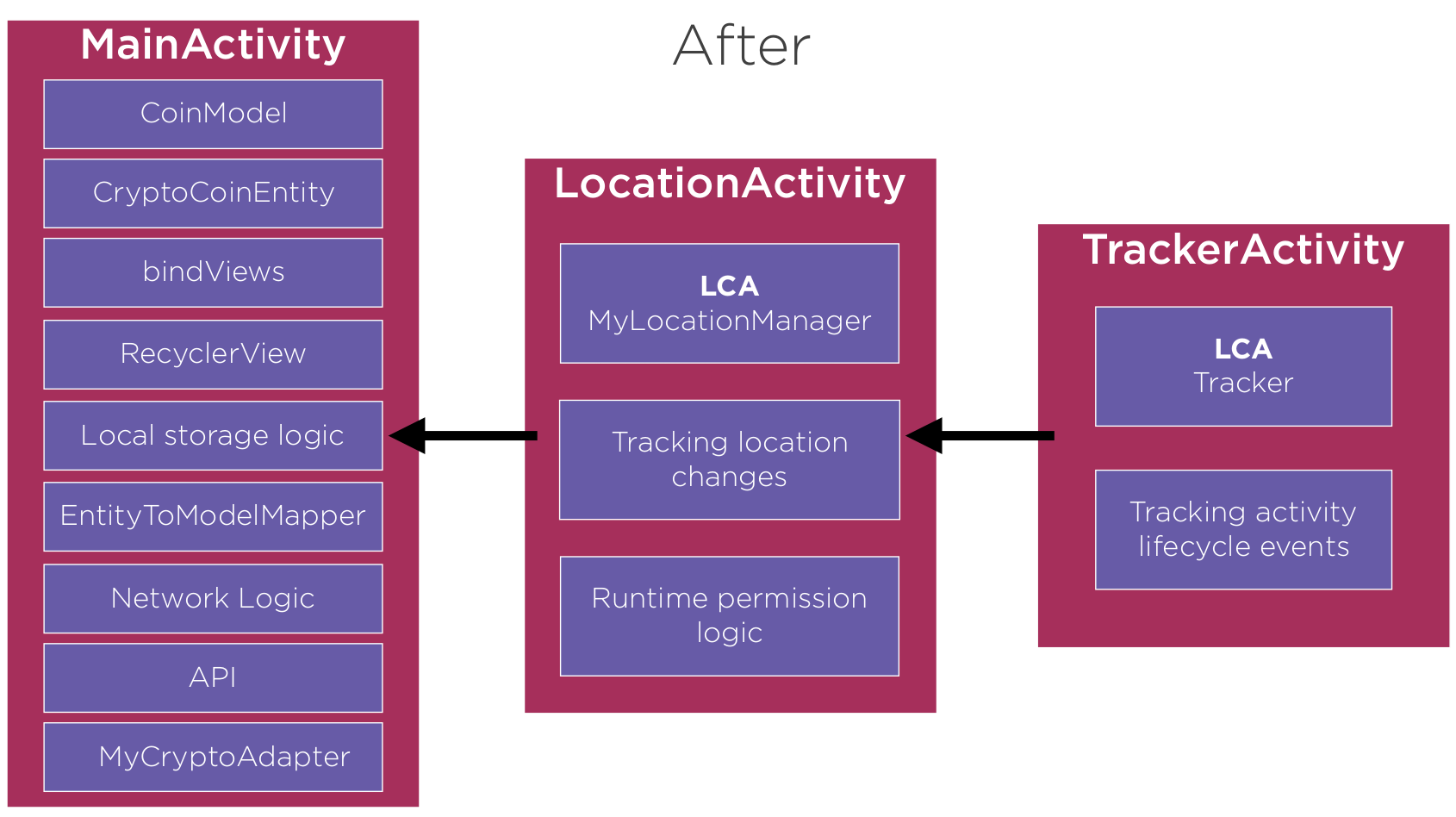
Step 3
- Created a LocationActivity to contain all of the logic for the runtime permission to use Location
- Add LocationManger to LocationActivity
- Change MainActivity to be derived from LocationActivity
Current State 01
Step 4 And Manual View Model and Interface
- Create a crypto view model
- Move network calling to ViewModel
- Move storage calls to to ViewModel
- Create an interface from the model to the view with updateData and setError
- MainActivity
- v*Change MainActivity to use ViewModel for fetchData
- Implement interface
@Override
public void updateData(List<CoinModel> data) {
mAdapter.setItems(data);
mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
mSwipeRefreshLayout.setRefreshing(false);
}
@Override
public void setError(String msg) {
showErrorToast(msg);
}
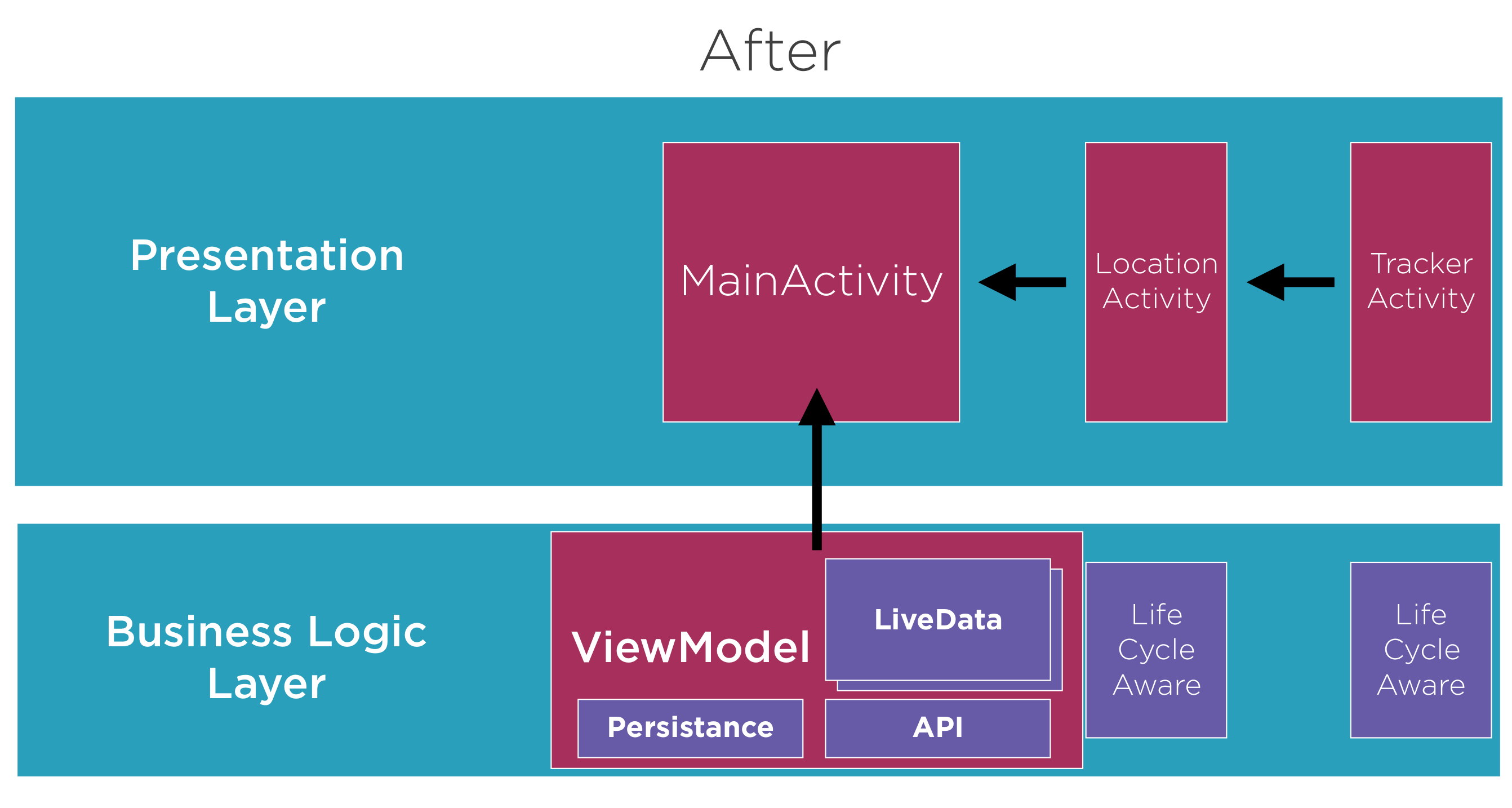
Step 5 And Android View Model and Interface
- Added package android.arch.lifecycle:extensions
- Extended view model from android ViewModel
- Replace manual viewmodel creation in MainActivity. The ViewModel requires you to pass the lifeCycle owner and the ViewModel class
mViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(CryptoViewModel.class);
Using ViewModel we should not reference other Android Components as the LifeCyle of them may differ e.g. MainActivity.
Step 6 LiveData A
With this step we will
- Wrap out data fetching with a LiveData Object
- Add an update interval logic
- Use the Transformations to map our data
- Use out ViewModel and LiveData objects to share data between out activity and a fragment
To achieve this we
- Create two LiveData objects for data and errors
- Created executor service
Once the data is wrapped in LiveData it can be sent to observers with either postValue to setValue depending if it is on the UI thread or not
public void fetchData() {
if (mQueue == null)
mQueue = Volley.newRequestQueue(mAppContext);
// Request a string response from the provided URL.
final JsonObjectRequest jsonObjReq = new JsonObjectRequest(
Request.Method.GET,
ENDPOINT_FETCH_CRYPTO_DATA,
null,
response -> {
...
List<CoinModel> mappedData = mapEntityToModel(data);
// UI thread so setValue
mDataApi.setValue(mappedData);
},
error -> {
Log.d(TAG, "Thread->" +
Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tGot some network error");
mError.setValue(error.toString());
// mView.setError(error.toString());
mExecutor.execute(() -> {
try {
JSONArray dataNew = readDataFromStorage();
ArrayList<CryptoCoinEntityNew> entitiesNew = parseJSON(dataNew.toString());
ArrayList<CryptoCoinEntity> entities = convertNewToOld(entitiesNew);
List<CoinModel> mappedData = mapEntityToModel(entities);
// Background thread so postValue
mDataApi.postValue(mappedData);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}) {
@Override
public Map<String, String> getHeaders() throws AuthFailureError {
...
}
@Override
protected Map<String, String> getParams() {
...
}
};
// Add the request to the RequestQueue.
mQueue.add(jsonObjReq);
}
Step 6 LiveData B
We now need to observe the live data being sent via postValue and setValue. To do this we
- Add observers
- Build a Error fragment to display the error
The frame must pass the activity and not this when using the ViewModelProviders
public class UILessFragment extends Fragment {
private static final String TAG = UILessFragment.class.getSimpleName();
private CryptoViewModel mViewModel;
private final Observer<Double> mObserver= totalMarketCap ->
Log.d(TAG, "onChanged() called with: aDouble = [" +totalMarketCap + "]");
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
//mViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(CryptoViewModel.class);
mViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(getActivity()).get(CryptoViewModel.class);
mViewModel.getTotalMarketCap().observe(this,mObserver);
}
In the Activity we use this with
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.add(new UILessFragment(),"UILessFragment").commit();
Current State 02
Step 7 Persistence
Hmmm api vs Implementation
Before going into the a side step
Suppose the MyLibrary build.gradle uses api configuration in dependencies{} like this:
dependencies {
api project(':InternalLibrary')
}
You want to use MyLibrary in your code so in your app's build.gradle you add this dependency:
dependencies {
implementation project(':MyLibrary')
}
Creating the Data Source and Classes
In this step we
- created data module
- moved CoinModel and CryptoCoinEntity to data CoinModel
- created an object mapper class to hold mapper functions
- created datasource interface
- created local datasource for the reading/writing from local storage
- created remote datasource for the network
Creating the Repository
In this step we create a repository interface which is the interface our app using when requiring data
public interface CryptoRepository {
LiveData<List<CoinModel>> getCryptoCoinsData();
LiveData<String> getErrorStream();
LiveData<Double> getTotalMarketCapStream();
void fetchData();
}
The implementation of this interface creates on change methods for each of the live data streams. <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> ...
private final RemoteDataSource mRemoteDataSource; private final LocalDataSource mLocalDataSource;
...
MediatorLiveData<List<CoinModel>> mDataMerger = new MediatorLiveData<>(); MediatorLiveData<String> mErrorMerger = new MediatorLiveData<>();
private CryptoRepositoryImpl(RemoteDataSource mRemoteDataSource, LocalDataSource mLocalDataSource, CryptoMapper mapper) {
this.mRemoteDataSource = mRemoteDataSource;
this.mLocalDataSource = mLocalDataSource;
mMapper = mapper;
mDataMerger.addSource(this.mRemoteDataSource.getDataStream(), entities ->
mExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mLocalDataSource.writeData(mMapper.mapEntitiesToString(entities));
List<CoinModel> list = mMapper.mapEntityToModel(entities);
mDataMerger.postValue(list);
}
})
);
mDataMerger.addSource(this.mLocalDataSource.getDataStream(), json ->
mExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
List<CryptoCoinEntity> entities = mMapper.mapJSONToEntity(json.toString());
List<CoinModel> models = mMapper.mapEntityToModel(entities);
mDataMerger.postValue(models);
}
})
);
mErrorMerger.addSource(mRemoteDataSource.getErrorStream(), errorStr -> {
mErrorMerger.setValue(errorStr);
Log.d(TAG, "Network error -> fetching from LocalDataSource");
mLocalDataSource.fetch();
}
);
mErrorMerger.addSource(mLocalDataSource.getErrorStream(), errorStr -> mErrorMerger.setValue(errorStr));
}