Android Fragments
Introduction
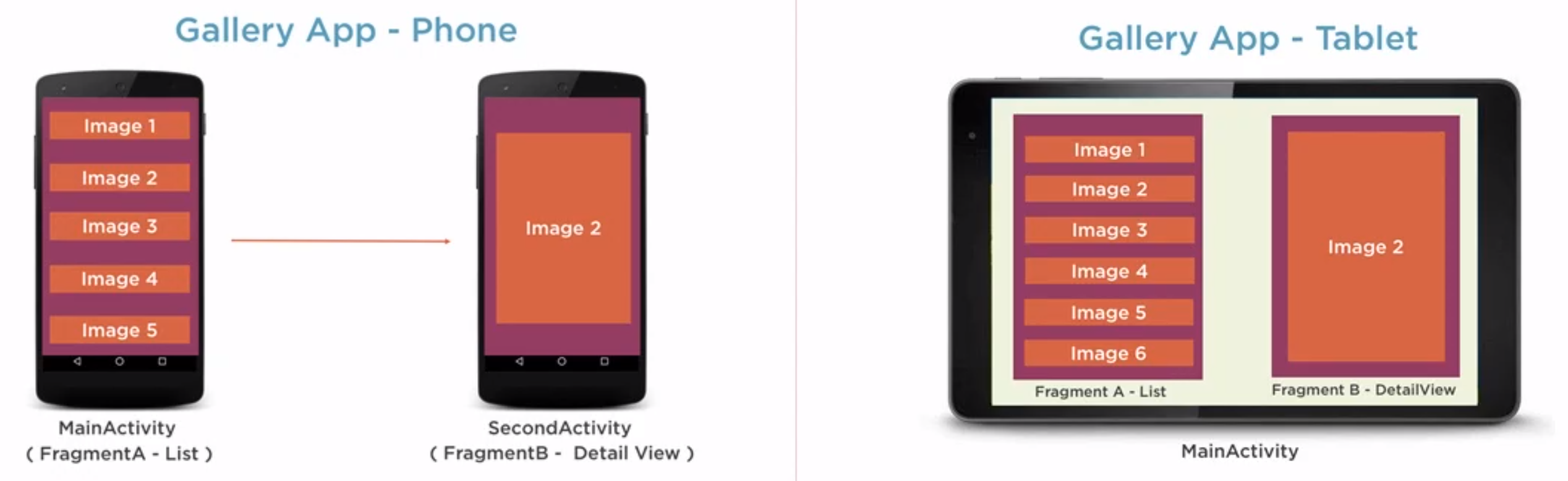
Introduced in API 11. They are a small piece of UI and must have an Activity. Fragments can be added or removed from the Activity. They allow you to capture the UI functionality where you may need to share it across different activities. If we look at phone vs tablet we might this it more appropriate to use to activities but the UI code will remain the same.
Creating Fragment
- Create layout
- Create a subclass and Link layout with Fragment
- Place the Fragment inside an Activity
Create layout
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FF0"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:text="Hello From Fragment"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"/>
</LinearLayout>
Create layout and Link layout with Fragment
We create a subclass of Fragment and override the onCreateView to link the layout with the view.
public class HelloFragment extends Fragment {
private static final String TAG = HelloFragment.class.getSimpleName();
@Override
public void onAttach(Context context) {
super.onAttach(context);
Log.i(TAG, "onAttach");
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.i(TAG, "onCreate");
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Log.i(TAG, "onCreateView");
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_hello, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
Log.i(TAG, "onActivityCreated");
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
Log.i(TAG, "onStart");
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
Log.i(TAG, "onResume");
}
....
Place the Fragment inside an Activity
Fragment Manager
We use a Fragment manager to manager the fragments transaction which are methods which add, remove or replace fragments for an activity.
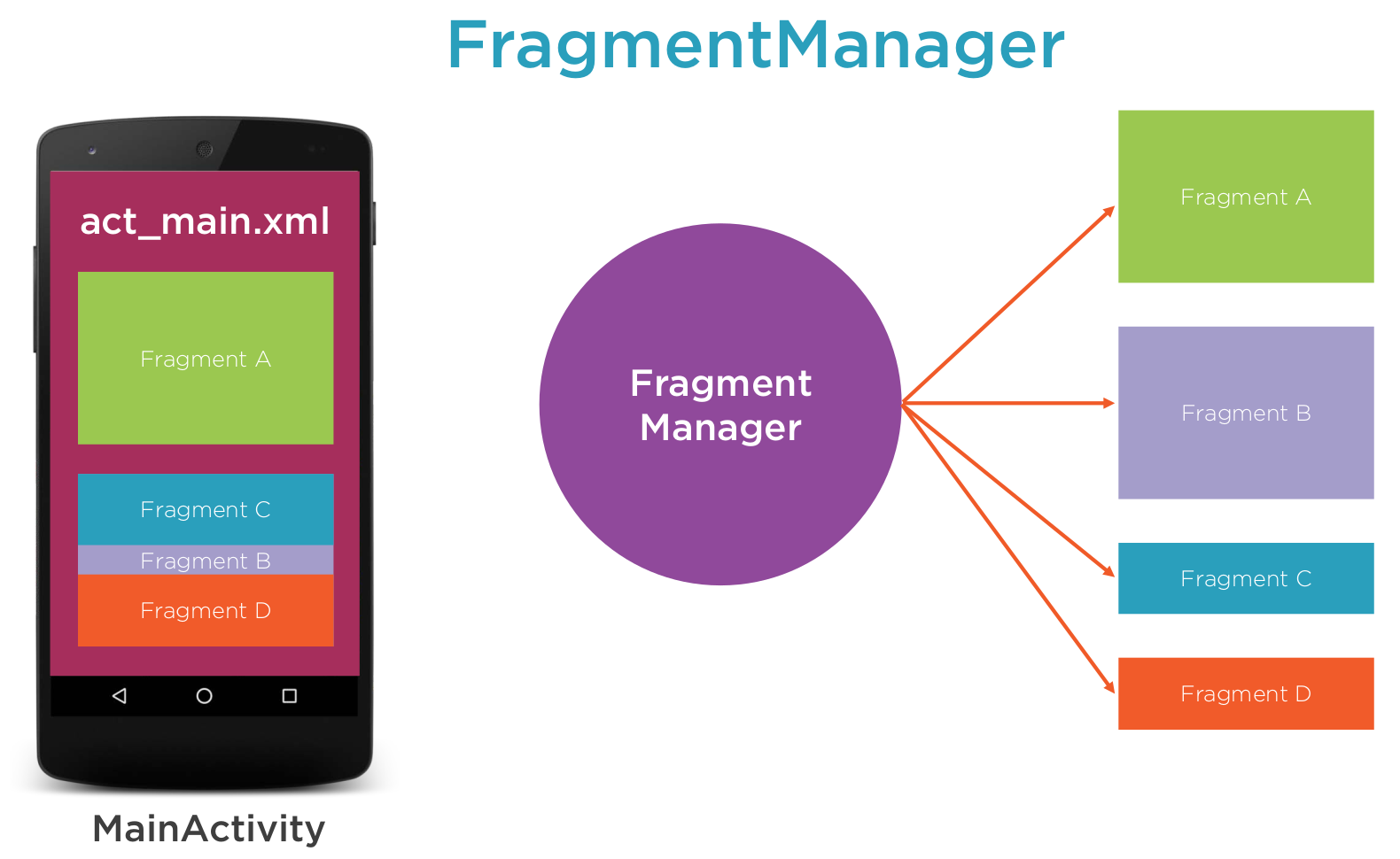 ==Using Fragment Manager
To get this working we need to
==Using Fragment Manager
To get this working we need to
- Initialize Fragment Manager
- Initialize Fragment Transaction
- Start/add/Removereplace operation
- Commit Transaction
Using the add we can name the container to add the fragment to.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName();
private FragmentManager manager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
manager = getFragmentManager();
}
public void addFragmentA(View view) {
FragmentA fragmentA = new FragmentA();
FragmentTransaction transaction = manager.beginTransaction();
transaction.add(R.id.container, fragmentA, "fragA");
transaction.commit();
}
...
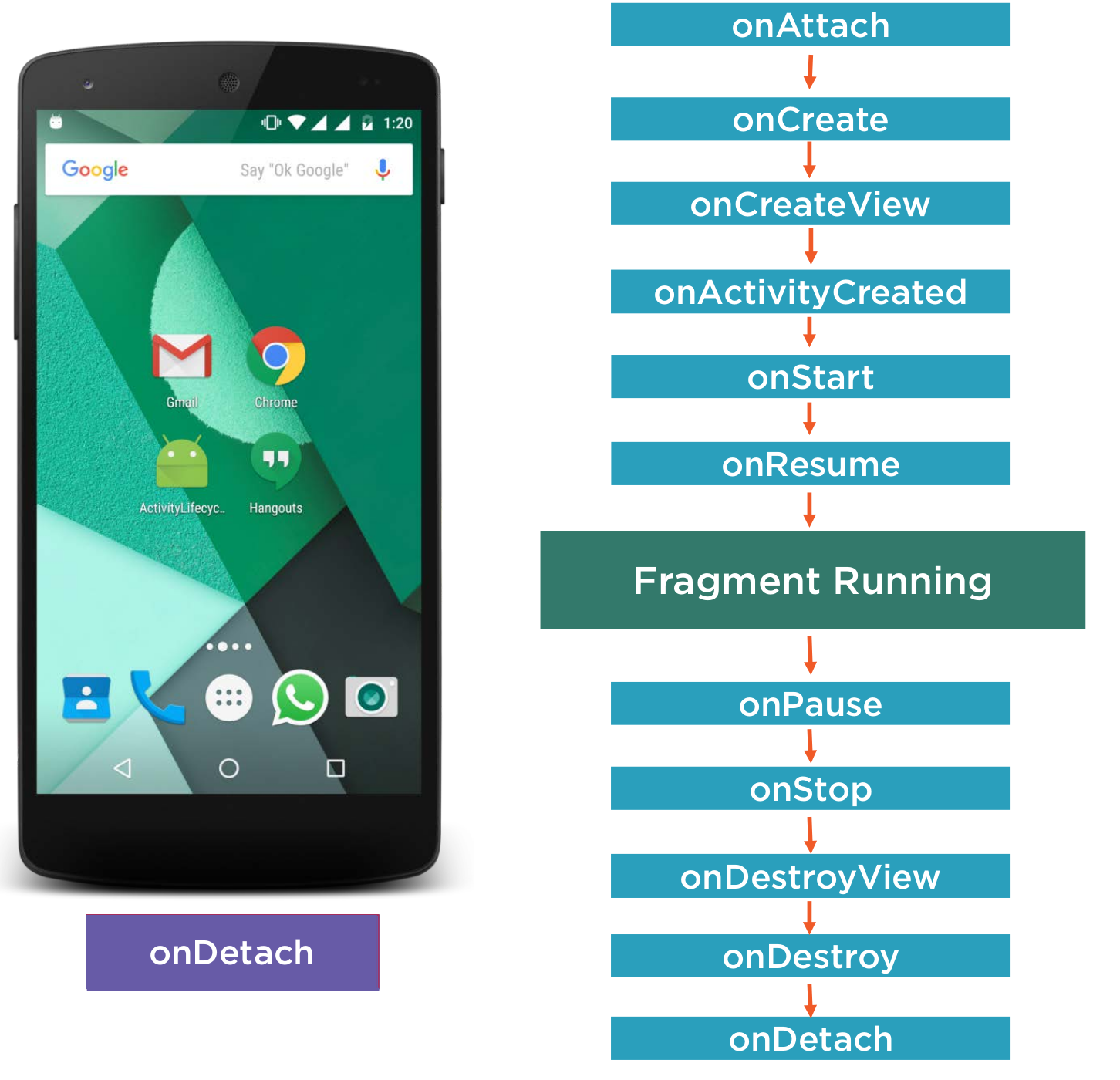
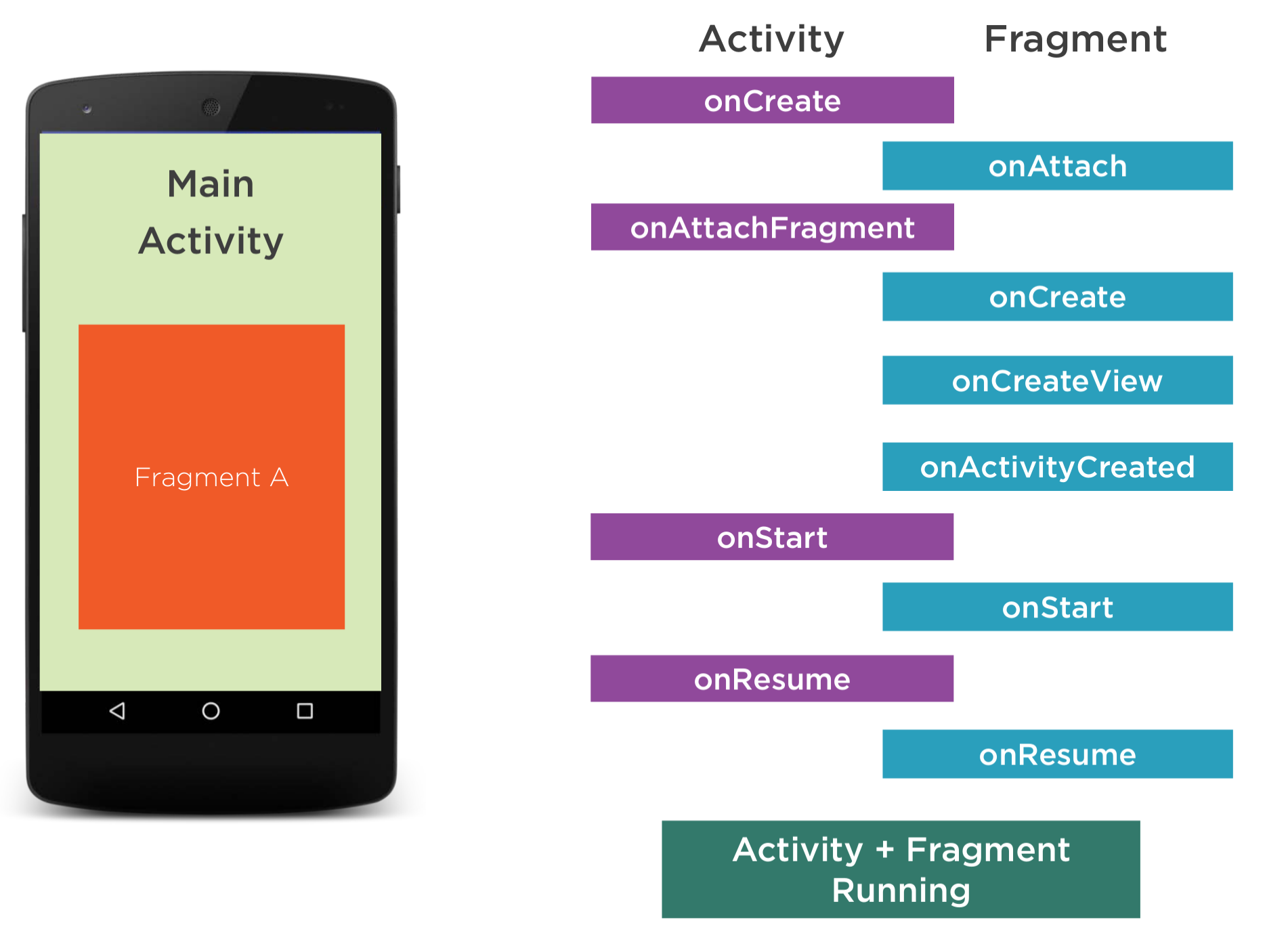
Fragment Lifecyle
Fragments are lifecycle aware.
 Here is the overall startup order
Here is the overall startup order
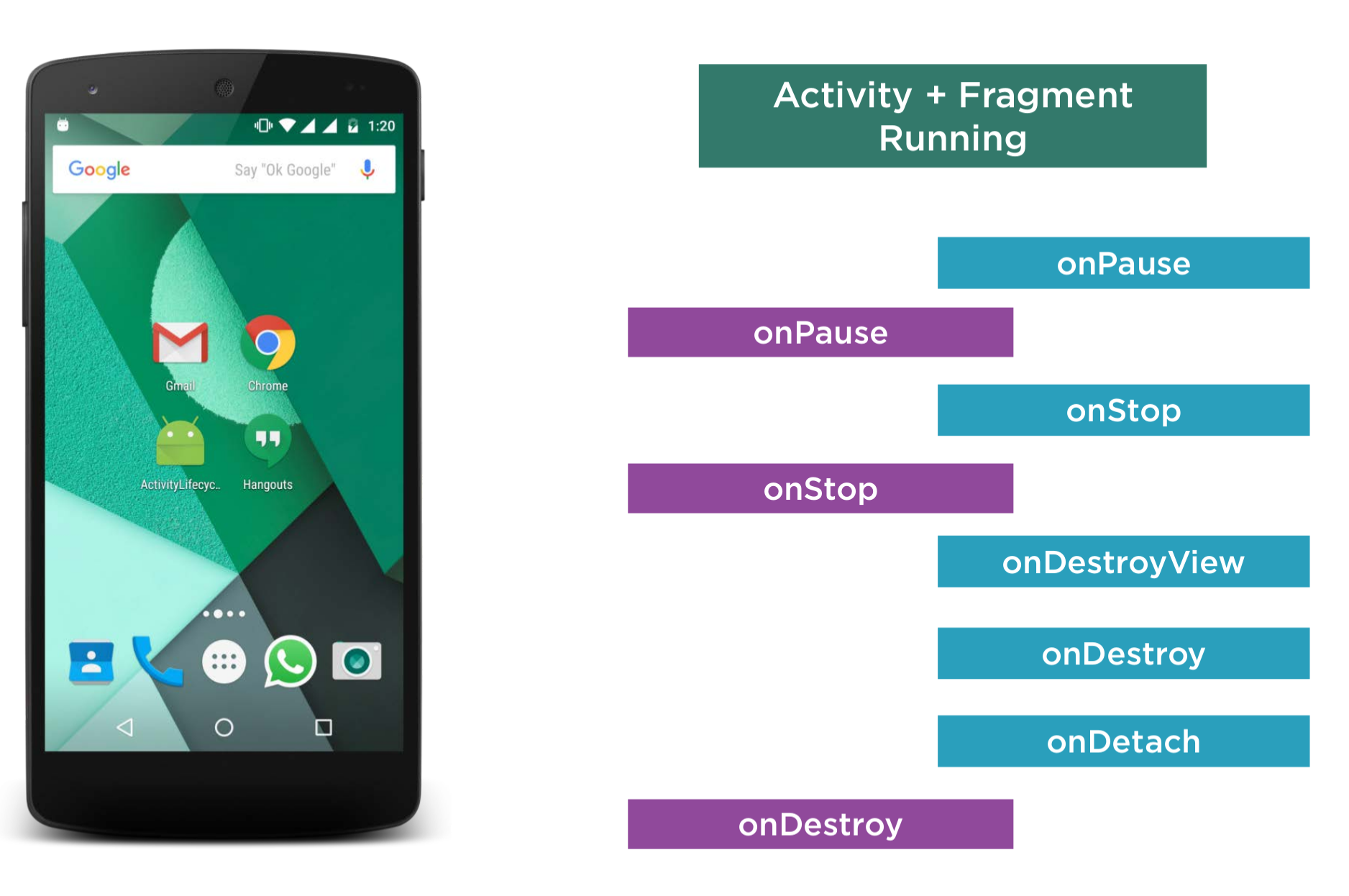
 Here is the overall shutdown order
Here is the overall shutdown order
Sending Data to and from a Fragment
Using a Bundle Object
Main Activity
int firstNumber = Integer.valueOf(eFirstNumber.getText().toString());
int secondNumber = Integer.valueOf(eSecondNumber.getText().toString());
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt("first_number",firstNumber);
bundle.putInt("second_number",secondNumber);
FragmentA fragmentA = new FragementA();
fragmentA.setArguments(bundle);
Fragment
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
...
Bundle bundle = getArguments();
int firstNumber = bundle.getInt("first_number",0) // default 0
int secondNumber = bundle.getInt("second_number",0) // default 0
Using Fragment Object
Main Activity
public void sendDataToFragmentB(View view) {
FragmentB fragmentB = (FragmentB) manager.findFragmentByTag("fragB");
if (fragmentB != null) {
fragmentB.addTwoNumbers(num1, num2);
}
}
Fragment
public void addTwoNumbers(int x, int y) {
int result = x + y;
txvResult.setText("Result : " + result);
}