Raspberry Pico
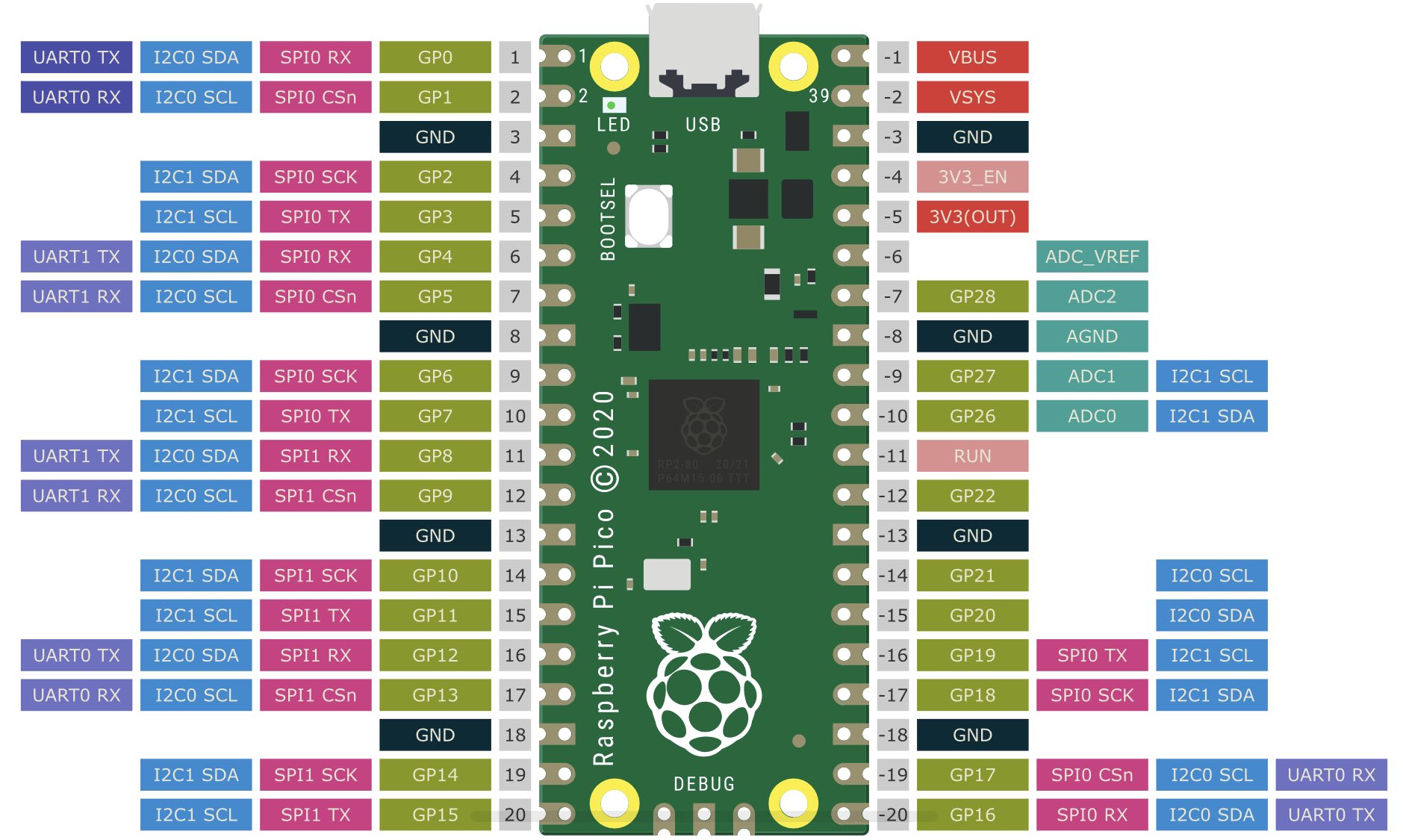
PICO Pinout
Always good to put at the top.
Introduction
Install the micro ros agent
sudo snap install micro-ros-agent
sudo snap set micro-ros-agent daemon=true
sudo systemctl restart snapd
Set up Environment Variables
Here are ones I use. I believe the build system rely on PICO_SDK_PATH and PICO_TOOLCHAIN_PATH
# Set up base directory
export PICO_ROOT=/home/$USER/dev/pico
export PICO_SDK_PATH=$PICO_ROOT/pico-sdk
export PICO_TOOLCHAIN_PATH=$PICO_ROOT/gcc-arm-none-eabi-10-2020-q4-major/bin
Get the compiler
This is how I got started.
Unzip and get the latest compiler from https://developer.arm.com/tools-and-software/open-source-software/developer-tools/gnu-toolchain/gnu-rm/downloads
I then extract it to $PICO_ROOT
Clone the SDK
Get the SDK
cd $PICO_ROOT
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/raspberrypi/pico-sdk.git
git clone https://github.com/micro-ROS/micro_ros_raspberrypi_pico_sdk.git
Make the sample
It using CMake so we goto the source make a build directory and make. This should produce a file pico_micro_ros_example.uf2
cd $PICO_ROOT
cd micro_ros_raspberrypi_pico_sdk
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
Copy to device
So plug in the PICO holding down the boot button
cp pico_micro_ros_example.uf2 /media/$USER/RPI-RP2
Next
We can now look and see if the snap:pico slot is present with
snap interface serial-port
This did not work the first time and the slots: section was missing. I ended up rebooting the PICO, copying the file.
name: serial-port
summary: allows accessing a specific serial port
plugs:
- micro-ros-agent
slots:
- snapd:pico (allows accessing a specific serial port)
New PICO Stuff
Spent lots of time doing lots of other stuff, ESP, learning React etc. Come back to PICO and this is note on this second view
Important
For a PICO to show up, you need to hold the BOOTSEL prior to plugging in the device. Release when powered and you should see
Bus 003 Device 004: ID 2e8a:0003 Raspberry Pi RP2 Boot
When you copy .uf2 software to the device /media/$USER/RPI-RP2/ the device will reboot and may or may not show up depending in what the software is. E.g.
cp ./blink.uf2 /media/$USER/RPI-RP2/
# No longer show device
# lsusb | grep 2e8a
# Disconnects but runs the software on the PICO (i.e. it starts blinking)
sudo dmesg
[80798.165244] FAT-fs (sdf1): unable to read boot sector to mark fs as dirty
Building MicroPython From Source
Revisiting build of this using the guild. Couple of glitches, repo was incorrect but this worked for me.
mkdir pico
cd pico
git clone https://github.com/micropython/micropython
cd micropython/
cd lib/pico-sdk
git submodule update --init
sudo apt install cmake gcc-arm-none-eabi build-essential
cd ../..
make -C mpy-cross
cd ports/rp2
make
Building picotool From Source
sudo apt install build-essential pkg-config libusb-1.0-0-dev
export PICO_SDK_PATH=/home/iwiseman/dev/projects/pico/pico/micropython/lib/pico-sdk
git clone https://github.com/raspberrypi/picotool
cd picotool
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
# optional
sudo cp /home/$USER/dev/projects/pico/pico/picotool/build/picotool /usr/bin/picotool
Using Ros 2 and Pico
- Followed the instructions for https://ubuntu.com/blog/getting-started-with-micro-ros-on-raspberry-pi-pico and managed to get this to work.
- Installed ROS on ubuntu 22.04 using https://docs.ros.org/en/rolling/Installation/Ubuntu-Install-Debians.html
This is important because I could not get the Pico to create a /dev/ttyACM0
Pico-Exampleas
Building
This took some time because I tried to build the examples individually.
# Clone and build
git clone https://github.com/raspberrypi/pico-examples
cd pico-examples
makedir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
Doing this with just an one example e.g.
cd hello_world/
mkdir build
cd build/
cmake ..
Results in the following error
CMake Warning (dev) in CMakeLists.txt:
No project() command is present. The top-level CMakeLists.txt file must
contain a literal, direct call to the project() command. Add a line of
code such as
project(ProjectName)
near the top of the file, but after cmake_minimum_required().
CMake is pretending there is a "project(Project)" command on the first
line.
This warning is for project developers. Use -Wno-dev to suppress it.
CMake Error at serial/CMakeLists.txt:9 (pico_add_extra_outputs):
Unknown CMake command "pico_add_extra_outputs".
Serial vs USB
They look the same but they are not. Here is the difference in the USB makefiles
# enable usb output, disable uart output
pico_enable_stdio_usb(hello_usb 1)
pico_enable_stdio_uart(hello_usb 0)
C++ Example
Create demo program
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pico/stdlib.h>
int main()
{
stdio_init_all();
while (true) {
printf("Hello world\n");
sleep_ms(1000);
}
}
And a CMakefile
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.13)
include($ENV{PICO_SDK_PATH}/external/pico_sdk_import.cmake)
project(myapp C CXX ASM)
set(CMAKE_C_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
pico_sdk_init()
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} main.c)
pico_add_extra_outputs(${PROJECT_NAME})
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} pico_stdlib)
pico_enable_stdio_usb(${PROJECT_NAME} 1)
pico_enable_stdio_uart(${PROJECT_NAME} 0)
Create a build directory and build
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make -j$(nproc)
Copying the software to the Pico and monitoring with screen gives
cp myapp.uf2 /media/iwiseman/RPI-RP2/
sudo screen /dev/ttyACM0 115200
Hello world
Hello world
Hello world
....
# CTRL+A \ to exit
PIO and the PICO
Sounds like a new book but this is reminding myself of the old C64 and assembly. Starting with the blink project and reading until tired.
Blink
Prerequisites
We need to have a working PICO sdk mine is in
PICO_SDK_PATH=/opt/pico/pico-sdk
CMake file
For CMake I have cmake 3.22.1
# Set minimum required version of CMake
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.12)
# Include build functions from Pico SDK
include($ENV{PICO_SDK_PATH}/external/pico_sdk_import.cmake)
include($ENV{PICO_SDK_PATH}/tools/CMakeLists.txt)
# Set name of project (as PROJECT_NAME) and C/C standards
project(blink C CXX ASM)
set(CMAKE_C_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
# Creates a pico-sdk subdirectory in our project for the libraries
pico_sdk_init()
# Tell CMake where to find the executable source file
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME}
src/main.c
)
# Create C header file with the name <pio program>.pio.h
pico_generate_pio_header(${PROJECT_NAME}
${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/src/blink.pio
)
# Create map/bin/hex/uf2 files
pico_add_extra_outputs(${PROJECT_NAME})
# Link to pico_stdlib (gpio, time, etc. functions)
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}
pico_stdlib
hardware_pio
)
# Enable usb output, disable uart output
pico_enable_stdio_usb(${PROJECT_NAME} 0)
pico_enable_stdio_uart(${PROJECT_NAME} 1)
C Code
Nothing special here
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <pico/stdlib.h>
#include <hardware/pio.h>
#include <blink.pio.h>
#define LED_BUILTIN 25
int main() {
stdio_init_all();
PIO pio = pio0;
uint state_machine_id = 0;
uint offset = pio_add_program(pio, &blink_program);
blink_program_init(pio, state_machine_id, offset, LED_BUILTIN);
while(1) {
//do nothing
}
}
PIO Code
This is the C64 bit you make a file call blink.pio which contains assembly and C-SDK bindings which seem like a bit of voodoo and hope to learn more. The assembly is straight forward.
.program blink
set pindirs, 1 ; Set pin to output
loop:
set pins, 1 [31] ; Drive pin high and then delay for 31 cycles
set pins, 0 [31] ; Drive pin low and then delay for 31 cycles
jmp loop
% c-sdk {
static inline void blink_program_init(PIO pio, uint sm, uint offset, uint pin) {
// 1. Define a config object
pio_sm_config config = blink_program_get_default_config(offset);
// 2. Set and initialize the output pins
sm_config_set_set_pins(&config, pin, 1);
// 3. Apply the configuration & activate the State Machine
pio_sm_init(pio, sm, offset, &config);
pio_sm_set_enabled(pio, sm, true);
}
%}
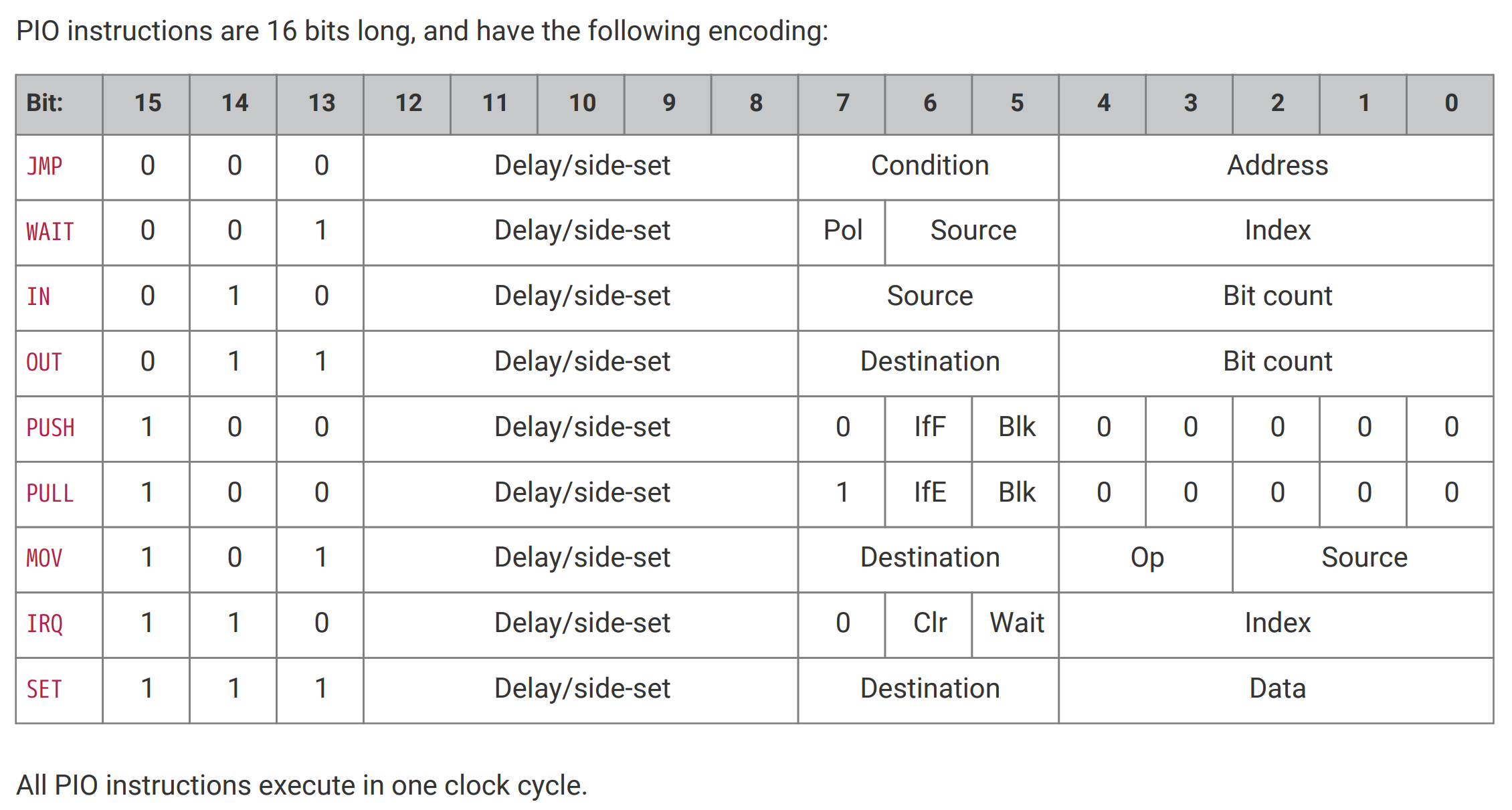
Breakdown of PIO Instructions
The SDK provides